Cultural elasticity allows societies to adapt and evolve by integrating new ideas while preserving core traditions, fostering innovation and resilience. In contrast, cultural rigidity resists change, often leading to stagnation and conflict as societies struggle to address contemporary challenges. Balancing elasticity and rigidity is crucial for sustaining cultural identity while promoting growth and social harmony.
Table of Comparison
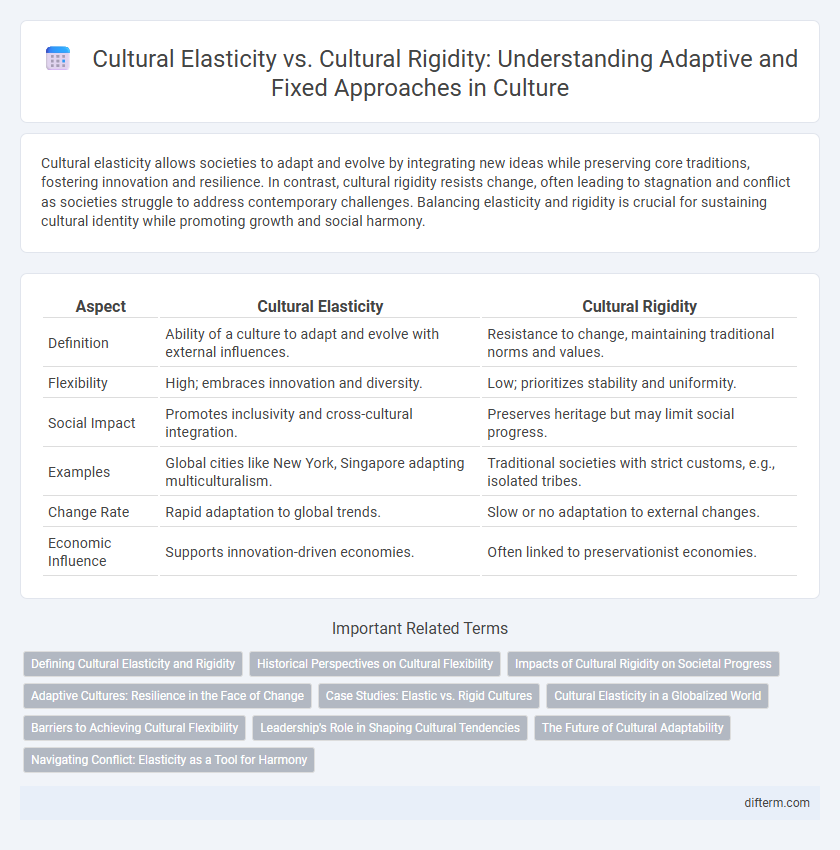
| Aspect | Cultural Elasticity | Cultural Rigidity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability of a culture to adapt and evolve with external influences. | Resistance to change, maintaining traditional norms and values. |
| Flexibility | High; embraces innovation and diversity. | Low; prioritizes stability and uniformity. |
| Social Impact | Promotes inclusivity and cross-cultural integration. | Preserves heritage but may limit social progress. |
| Examples | Global cities like New York, Singapore adapting multiculturalism. | Traditional societies with strict customs, e.g., isolated tribes. |
| Change Rate | Rapid adaptation to global trends. | Slow or no adaptation to external changes. |
| Economic Influence | Supports innovation-driven economies. | Often linked to preservationist economies. |
Defining Cultural Elasticity and Rigidity
Cultural elasticity refers to a society's ability to adapt and incorporate new ideas, practices, and values while maintaining its core identity, promoting innovation and social cohesion. In contrast, cultural rigidity describes a fixed adherence to traditional beliefs and norms, often resisting change and limiting social progress. The balance between elasticity and rigidity influences how cultures respond to globalization, technological advances, and intercultural interactions.
Historical Perspectives on Cultural Flexibility
Historical perspectives on cultural flexibility reveal societies that adapt resiliently to external influences often experience enhanced innovation and social cohesion. Cultural elasticity enables traditions to evolve while maintaining core identities, contrasting sharply with cultural rigidity, which can lead to social stagnation or conflict. Key examples include the dynamic cultural syncretism seen in the Silk Road exchanges and the adaptive revivals during the Renaissance period.
Impacts of Cultural Rigidity on Societal Progress
Cultural rigidity often stifles innovation and adaptability, leading to slowed societal progress and resistance to change. Societies anchored in rigid cultural norms may experience diminished creativity, reduced social cohesion, and hindered economic development. This resistance to evolving social values and technologies can ultimately restrict opportunities for growth and global integration.
Adaptive Cultures: Resilience in the Face of Change
Adaptive cultures exhibit high cultural elasticity, enabling organizations and societies to respond flexibly to external pressures and evolving environments. This resilience fosters innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning, which are critical for navigating globalization and technological advancements. Conversely, cultural rigidity often limits growth by resisting change, leading to stagnation and decreased competitive advantage.
Case Studies: Elastic vs. Rigid Cultures
Case studies comparing cultural elasticity and rigidity reveal that elastic cultures, such as those in Scandinavian countries, adapt quickly to social and technological changes, fostering innovation and inclusivity. In contrast, rigid cultures, exemplified by some traditionalist societies, maintain strict adherence to established norms and values, often resisting change and prioritizing stability. This dynamic impacts organizational behavior, economic development, and social cohesion across diverse cultural contexts.
Cultural Elasticity in a Globalized World
Cultural elasticity enables societies to adapt and integrate diverse customs, fostering innovation and cross-cultural collaboration in a globalized world. This flexibility supports the preservation of core identities while embracing transformative influences, enhancing social cohesion and economic resilience. Emphasizing cultural elasticity boosts intercultural communication and global business success by accommodating dynamic cultural exchanges.
Barriers to Achieving Cultural Flexibility
Cultural elasticity allows societies to adapt and integrate new ideas, promoting innovation and cooperation across diverse groups. Barriers to achieving cultural flexibility often include deeply ingrained traditions, resistance to change, and ethnocentric attitudes that hinder open-mindedness. Overcoming these obstacles requires deliberate efforts to foster intercultural dialogue and embrace pluralism within social institutions.
Leadership's Role in Shaping Cultural Tendencies
Leadership significantly influences cultural elasticity by promoting openness to change and adaptability within organizations. Leaders who encourage continuous learning and embrace diverse perspectives foster environments where cultural flexibility thrives. Conversely, rigid leadership styles often reinforce traditional norms, limiting innovation and cultural evolution.
The Future of Cultural Adaptability
Cultural elasticity enhances a society's ability to embrace change, fostering innovation and resilience in a rapidly globalizing world. In contrast, cultural rigidity limits adaptation, often leading to social stagnation and conflict. The future of cultural adaptability depends on balancing preservation of core values with openness to new ideas and diverse perspectives.
Navigating Conflict: Elasticity as a Tool for Harmony
Cultural elasticity enables societies to adapt and find common ground during conflicts, promoting harmony by embracing diverse perspectives and flexible norms. In contrast, cultural rigidity often intensifies disputes by enforcing strict adherence to traditions and resisting change. Navigating conflict effectively requires leveraging cultural elasticity to facilitate understanding, reduce tension, and foster collaborative solutions.
Cultural elasticity vs cultural rigidity Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com