Holistic grading evaluates a student's work as a whole, emphasizing overall quality and coherence, which can capture creativity and critical thinking more effectively. Analytic grading breaks down evaluation into specific components, such as grammar, content, and organization, providing detailed feedback and clear criteria for improvement. Both methods serve distinct educational purposes, with holistic grading fostering broad understanding and analytic grading promoting targeted skill development.
Table of Comparison
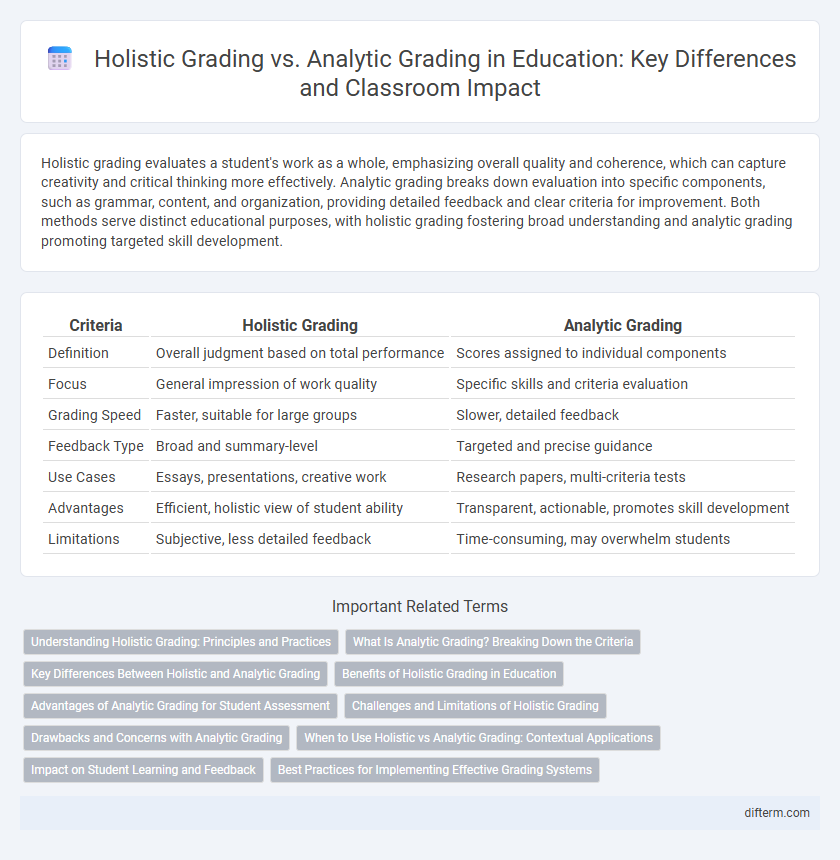
| Criteria | Holistic Grading | Analytic Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overall judgment based on total performance | Scores assigned to individual components |
| Focus | General impression of work quality | Specific skills and criteria evaluation |
| Grading Speed | Faster, suitable for large groups | Slower, detailed feedback |
| Feedback Type | Broad and summary-level | Targeted and precise guidance |
| Use Cases | Essays, presentations, creative work | Research papers, multi-criteria tests |
| Advantages | Efficient, holistic view of student ability | Transparent, actionable, promotes skill development |
| Limitations | Subjective, less detailed feedback | Time-consuming, may overwhelm students |
Understanding Holistic Grading: Principles and Practices
Holistic grading evaluates student work based on an overall impression, considering multiple dimensions such as content quality, coherence, and creativity simultaneously, which promotes a more integrated assessment of learning outcomes. This method streamlines the grading process, allowing educators to quickly gauge the effectiveness of student submissions by focusing on the overall impact rather than isolated components. Effective holistic grading relies on clear criteria and consistent rubrics to ensure fairness and reliability in assessing diverse student performances.
