Myths and legends both serve as traditional narratives that explain cultural beliefs and values, but myths often involve gods or supernatural beings and convey fundamental truths about the world. Legends, in contrast, are usually grounded in historical events or figures, though they may be exaggerated or embellished over time. Understanding the distinction between myth and legend helps preserve cultural heritage while exploring the origins of societal norms.
Table of Comparison
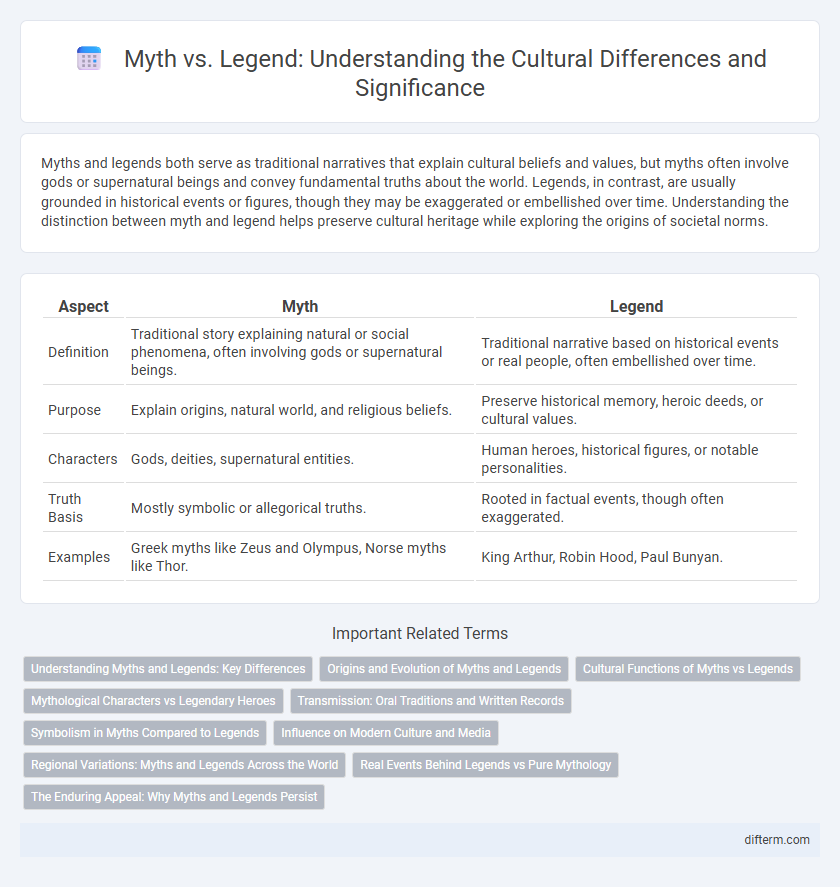
| Aspect | Myth | Legend |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional story explaining natural or social phenomena, often involving gods or supernatural beings. | Traditional narrative based on historical events or real people, often embellished over time. |
| Purpose | Explain origins, natural world, and religious beliefs. | Preserve historical memory, heroic deeds, or cultural values. |
| Characters | Gods, deities, supernatural entities. | Human heroes, historical figures, or notable personalities. |
| Truth Basis | Mostly symbolic or allegorical truths. | Rooted in factual events, though often exaggerated. |
| Examples | Greek myths like Zeus and Olympus, Norse myths like Thor. | King Arthur, Robin Hood, Paul Bunyan. |
Understanding Myths and Legends: Key Differences
Myths are ancient narratives rooted in religious or spiritual beliefs explaining natural phenomena or the origins of the world, often featuring gods or supernatural beings. Legends are traditional stories grounded in historical events or figures, embellished over time to highlight heroic deeds or moral lessons. Understanding myths centers on their function to convey cultural values and explain existential questions, while legends focus on preserving cultural identity through heroic or noteworthy human experiences.
Origins and Evolution of Myths and Legends
Myths originate from ancient oral traditions, serving to explain natural phenomena and cultural beliefs through divine or supernatural narratives. Legends evolve from historical events or figures, often embellished over time to embody societal values and collective memory. Both forms adapt across generations, influencing cultural identity and storytelling practices worldwide.
Cultural Functions of Myths vs Legends
Myths serve as foundational narratives that explain the origins of the world, natural phenomena, and societal customs, often embodying sacred truths and spiritual beliefs within a culture. Legends, rooted in historical events or figures, function to reinforce cultural identity and moral values by connecting communities with their past and inspiring collective pride. Both myths and legends play crucial roles in preserving cultural heritage, guiding ethical behavior, and shaping a society's worldview through storytelling.
Mythological Characters vs Legendary Heroes
Mythological characters often embody supernatural traits and divine origins, serving as symbolic representations of cultural beliefs and natural phenomena. Legendary heroes, by contrast, are typically mortals celebrated for extraordinary feats and virtuous qualities rooted in historical or semi-historical contexts. The distinction highlights differing narrative roles: myths explain existential questions, while legends inspire moral values through human achievements.
Transmission: Oral Traditions and Written Records
Myths and legends both rely heavily on oral traditions and written records for transmission, yet myths often serve to explain universal truths or natural phenomena, passed down through generations with symbolic meaning. Legends typically center on historical events or figures, blending fact with storytelling, and are preserved in both local folklore and documented chronicles. The dual channels of oral narration and textual documentation ensure the endurance and evolution of these cultural narratives across societies.
Symbolism in Myths Compared to Legends
Myths often embody profound symbolism representing cosmic forces, gods, and universal truths that shape cultural worldviews, while legends typically symbolize historical events or heroic deeds infused with moral lessons. Myths use archetypal symbols to convey spiritual or existential meanings, whereas legends anchor their symbolism in tangible human experiences and community identity. The symbolic depth in myths fosters collective meaning-making, contrasting with the more localized and historically grounded symbolism found in legends.
Influence on Modern Culture and Media
Myths and legends profoundly shape modern culture and media by inspiring countless films, literature, and art that reinterpret ancient narratives for contemporary audiences. Iconic mythological themes, such as heroism, morality, and the supernatural, underpin popular genres like fantasy and science fiction, fueling creativity and storytelling. The enduring appeal of these traditional tales fosters cultural identity and offers a shared symbolic language across diverse societies.
Regional Variations: Myths and Legends Across the World
Myths and legends vary significantly across regions, reflecting diverse cultural values, histories, and natural environments. For example, Greek myths emphasize gods and heroes with human traits, while Native American legends often incorporate animals as spiritual guides. These regional variations influence storytelling traditions, shaping local identities and preserving communal beliefs through generations.
Real Events Behind Legends vs Pure Mythology
Legends often stem from real historical events or figures, transforming over time through oral tradition into embellished narratives that preserve cultural memory with a blend of fact and fiction. In contrast, pure mythology comprises symbolic stories created to explain natural phenomena, human behavior, or spiritual beliefs without direct ties to actual occurrences. Analyzing the origins of legends helps distinguish the factual foundation beneath the mythical elements, revealing insights into the values and experiences of ancient societies.
The Enduring Appeal: Why Myths and Legends Persist
Myths and legends persist across cultures due to their deep-rooted roles in shaping collective identity and explaining natural phenomena through symbolic narratives. These stories convey universal themes such as heroism, morality, and the human connection to the divine, resonating across generations. Their enduring appeal lies in their capacity to provide meaning, inspire creativity, and preserve cultural heritage worldwide.
myth vs legend Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com