Instructional design emphasizes creating structured educational materials and courses focused on delivering content efficiently. Learning design takes a broader approach by considering learner experiences, interactions, and environments to foster deeper engagement and knowledge retention. Both disciplines aim to enhance learning outcomes but differ in their emphasis on content delivery versus holistic learner-centered strategies.
Table of Comparison
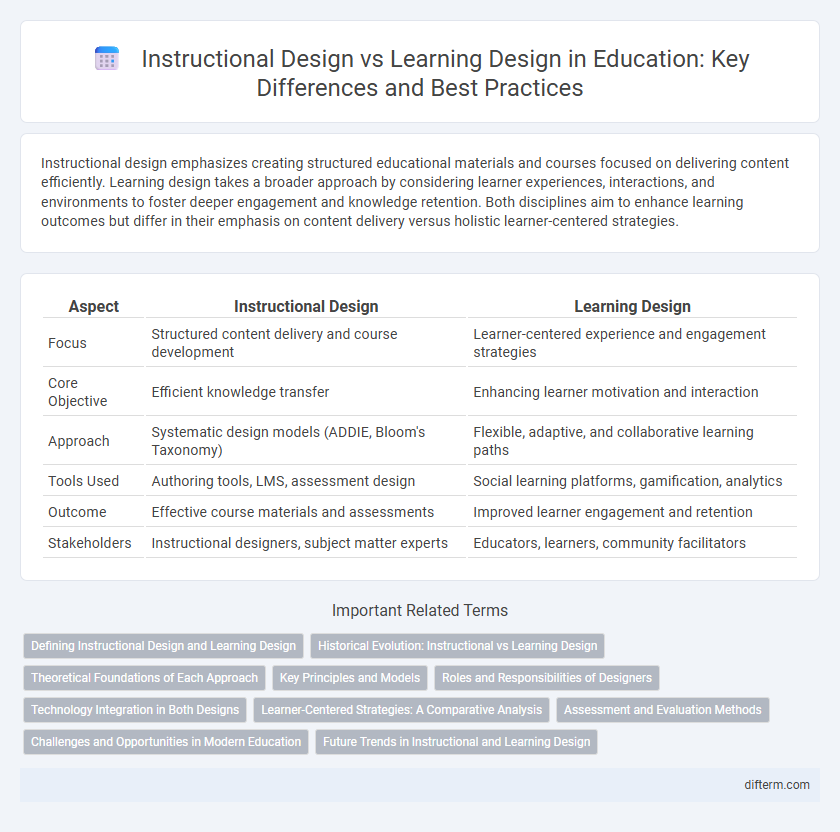
| Aspect | Instructional Design | Learning Design |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Structured content delivery and course development | Learner-centered experience and engagement strategies |
| Core Objective | Efficient knowledge transfer | Enhancing learner motivation and interaction |
| Approach | Systematic design models (ADDIE, Bloom's Taxonomy) | Flexible, adaptive, and collaborative learning paths |
| Tools Used | Authoring tools, LMS, assessment design | Social learning platforms, gamification, analytics |
| Outcome | Effective course materials and assessments | Improved learner engagement and retention |
| Stakeholders | Instructional designers, subject matter experts | Educators, learners, community facilitators |
Defining Instructional Design and Learning Design
Instructional design focuses on the systematic development of educational experiences and materials to facilitate learning, emphasizing the structuring of content, assessments, and delivery methods. Learning design centers on the broader process of orchestrating learning activities and environments to support learner engagement and knowledge application. Both fields aim to optimize educational outcomes but differ in scope, with instructional design concentrating on content creation and learning design emphasizing holistic learning experiences.
Historical Evolution: Instructional vs Learning Design
Instructional design emerged in the mid-20th century, primarily focusing on systematic curriculum development and behaviorist theories to enhance educational efficiency. Learning design evolved later, integrating constructivist and connectivist principles that emphasize learner-centered approaches and collaborative knowledge construction. The shift reflects a transition from structured, instructor-led content delivery to flexible, learner-driven environments supported by digital technologies.
Theoretical Foundations of Each Approach
Instructional design is grounded in behaviorist and cognitive learning theories, emphasizing structured content delivery and measurable learning outcomes. Learning design incorporates constructivist and connectivist theories, prioritizing learner-centered experiences and social interactions to foster deeper understanding. Both approaches draw from educational psychology but differ in their theoretical focus on content sequencing versus learner engagement.
Key Principles and Models
Instructional design centers on developing structured content using models like ADDIE and SAM to optimize knowledge transfer, while learning design emphasizes learner engagement and adaptability through frameworks such as Universal Design for Learning (UDL) and Constructivist theories. Key principles in instructional design include clear objectives, systematic sequencing, and formative assessment integration, whereas learning design prioritizes learner autonomy, social interaction, and personalized learning pathways. Both approaches utilize iterative evaluation to enhance effectiveness, but instructional design often targets content delivery, and learning design focuses on holistic learning experiences.
Roles and Responsibilities of Designers
Instructional designers primarily focus on creating structured curriculum materials, assessments, and learning objectives aligned with educational standards. Learning designers emphasize learner experience by integrating technology, engagement strategies, and adaptive learning paths tailored to diverse audiences. Both roles collaborate to optimize educational outcomes but differ in scope, with instructional designers concentrating on content delivery and learning designers enhancing interaction and personalization.
Technology Integration in Both Designs
Instructional design emphasizes structured curriculum development and technology integration through multimedia tools, learning management systems (LMS), and adaptive software to enhance content delivery and learner engagement. Learning design focuses on creating interactive, learner-centered experiences by incorporating collaborative technologies, mobile applications, and analytics to support personalized learning pathways. Both approaches leverage emerging technologies like virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and gamification to optimize educational outcomes and facilitate seamless digital learning environments.
Learner-Centered Strategies: A Comparative Analysis
Learner-centered strategies in instructional design prioritize structured objectives and content sequencing to guide knowledge acquisition, while learning design emphasizes adaptive, personalized experiences tailored to diverse learner needs. Instructional design often relies on systematic models such as ADDIE, focusing on efficient delivery and assessment, compared to learning design's flexible frameworks that incorporate real-time feedback and social interaction. Both approaches aim to enhance engagement and retention, but learning design integrates technology and learner autonomy more deeply to support self-directed learning.
Assessment and Evaluation Methods
Instructional design primarily focuses on creating structured content and activities aligned with specific learning objectives, integrating formative and summative assessments to measure learner progress. Learning design emphasizes a more holistic approach, considering diverse learner needs and contexts, and incorporates varied evaluation methods such as authentic assessments and feedback loops to enhance learning experiences. Both frameworks utilize data-driven evaluation techniques to ensure instructional effectiveness and continuous improvement in educational outcomes.
Challenges and Opportunities in Modern Education
Instructional design often faces challenges in adapting rigid frameworks to diverse learner needs, while learning design emphasizes flexible, learner-centered approaches that enhance engagement and retention. Technological advancements create opportunities for personalized, data-driven learning experiences but require educators to continuously update skills and integrate innovative tools effectively. Balancing standardized curricula with adaptive strategies remains crucial to overcoming barriers and maximizing educational outcomes.
Future Trends in Instructional and Learning Design
Future trends in instructional and learning design emphasize personalized, AI-driven learning experiences that adapt to individual learner needs and preferences. Emerging technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and data analytics enhance engagement and provide real-time feedback to optimize learning outcomes. The shift towards hybrid and competency-based education models drives the integration of instructional design with learning design to create flexible, scalable, and learner-centered environments.
instructional design vs learning design Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com