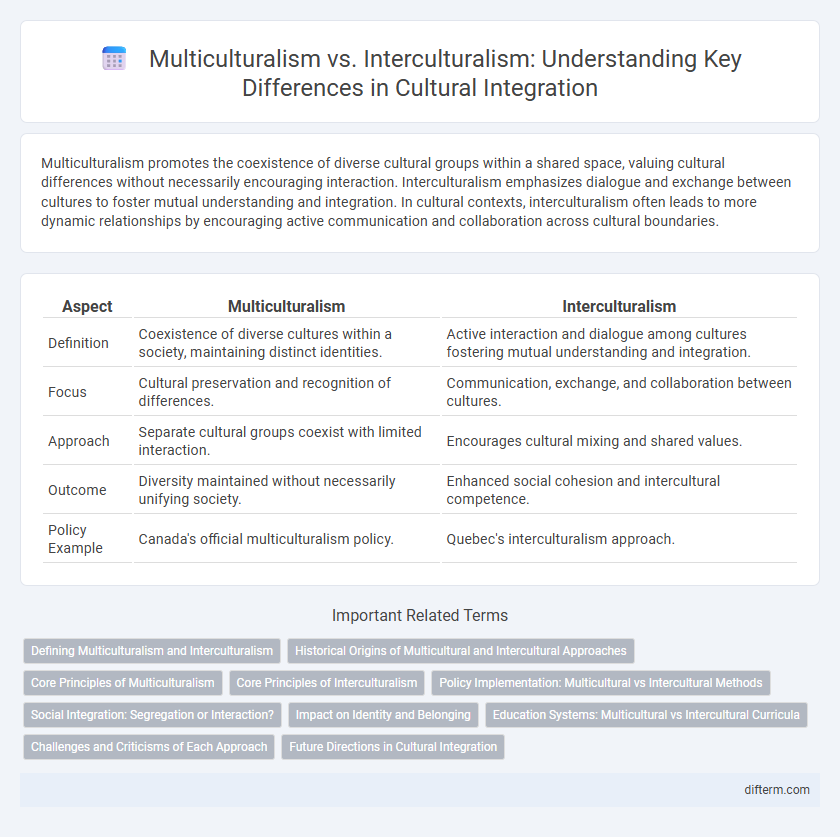
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a shared space, valuing cultural differences without necessarily encouraging interaction. Interculturalism emphasizes dialogue and exchange between cultures to foster mutual understanding and integration. In cultural contexts, interculturalism often leads to more dynamic relationships by encouraging active communication and collaboration across cultural boundaries.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Interculturalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures within a society, maintaining distinct identities. | Active interaction and dialogue among cultures fostering mutual understanding and integration. |
| Focus | Cultural preservation and recognition of differences. | Communication, exchange, and collaboration between cultures. |
| Approach | Separate cultural groups coexist with limited interaction. | Encourages cultural mixing and shared values. |
| Outcome | Diversity maintained without necessarily unifying society. | Enhanced social cohesion and intercultural competence. |
| Policy Example | Canada's official multiculturalism policy. | Quebec's interculturalism approach. |
Defining Multiculturalism and Interculturalism
Multiculturalism emphasizes the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a society, promoting the preservation of distinct cultural identities and equal recognition under the law. Interculturalism focuses on active dialogue and interaction between cultures to foster mutual understanding, social cohesion, and shared values. While multiculturalism stresses cultural pluralism, interculturalism prioritizes communication and integration across cultural boundaries.
Historical Origins of Multicultural and Intercultural Approaches
Multiculturalism originated in the 1960s and 1970s, primarily in Canada and Australia, as a policy response to immigration and the need to recognize cultural diversity within national frameworks. Interculturalism emerged later, notably in Quebec during the 1990s, emphasizing interaction, dialogue, and mutual respect among different cultural groups to promote social cohesion. While multiculturalism focuses on coexistence and recognition of distinct cultures, interculturalism promotes dynamic exchanges and integration across cultural boundaries.
Core Principles of Multiculturalism
Multiculturalism emphasizes the recognition and preservation of diverse cultural identities within a unified society, promoting equality and respect for all ethnic groups. Core principles include cultural pluralism, equal participation in social and political life, and protection of minority rights to maintain distinct cultural traditions. This approach seeks to foster social cohesion by valuing diversity without forcing assimilation or cultural homogenization.
Core Principles of Interculturalism
Interculturalism centers on promoting active dialogue and mutual respect among diverse cultural groups within a shared social framework, emphasizing interaction and understanding over mere coexistence. It prioritizes social cohesion, inclusion, and shared values, fostering meaningful exchanges that transcend cultural boundaries while acknowledging individual cultural identities. Core principles include dialogue, equality, recognition of cultural diversity as a societal asset, and collaboration to address common challenges.
Policy Implementation: Multicultural vs Intercultural Methods
Multiculturalism policies emphasize the recognition and preservation of distinct cultural identities within a society, promoting diversity through cultural autonomy and group-specific rights. Interculturalism focuses on fostering meaningful interaction, dialogue, and integration among different cultural groups to build shared values and social cohesion. Policy implementation of multiculturalism often involves support for cultural institutions and minority language rights, whereas intercultural approaches prioritize education, cross-cultural communication programs, and collaborative community initiatives.
Social Integration: Segregation or Interaction?
Multiculturalism emphasizes the coexistence of diverse cultural groups often resulting in cultural segregation, while interculturalism promotes active interaction and dialogue among different communities to foster social cohesion. Social integration under multiculturalism may risk isolated ethnic enclaves, whereas interculturalism encourages shared spaces and mutual understanding, reducing social fragmentation. Policies favoring interculturalism typically lead to stronger community bonds and inclusive participation in social, economic, and political life.
Impact on Identity and Belonging
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, often emphasizing the recognition and preservation of distinct group identities, which strengthens individuals' sense of belonging to their heritage communities. Interculturalism encourages active dialogue and interaction among different cultural groups, fostering shared identities and mutual understanding that can reshape personal and collective identities over time. Both approaches impact identity by either reinforcing separate cultural boundaries or by cultivating hybrid identities through cultural exchange and integration.
Education Systems: Multicultural vs Intercultural Curricula
Multicultural education systems emphasize the coexistence of diverse cultures through curricula that represent multiple cultural perspectives without necessarily fostering interaction among them. Intercultural curricula prioritize active dialogue and integration between cultures, promoting understanding, empathy, and collaboration among students from diverse backgrounds. Educational frameworks that implement intercultural approaches demonstrate improved student engagement and social cohesion compared to traditional multicultural models.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Multiculturalism faces challenges such as fostering social fragmentation and perpetuating cultural enclaves, which can hinder national cohesion and integration. Interculturalism, while promoting dialogue and interaction, struggles with implementation complexities and may inadvertently suppress minority identities by emphasizing majority norms. Both approaches encounter criticism for balancing cultural recognition with social unity, highlighting the need for policies that navigate diversity without reinforcing divisions.
Future Directions in Cultural Integration
Future directions in cultural integration emphasize blending multiculturalism's celebration of diverse identities with interculturalism's focus on dialogue and mutual understanding. Emerging policies advocate for inclusive frameworks that foster active cultural exchange and collaboration, ensuring social cohesion while respecting distinct cultural expressions. Technological advancements and global connectivity are driving innovative platforms for intercultural communication, reshaping integration strategies toward more dynamic and participatory cultural interactions.
Multiculturalism vs Interculturalism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com