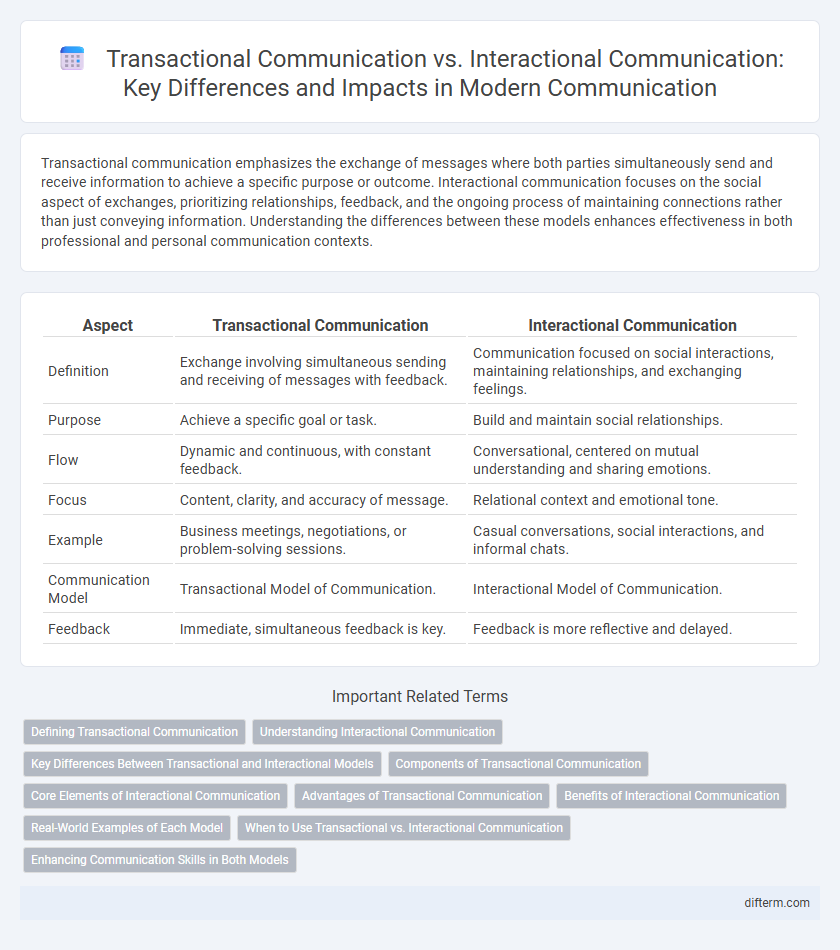
Transactional communication emphasizes the exchange of messages where both parties simultaneously send and receive information to achieve a specific purpose or outcome. Interactional communication focuses on the social aspect of exchanges, prioritizing relationships, feedback, and the ongoing process of maintaining connections rather than just conveying information. Understanding the differences between these models enhances effectiveness in both professional and personal communication contexts.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Transactional Communication | Interactional Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exchange involving simultaneous sending and receiving of messages with feedback. | Communication focused on social interactions, maintaining relationships, and exchanging feelings. |
| Purpose | Achieve a specific goal or task. | Build and maintain social relationships. |
| Flow | Dynamic and continuous, with constant feedback. | Conversational, centered on mutual understanding and sharing emotions. |
| Focus | Content, clarity, and accuracy of message. | Relational context and emotional tone. |
| Example | Business meetings, negotiations, or problem-solving sessions. | Casual conversations, social interactions, and informal chats. |
| Communication Model | Transactional Model of Communication. | Interactional Model of Communication. |
| Feedback | Immediate, simultaneous feedback is key. | Feedback is more reflective and delayed. |
Defining Transactional Communication
Transactional communication is a dynamic process where participants simultaneously send and receive messages, emphasizing mutual influence and feedback in real-time. It involves continuous exchange of information with both verbal and nonverbal cues contributing to meaning construction. Unlike one-way communication models, transactional communication highlights the interconnectedness and co-creation of understanding between communicators.
Understanding Interactional Communication
Interactional communication emphasizes the dynamic exchange of messages where participants actively interpret and respond to each other's verbal and nonverbal cues, fostering mutual understanding and relationship building. This type of communication relies heavily on feedback, turn-taking, and context, highlighting the co-constructive nature of meaning. Understanding interactional communication is essential for enhancing interpersonal connections and promoting effective dialogue in social and professional settings.
Key Differences Between Transactional and Interactional Models
Transactional communication involves simultaneous sending and receiving of messages, emphasizing dynamic feedback and mutual influence, whereas interactional communication follows a sequential exchange with defined sender and receiver roles. The transactional model highlights the complexity of communication through continuous, overlapping processes, while the interactional model focuses on turn-taking and contextual feedback loops. Key differences lie in timing, feedback immediacy, and the active participation of communicators within their environment.
Components of Transactional Communication
Transactional communication consists of essential components including the sender, receiver, message, channel, feedback, and context. Each participant simultaneously acts as sender and receiver, exchanging messages through verbal and nonverbal signals within a specific environment. Effective transactional communication relies on continuous feedback, noise management, and shared understanding to facilitate dynamic and real-time exchanges between communicators.
Core Elements of Interactional Communication
Interactional communication centers on core elements such as feedback, mutual understanding, and context, emphasizing a continuous two-way exchange between participants. Unlike transactional communication, which prioritizes the transmission of a message from sender to receiver, interactional communication involves shared meaning construction through dialogue and response. Key components include active listening, nonverbal cues, and relational dynamics that foster effective interpersonal connections.
Advantages of Transactional Communication
Transactional communication enhances efficiency by enabling rapid message exchange and immediate feedback, which reduces misunderstandings and accelerates decision-making. It supports goal-oriented conversations that streamline problem-solving in professional settings, ensuring clarity and precision. The structured nature of transactional communication fosters accountability, as each party's role and responsibility are clearly defined during exchanges.
Benefits of Interactional Communication
Interactional communication fosters deeper interpersonal relationships by enabling feedback, emotional exchange, and mutual understanding. It enhances collaboration and trust within teams through continuous dialogue and shared meaning. This dynamic process supports adaptability and conflict resolution, promoting more effective and meaningful interactions.
Real-World Examples of Each Model
Transactional communication is exemplified in customer service calls where both parties simultaneously exchange information and adjust messages based on feedback to achieve a specific goal. Interactional communication is evident in casual conversations among friends, where the focus is on building relationships and maintaining social bonds through ongoing, reciprocal exchanges. Real-world examples highlight transactional communication's goal-oriented nature, while interactional communication emphasizes relational and emotional connection.
When to Use Transactional vs. Interactional Communication
Transactional communication is best used in situations requiring clear, goal-oriented exchanges such as business transactions, technical support, or instructional settings where efficiency and accuracy are paramount. Interactional communication thrives in relationship-building contexts like social conversations, team collaborations, and conflict resolution, emphasizing emotional connection and mutual understanding. Selecting the appropriate communication style depends on the desired outcome--whether achieving a specific task or fostering interpersonal rapport.
Enhancing Communication Skills in Both Models
Enhancing communication skills in transactional communication emphasizes clear message encoding and decoding to ensure accurate information exchange, while interactional communication focuses on active listening and feedback to build relationships and interpersonal understanding. Mastery of both models involves developing the ability to adapt communication strategies based on context, audience, and purpose for effective message delivery and reception. Training in nonverbal cues, empathy, and clarification techniques significantly improves competence across transactional and interactional communication styles.
transactional communication vs interactional communication Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com