Scaffolding in education involves providing structured support to students as they develop new skills or understand complex concepts, ensuring they build confidence and competence. Fading gradually reduces this support, encouraging learners to become independent and apply their knowledge autonomously. Effective teaching balances scaffolding and fading to optimize student growth and mastery over time.
Table of Comparison
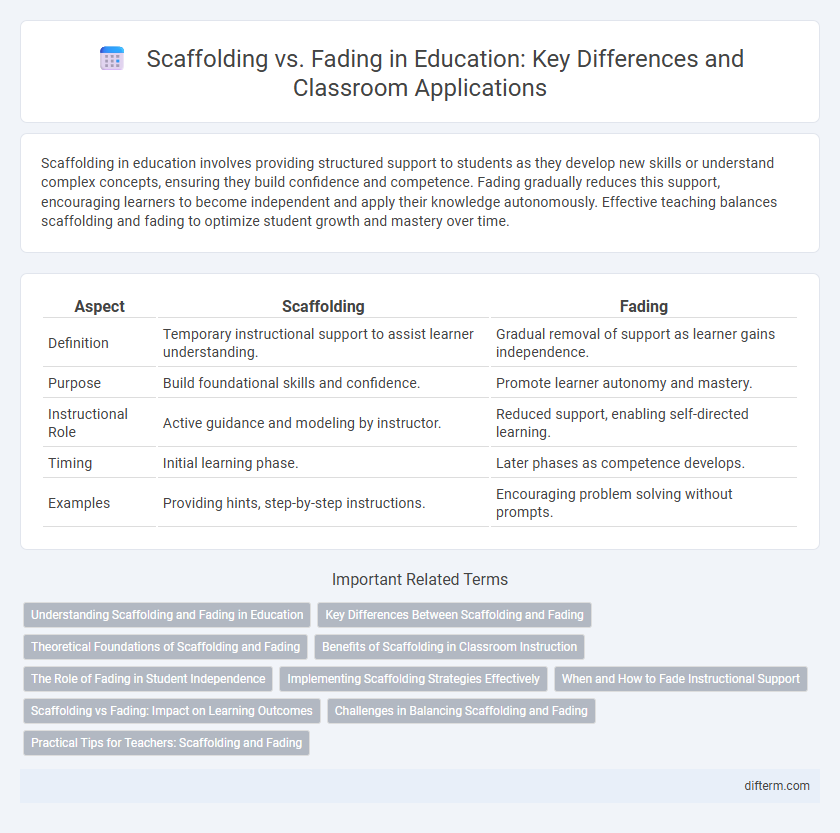
| Aspect | Scaffolding | Fading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary instructional support to assist learner understanding. | Gradual removal of support as learner gains independence. |
| Purpose | Build foundational skills and confidence. | Promote learner autonomy and mastery. |
| Instructional Role | Active guidance and modeling by instructor. | Reduced support, enabling self-directed learning. |
| Timing | Initial learning phase. | Later phases as competence develops. |
| Examples | Providing hints, step-by-step instructions. | Encouraging problem solving without prompts. |
Understanding Scaffolding and Fading in Education
Scaffolding in education involves providing temporary support to students to enhance learning and skill development, such as guided practice or hints, which gradually diminishes as learners gain independence. Fading refers to the systematic removal of these supports, allowing students to apply knowledge autonomously and build confidence in their abilities. Effective use of scaffolding and fading strategies improves student engagement, critical thinking, and mastery of complex concepts.
Key Differences Between Scaffolding and Fading
Scaffolding in education involves providing structured support and guidance to learners as they develop new skills, ensuring they can complete tasks beyond their current capabilities. Fading refers to the gradual removal of this support, encouraging students to become more independent and confident in applying knowledge without assistance. The key difference lies in scaffolding's role in building competency through direct aid, while fading emphasizes autonomy by reducing external help over time.
Theoretical Foundations of Scaffolding and Fading
Scaffolding is rooted in Vygotsky's Zone of Proximal Development theory, emphasizing guided support to bridge learners' current abilities and potential skills. Fading involves gradually reducing instructional assistance, encouraging learner autonomy while reinforcing internalization of knowledge. Both approaches leverage cognitive apprenticeship principles to optimize skill acquisition and transfer through adaptive, context-sensitive support.
Benefits of Scaffolding in Classroom Instruction
Scaffolding in classroom instruction enhances student learning by providing structured support tailored to individual needs, which boosts confidence and promotes mastery of complex concepts. This approach encourages active engagement through guided practice and timely feedback, resulting in improved problem-solving skills and independent learning. Educators leveraging scaffolding techniques report higher student achievement and more effective knowledge retention compared to traditional teaching methods.
The Role of Fading in Student Independence
Fading in education gradually reduces teacher support to promote student independence and mastery of skills. This technique ensures learners develop confidence by applying knowledge without reliance on prompts or guidance. Effective fading fosters critical thinking and problem-solving abilities essential for lifelong learning.
Implementing Scaffolding Strategies Effectively
Implementing scaffolding strategies effectively involves providing structured support tailored to learners' current abilities, gradually increasing task complexity to build competence. Techniques such as modeling, guided practice, and prompting help students acquire skills while maintaining engagement and motivation. Fading support strategically ensures learners develop autonomy by slowly removing assistance as their confidence and mastery grow.
When and How to Fade Instructional Support
Fading instructional support should begin once learners demonstrate consistent mastery of targeted skills, allowing gradual independence in problem-solving. Effective fading involves systematically reducing prompts and cues, shifting responsibility from instructor to student to enhance self-regulation and confidence. Timing fade phases carefully ensures learners retain core concepts while adapting to autonomous application in diverse educational settings.
Scaffolding vs Fading: Impact on Learning Outcomes
Scaffolding provides structured support that helps students progressively master complex tasks by breaking down learning into manageable parts, fostering independence and confidence. Fading gradually removes this assistance, promoting autonomous problem-solving and deeper cognitive processing, which strengthens retention and transfer of knowledge. Effective balance between scaffolding and fading enhances learning outcomes by adapting support to individual learner needs and ensuring sustained academic growth.
Challenges in Balancing Scaffolding and Fading
Balancing scaffolding and fading presents challenges such as determining the optimal timing for reducing support to ensure learner independence without causing frustration or confusion. Educators must continuously assess students' progress to provide just enough assistance while encouraging critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Misjudging the fading process can hinder skill acquisition or lead to dependency, impacting overall learning outcomes.
Practical Tips for Teachers: Scaffolding and Fading
Implement practical scaffolding techniques such as modeling, guided questioning, and chunking tasks to support student learning effectively. Gradually implement fading by reducing assistance as students demonstrate increased competence, promoting independence. Use formative assessments to determine the optimal timing for fading support, ensuring students remain challenged yet capable.
scaffolding vs fading Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com