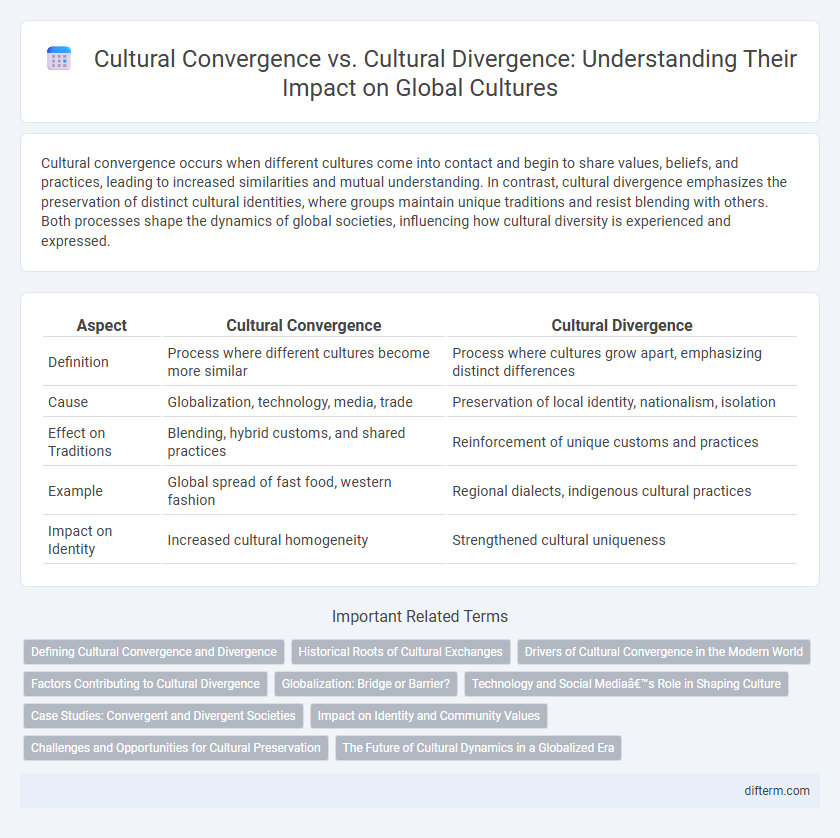
Cultural convergence occurs when different cultures come into contact and begin to share values, beliefs, and practices, leading to increased similarities and mutual understanding. In contrast, cultural divergence emphasizes the preservation of distinct cultural identities, where groups maintain unique traditions and resist blending with others. Both processes shape the dynamics of global societies, influencing how cultural diversity is experienced and expressed.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cultural Convergence | Cultural Divergence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process where different cultures become more similar | Process where cultures grow apart, emphasizing distinct differences |
| Cause | Globalization, technology, media, trade | Preservation of local identity, nationalism, isolation |
| Effect on Traditions | Blending, hybrid customs, and shared practices | Reinforcement of unique customs and practices |
| Example | Global spread of fast food, western fashion | Regional dialects, indigenous cultural practices |
| Impact on Identity | Increased cultural homogeneity | Strengthened cultural uniqueness |
Defining Cultural Convergence and Divergence
Cultural convergence refers to the process where different cultures become more similar through increased interaction, communication, and exchange of ideas, often driven by globalization and technological advancements. In contrast, cultural divergence occurs when cultures become more distinct and emphasize their unique traditions, values, and practices to preserve identity amidst external influences. Understanding these concepts highlights the dynamic tension between global integration and local cultural preservation.
Historical Roots of Cultural Exchanges
Historical roots of cultural exchanges reveal that trade routes like the Silk Road and maritime networks facilitated cultural convergence by spreading languages, religions, and technologies across continents. Conversely, geographic barriers and distinct social structures often led to cultural divergence, preserving unique traditions and identities. These dynamics shaped civilizations by blending and differentiating cultural elements over centuries.
Drivers of Cultural Convergence in the Modern World
Globalization, technological advancements, and increased international trade serve as primary drivers of cultural convergence in the modern world. Social media platforms and digital communication enable rapid exchange and blending of cultural values, languages, and customs across diverse populations. Economic interdependence and multinational corporations further promote the adoption of shared cultural practices and consumption patterns worldwide.
Factors Contributing to Cultural Divergence
Geographical isolation, language barriers, and strong adherence to traditional customs are primary factors contributing to cultural divergence. Economic disparities and political conflicts further deepen cultural divides by limiting cross-cultural interaction and exchange. These elements reinforce distinct cultural identities, reducing the likelihood of convergence despite globalization pressures.
Globalization: Bridge or Barrier?
Globalization acts as a powerful agent of cultural convergence by facilitating the exchange of ideas, traditions, and values across borders, leading to increased cultural blending and shared global identities. However, it can also amplify cultural divergence when local communities resist homogenization to preserve unique heritage and customs, creating distinct cultural boundaries. The dynamic interplay between these forces determines whether globalization serves as a bridge connecting diverse cultures or a barrier reinforcing cultural differences.
Technology and Social Media’s Role in Shaping Culture
Technology and social media accelerate cultural convergence by facilitating instantaneous communication and the global exchange of ideas, customs, and values. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter disseminate trends rapidly, creating shared cultural experiences across diverse populations. However, these digital channels also highlight cultural divergence by enabling niche communities to preserve and promote distinct identities, languages, and traditions in the digital space.
Case Studies: Convergent and Divergent Societies
Cultural convergence occurs when different societies adopt shared values, languages, and practices, as seen in the global spread of technology in South Korea and the United States, fostering similar consumer behaviors and digital cultures. In contrast, cultural divergence is evident in regions like Catalonia and Quebec, where distinct linguistic identities and traditions reinforce social separation despite global influences. By examining these case studies, scholars gain insights into how globalization impacts cultural identity and social cohesion in diverse contexts.
Impact on Identity and Community Values
Cultural convergence promotes shared identities and common community values through increased interaction and exchange, fostering unity in diverse societies. In contrast, cultural divergence emphasizes unique identities and preservation of local traditions, often strengthening community bonds by resisting external influences. Both processes significantly shape social cohesion and the evolution of collective values within communities.
Challenges and Opportunities for Cultural Preservation
Cultural convergence fosters global connectivity and shared values but challenges the preservation of unique traditions, languages, and identities at risk of assimilation. Cultural divergence emphasizes the protection of distinct heritage and diverse practices, yet may hinder cross-cultural dialogue and cooperation. Balancing these dynamics requires adaptive strategies that promote cultural resilience while embracing beneficial exchange.
The Future of Cultural Dynamics in a Globalized Era
Cultural dynamics in a globalized era reveal a complex interplay between cultural convergence, driven by technological advancements and increased communication, and cultural divergence, preserved through local traditions and identity assertion. Global media platforms facilitate the rapid exchange of cultural elements, fostering shared values and hybrid cultures across borders. Despite this integration, communities actively maintain distinct languages, rituals, and social norms, ensuring cultural diversity persists amid globalization's homogenizing forces.
cultural convergence vs cultural divergence Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com