Social identity shapes how individuals define themselves based on group memberships such as family, friends, or community, influencing behavior and self-perception. Cultural identity encompasses shared customs, traditions, language, and values passed through generations, providing a deeper sense of belonging and heritage. Understanding the interplay between social and cultural identity helps explain how people navigate personal and collective experiences within diverse cultural contexts.
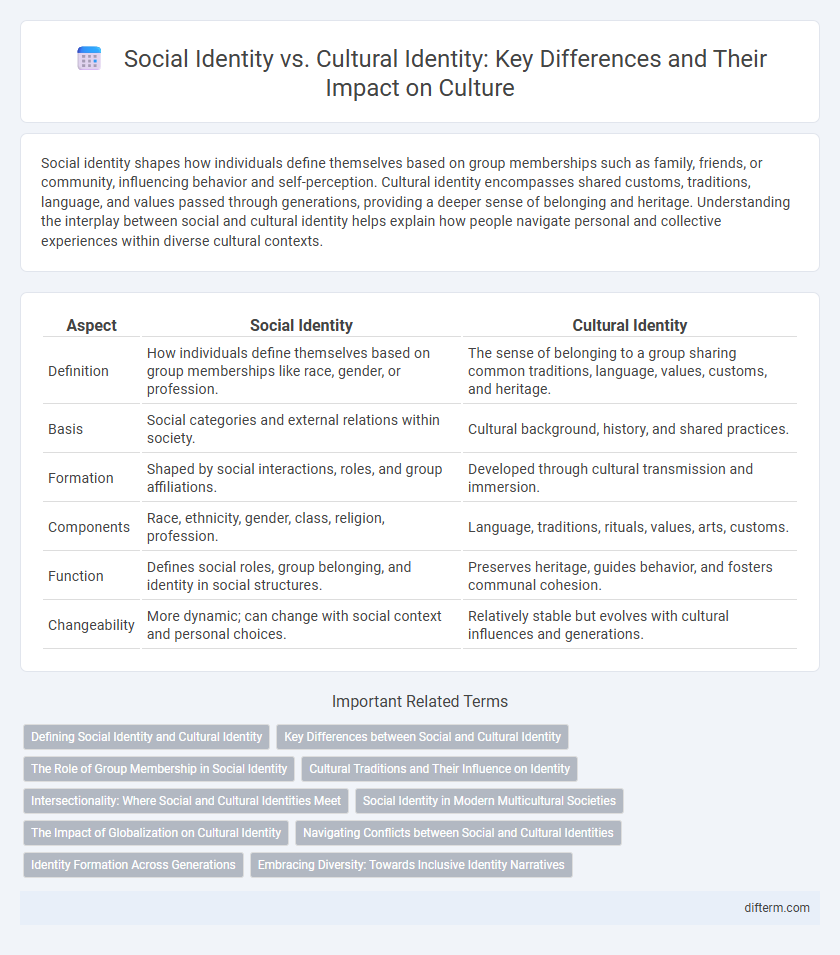
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Identity | Cultural Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | How individuals define themselves based on group memberships like race, gender, or profession. | The sense of belonging to a group sharing common traditions, language, values, customs, and heritage. |
| Basis | Social categories and external relations within society. | Cultural background, history, and shared practices. |
| Formation | Shaped by social interactions, roles, and group affiliations. | Developed through cultural transmission and immersion. |
| Components | Race, ethnicity, gender, class, religion, profession. | Language, traditions, rituals, values, arts, customs. |
| Function | Defines social roles, group belonging, and identity in social structures. | Preserves heritage, guides behavior, and fosters communal cohesion. |
| Changeability | More dynamic; can change with social context and personal choices. | Relatively stable but evolves with cultural influences and generations. |
Defining Social Identity and Cultural Identity
Social identity refers to an individual's sense of who they are based on their group memberships, such as nationality, ethnicity, religion, and social class, shaping how they perceive themselves and relate to others. Cultural identity encompasses the shared customs, beliefs, values, language, and traditions that define a group's way of life and create a collective sense of belonging. Both social and cultural identities influence personal and communal experiences, yet social identity emphasizes membership in social groups while cultural identity centers on inherited cultural elements.