What Is Analytic Grading? Breaking Down the Criteria
Analytic grading evaluates student work by breaking down performance into specific criteria such as content accuracy, organization, grammar, and creativity, allowing for detailed feedback on each aspect. This method provides a clear rubric that highlights strengths and weaknesses across different components rather than assigning a single overall score. Educators use analytic grading to enhance transparency and support targeted improvement in key skill areas.
Key Differences Between Holistic and Analytic Grading
Holistic grading evaluates student work as a whole, emphasizing overall impact and coherence, while analytic grading breaks down the assessment into specific criteria, such as grammar, content, and organization. Holistic grading offers efficiency and a global judgment, making it suitable for quick evaluations, whereas analytic grading provides detailed feedback, helping students identify strengths and weaknesses in each component. These differences influence grading consistency, feedback quality, and instructional improvement in educational settings.
Benefits of Holistic Grading in Education
Holistic grading enhances the evaluation process by assessing a student's overall performance and comprehension, promoting critical thinking and creativity beyond mere correctness. This method encourages a more personalized feedback approach, fostering student motivation and deeper learning engagement. Educators benefit from its efficiency, as it reduces the time required to grade while capturing the essence of student work in diverse educational contexts.
Advantages of Analytic Grading for Student Assessment
Analytic grading offers detailed feedback by breaking down assessments into specific criteria, which helps students identify their strengths and areas for improvement more clearly. This method enhances transparency and consistency in grading, allowing educators to provide targeted support tailored to each student's needs. By highlighting distinct skill components, analytic grading promotes deeper learning and encourages mastery of individual concepts within a subject.
Challenges and Limitations of Holistic Grading
Holistic grading presents challenges such as subjectivity and inconsistent scoring due to its reliance on overall impression rather than specific criteria. This approach may lead to bias and reduced reliability, complicating fair assessment across diverse student populations. The lack of detailed feedback for students also limits opportunities for targeted improvement compared to analytic grading methods.
Drawbacks and Concerns with Analytic Grading
Analytic grading, which breaks down assignments into distinct criteria scored separately, often faces criticism for potentially overlooking the overall coherence and flow of a student's work. This method can lead to fragmented assessments, where strong performance in one area might mask weaknesses in others, diminishing the holistic understanding of student learning. Concerns also arise regarding time consumption and increased subjectivity in assigning scores to multiple components, which may affect grading consistency and fairness.
When to Use Holistic vs Analytic Grading: Contextual Applications
Holistic grading is most effective in settings where overall comprehension and communication skills are prioritized, such as in narrative essays or creative writing, allowing educators to assess the general quality and coherence of a student's work. Analytic grading is better suited for assignments requiring detailed feedback on specific criteria, including research papers or lab reports, where evaluating distinct components like organization, grammar, and content accuracy is crucial. Choosing between holistic and analytic grading depends on the learning objectives and the complexity of the task, ensuring alignment with educational goals and assessment clarity.
Impact on Student Learning and Feedback
Holistic grading evaluates student work as an overall impression, encouraging creativity and critical thinking by focusing on the general quality rather than isolated components, which fosters intrinsic motivation and deeper learning. Analytic grading breaks down assignments into specific criteria, providing detailed, targeted feedback that helps students identify strengths and weaknesses, promoting skill development and incremental improvement. Both methods impact student learning differently; holistic grading supports cohesive understanding and expression, while analytic grading enhances clarity and mastery through precise, actionable feedback.
Best Practices for Implementing Effective Grading Systems
Implementing effective grading systems requires balancing holistic grading's focus on overall student understanding with analytic grading's detailed assessment of specific skills and criteria. Best practices include clearly defining rubrics that align with learning objectives, providing transparent feedback to support student growth, and training educators to apply grading methods consistently to ensure fairness and reliability. Integrating technology tools can streamline rubric creation, data collection, and feedback delivery, enhancing both holistic and analytic grading processes.
holistic grading vs analytic grading Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com