Culture pet preferences reflect attitudes toward power distance, where some owners emphasize hierarchy and authority in training and care, while others adopt an egalitarian approach that values mutual respect and equality between pet and owner. Societies with high power distance often expect pets to obey commands without question, reinforcing clear dominance. In contrast, egalitarian cultures promote interactive bonds and cooperative behavior, fostering a partnership dynamic in the pet-owner relationship.
Table of Comparison
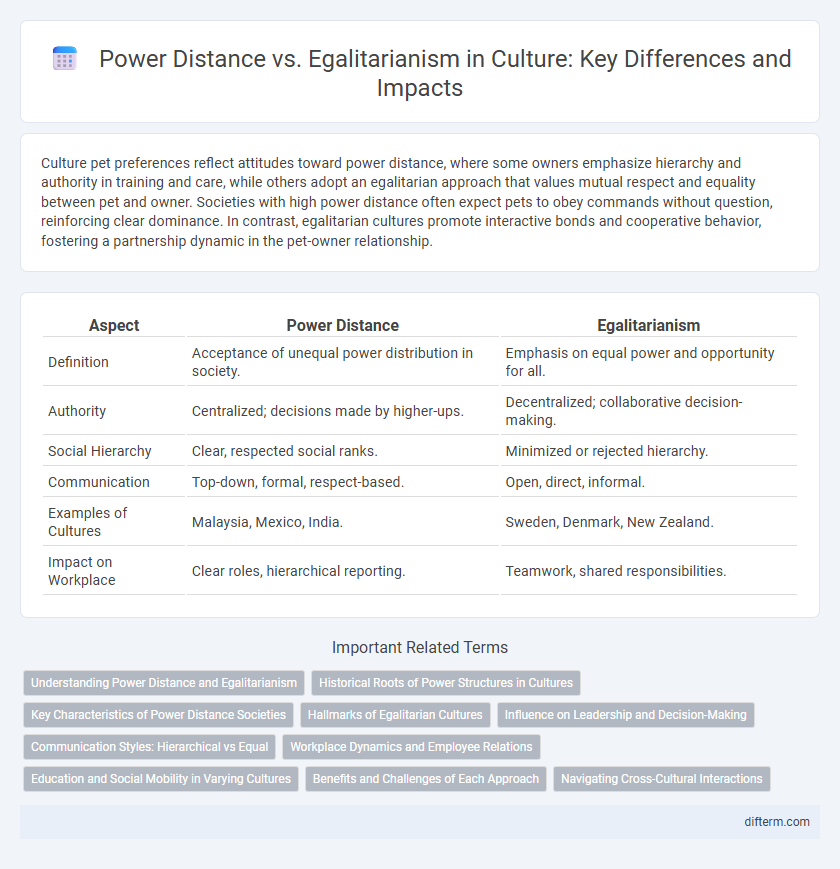
| Aspect | Power Distance | Egalitarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acceptance of unequal power distribution in society. | Emphasis on equal power and opportunity for all. |
| Authority | Centralized; decisions made by higher-ups. | Decentralized; collaborative decision-making. |
| Social Hierarchy | Clear, respected social ranks. | Minimized or rejected hierarchy. |
| Communication | Top-down, formal, respect-based. | Open, direct, informal. |
| Examples of Cultures | Malaysia, Mexico, India. | Sweden, Denmark, New Zealand. |
| Impact on Workplace | Clear roles, hierarchical reporting. | Teamwork, shared responsibilities. |
Understanding Power Distance and Egalitarianism
Power distance measures the extent to which less powerful members expect and accept unequal power distribution within organizations and institutions. Egalitarianism emphasizes equal rights, opportunities, and status for all individuals, minimizing hierarchical differences. Understanding power distance versus egalitarianism is crucial for navigating cultural norms, leadership styles, and communication patterns in diverse global environments.
Historical Roots of Power Structures in Cultures
Historical roots of power structures in cultures often stem from feudal systems, monarchies, and colonialism, which entrenched hierarchical relationships and power distance. Societies with centralized authority and rigid class systems tend to exhibit high power distance, while those influenced by democratic ideals and communal living promote egalitarianism. These foundational legacies shape contemporary cultural attitudes toward authority, social stratification, and interpersonal dynamics across various regions.
Key Characteristics of Power Distance Societies
Power distance societies exhibit hierarchical structures where unequal power distribution is accepted and expected, with authority figures granted significant respect and decision-making power. Communication tends to be top-down, and subordinates often refrain from questioning or challenging superiors, reinforcing social stratification. These cultures emphasize formality, clear status distinctions, and centralized control in organizational and social interactions.
Hallmarks of Egalitarian Cultures
Egalitarian cultures emphasize equal power distribution, fostering open communication and collaborative decision-making among members. Hallmarks include flat organizational structures, shared leadership roles, and valuing individual autonomy and inclusiveness. These societies prioritize consensus-building and minimize hierarchical barriers, promoting mutual respect and collective responsibility.
Influence on Leadership and Decision-Making
Power distance significantly shapes leadership styles, with high power distance cultures favoring hierarchical decision-making where leaders hold substantial authority. In contrast, egalitarian cultures promote participative leadership, encouraging collaboration and shared decision-making among team members. These cultural dimensions influence organizational communication patterns and employee engagement, impacting overall effectiveness and innovation.
Communication Styles: Hierarchical vs Equal
In cultures with high power distance, communication styles tend to be hierarchical, where subordinates speak formally and deferentially to superiors, and decision-making is centralized. Egalitarian cultures favor open, direct communication, encouraging feedback and collaboration across all levels regardless of status. This contrast influences workplace interactions, with hierarchical communication often limiting open dialogue and egalitarianism promoting inclusivity and transparency.
Workplace Dynamics and Employee Relations
Workplace dynamics are profoundly shaped by the cultural dimension of power distance, influencing hierarchical communication and decision-making processes within organizations. In high power distance cultures, employee relations tend to be formal, with clear authority gradients and limited upward feedback, whereas egalitarian cultures promote open dialogue, collaborative problem-solving, and decentralized authority. Optimizing organizational performance requires aligning management practices with these cultural expectations, fostering trust and engagement through culturally appropriate leadership styles.
Education and Social Mobility in Varying Cultures
Power distance influences education systems by shaping hierarchical structures where authority is respected and students often accept teacher-centered learning, limiting social mobility in high power distance cultures. Egalitarian societies promote inclusive education with collaborative learning, critical thinking, and equal opportunities that enhance social mobility and reduce class barriers. Variations in cultural attitudes toward power and equality significantly affect access to education and the potential for upward social movement.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Approach
Power distance cultures benefit from clear hierarchies that enhance decision-making efficiency and maintain organizational order, yet they face challenges such as limited open communication and reduced employee empowerment. Egalitarian cultures foster collaboration and innovation by promoting equal participation and shared responsibility, though they may struggle with slower decision processes and potential conflicts due to diverse opinions. Balancing the benefits and challenges of power distance and egalitarianism is crucial for adapting leadership styles to cultural contexts.
Navigating Cross-Cultural Interactions
Understanding power distance and egalitarianism is crucial for navigating cross-cultural interactions effectively. Cultures with high power distance emphasize hierarchical structures and respect for authority, while egalitarian cultures promote equal distribution of power and collaboration. Adapting communication styles and leadership approaches to align with these cultural dimensions enhances mutual respect and reduces misunderstandings in global interactions.
power distance vs egalitarianism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com