Key Differences between Social and Cultural Identity
Social identity derives from group memberships such as nationality, ethnicity, or professional affiliation, influencing how individuals perceive themselves within societal structures. Cultural identity encompasses shared beliefs, traditions, language, and values that shape collective heritage and personal sense of belonging. The key difference lies in social identity's emphasis on external group classification, while cultural identity centers on internalized cultural experiences and practices.
The Role of Group Membership in Social Identity
Group membership serves as a cornerstone in shaping social identity by providing individuals with a sense of belonging and self-definition within a larger community. Social identity theory emphasizes how identification with cultural, ethnic, or social groups influences perceptions, behaviors, and intergroup dynamics. This collective affiliation helps differentiate social identity from cultural identity, as the former centers on group-based self-concept, while the latter encompasses shared traditions, values, and practices intrinsic to a cultural group.
Cultural Traditions and Their Influence on Identity
Cultural traditions shape social identity by providing shared rituals, symbols, and values that foster a sense of belonging within a community. These traditions influence individual behaviors, language, and worldview, reinforcing a collective cultural identity distinct from social identity's focus on group roles and social status. Understanding the interplay between cultural heritage and identity formation highlights the importance of preserving customs in maintaining cultural continuity and social cohesion.
Intersectionality: Where Social and Cultural Identities Meet
Intersectionality highlights the complex ways social identity categories such as race, gender, and class intersect with cultural identity, shaping individual experiences and social dynamics. Cultural identity reflects shared languages, traditions, and values within a group, while social identity encompasses broader societal roles and categories assigned or adopted by individuals. Understanding their intersection is crucial for addressing multidimensional inequality and promoting inclusive cultural policies.
Social Identity in Modern Multicultural Societies
Social identity in modern multicultural societies is shaped by individuals' affiliation with diverse social groups, including ethnicity, nationality, religion, and language. This dynamic identity influences social interactions, group cohesion, and the negotiation of belonging within heterogeneous communities. Understanding social identity is crucial for addressing issues of inclusion, discrimination, and intercultural dialogue in increasingly pluralistic environments.
The Impact of Globalization on Cultural Identity
Globalization transforms cultural identity by blending traditions, languages, and customs, challenging individuals to maintain distinct social identities within a global context. Social identity, grounded in group memberships such as ethnicity and nationality, often evolves as people adapt to diverse cultural influences brought by globalization. This dynamic interaction reshapes cultural identity, fostering hybrid identities while sometimes causing tension between global integration and local cultural preservation.
Navigating Conflicts between Social and Cultural Identities
Navigating conflicts between social and cultural identities often involves balancing individual group affiliations with broader cultural heritage, as social identity stems from membership in specific social groups while cultural identity relates to shared traditions, values, and history. Conflicts arise when social groups impose expectations that clash with cultural norms, leading to internal tension and identity negotiation. Effective resolution requires recognizing the fluidity of identity, fostering intercultural dialogue, and cultivating inclusion practices that respect both social contexts and cultural backgrounds.
Identity Formation Across Generations
Social identity shapes individual self-concept through membership in groups defined by race, gender, or profession, while cultural identity encompasses shared traditions, languages, and values passed through generations. Identity formation across generations involves the dynamic interplay of preserving heritage and adapting to societal changes, influencing how individuals relate to both their social groups and cultural backgrounds. Intergenerational transmission of narratives and practices reinforces cultural continuity, yet evolving social contexts can lead to hybrid identities reflecting both stability and transformation.
Embracing Diversity: Towards Inclusive Identity Narratives
Social identity shapes individuals' sense of belonging within specific groups based on characteristics such as ethnicity, gender, or nationality, while cultural identity reflects shared heritage, customs, and values passed through generations. Embracing diversity in identity narratives requires integrating multiple cultural perspectives to foster inclusivity and mutual respect across communities. Inclusive identity frameworks promote dialogue, reduce prejudice, and strengthen social cohesion by validating the complexity of diverse experiences within society.
social identity vs cultural identity Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com