Norms are the specific rules and expectations that guide behavior within a culture, while values represent the deeply held beliefs and principles that shape those norms. Understanding the distinction between norms and values is essential to grasp how cultural practices develop and influence social interactions. Differences in values between cultures often lead to variations in norms, reflecting diverse priorities and worldviews.
Table of Comparison
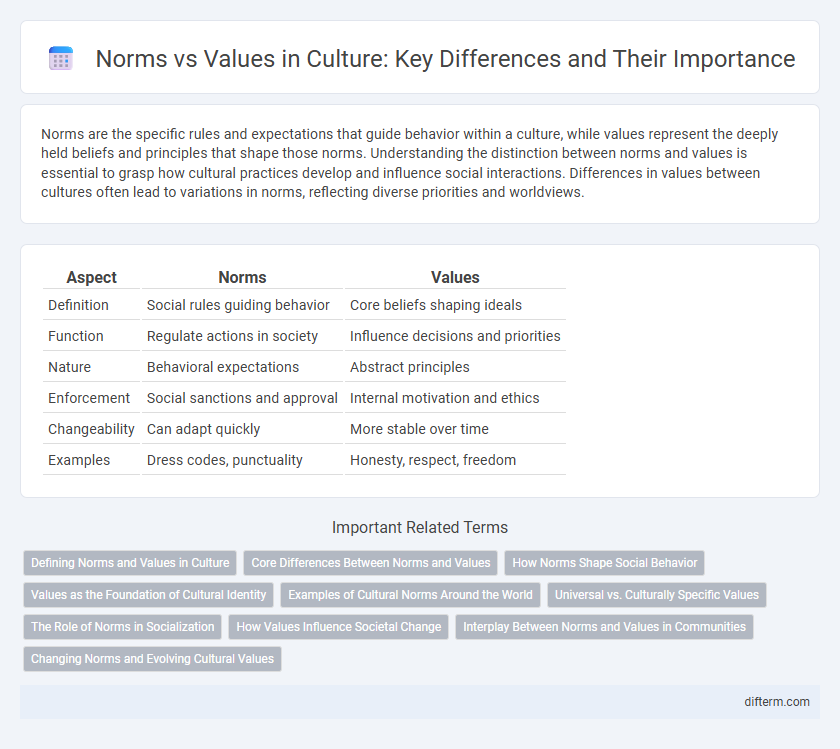
| Aspect | Norms | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social rules guiding behavior | Core beliefs shaping ideals |
| Function | Regulate actions in society | Influence decisions and priorities |
| Nature | Behavioral expectations | Abstract principles |
| Enforcement | Social sanctions and approval | Internal motivation and ethics |
| Changeability | Can adapt quickly | More stable over time |
| Examples | Dress codes, punctuality | Honesty, respect, freedom |
Defining Norms and Values in Culture
Norms in culture are specific rules and expectations that guide behavior within a group, shaping social interactions and maintaining order. Values represent deeply held beliefs about what is important and desirable, influencing individuals' attitudes and priorities. Together, norms and values form the foundation of cultural identity and social cohesion.
Core Differences Between Norms and Values
Norms are specific rules and expectations that guide behavior within a culture, while values represent deeply held beliefs about what is important and desirable. Norms dictate how individuals act in particular situations, whereas values shape the overall worldview and priorities of a society. Understanding core differences between norms and values reveals how social order is maintained through behavior regulation versus underlying moral principles.
How Norms Shape Social Behavior
Norms establish expected patterns of behavior within a culture, guiding individuals on acceptable actions and creating social order. These unwritten rules influence everyday interactions by promoting conformity and discouraging deviance, which reinforces group cohesion. Values underpin norms by providing the foundational beliefs that define what is considered important or desirable in a society.
Values as the Foundation of Cultural Identity
Values serve as the core foundation of cultural identity, shaping collective beliefs and guiding social behavior within communities. They influence norms by providing the underlying reasons for why certain practices are accepted or rejected, embedding deep significance beyond mere rules. Understanding values offers critical insight into the motivations that sustain cultural traditions and interpersonal relationships.
Examples of Cultural Norms Around the World
Cultural norms vary widely, such as bowing in Japan to show respect versus shaking hands in the United States as a common greeting. In India, removing shoes before entering a home reflects a norm tied to cleanliness and respect, while in many Middle Eastern countries, offering and accepting coffee symbolizes hospitality. These examples illustrate how cultural norms guide social behavior and differ significantly across regions.
Universal vs. Culturally Specific Values
Universal values such as human rights and freedom of expression transcend cultural boundaries, forming a common ethical foundation globally. Norms, however, are culturally specific, reflecting distinct traditions, behaviors, and social expectations unique to each society. Understanding the interplay between universal values and culturally specific norms is crucial for fostering cross-cultural communication and respect.
The Role of Norms in Socialization
Norms serve as unwritten rules that guide behavior within a culture, shaping social interactions and expectations. They play a crucial role in socialization by teaching individuals the accepted ways to act in various situations, reinforcing societal cohesion and stability. Through family, education, and peer groups, norms are internalized, influencing attitudes and behaviors consistent with cultural values.
How Values Influence Societal Change
Values serve as the foundation for societal norms by shaping collective beliefs about what is important and desirable, driving social behavior and expectations. When values evolve, they challenge existing norms, prompting shifts in laws, customs, and institutional practices that reflect new priorities. This dynamic relationship between values and norms fuels societal change by encouraging adaptation and reform within cultural frameworks.
Interplay Between Norms and Values in Communities
Norms function as explicit rules guiding behavior within a community, while values represent deeply held beliefs that shape those norms. The interplay between norms and values establishes social order, as shared values influence the creation and enforcement of norms that maintain cultural cohesion. This dynamic ensures that community practices align with collective ideals, reinforcing identity and fostering social harmony.
Changing Norms and Evolving Cultural Values
Changing norms reflect shifting societal expectations and behaviors, often driven by technological advances and generational perspectives. Evolving cultural values influence these norms, highlighting a dynamic interplay where core beliefs adapt to contemporary contexts. Understanding this relationship is crucial for analyzing social transformation and cultural adaptation globally.
norms vs values Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com