Redundancy in communication involves providing the same information in different ways to ensure clarity and understanding, while repetition simply restates the same message without variation. Effective use of redundancy reinforces key points and aids in information retention, whereas excessive repetition can lead to listener fatigue and reduced engagement. Balancing these techniques enhances message delivery and ensures the audience comprehends the intended meaning.
Table of Comparison
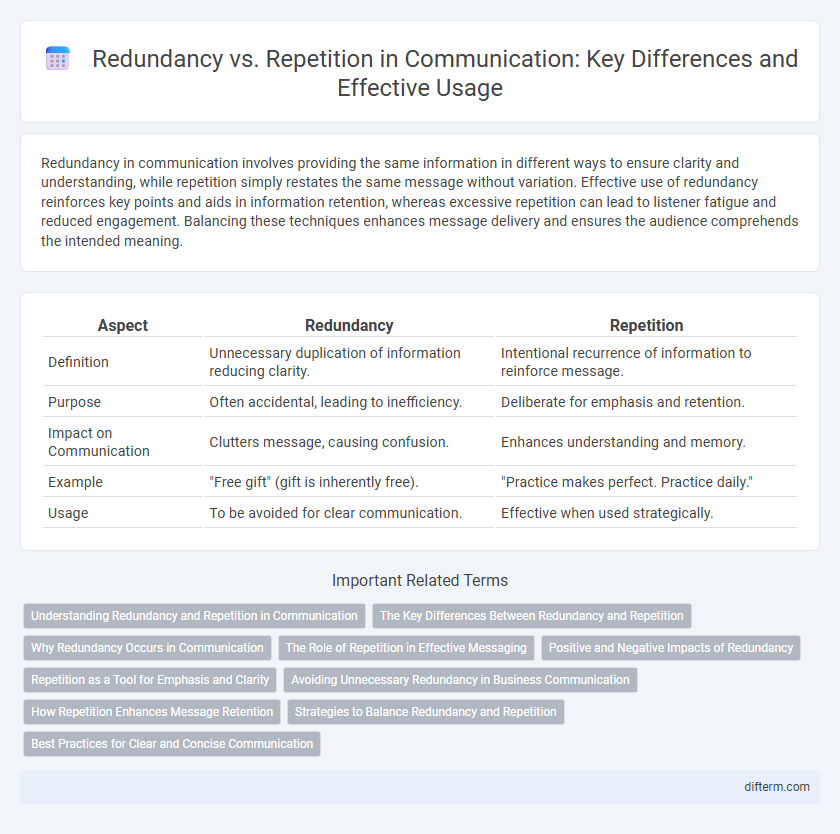
| Aspect | Redundancy | Repetition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unnecessary duplication of information reducing clarity. | Intentional recurrence of information to reinforce message. |
| Purpose | Often accidental, leading to inefficiency. | Deliberate for emphasis and retention. |
| Impact on Communication | Clutters message, causing confusion. | Enhances understanding and memory. |
| Example | "Free gift" (gift is inherently free). | "Practice makes perfect. Practice daily." |
| Usage | To be avoided for clear communication. | Effective when used strategically. |
Understanding Redundancy and Repetition in Communication
Redundancy in communication involves intentionally repeating information to enhance clarity and ensure the message is understood, while repetition often refers to unintentional or excessive reiteration that may cause confusion or frustration. Effective communication balances redundancy to reinforce key points without overwhelming the listener with repetitive content. Understanding this distinction helps optimize message delivery and improve overall comprehension.
The Key Differences Between Redundancy and Repetition
Redundancy involves unnecessary duplication of information that does not add value, often leading to inefficiency in communication, while repetition is the intentional restating of ideas to reinforce understanding and retention. Redundancy can cause confusion by cluttering the message, whereas repetition strategically emphasizes key points for clarity and emphasis. Understanding these distinctions improves the effectiveness of communication by balancing clarity without overwhelming the audience.
Why Redundancy Occurs in Communication
Redundancy occurs in communication to ensure message clarity and prevent misunderstandings by reinforcing key information through multiple channels or methods. It serves as a safeguard against noise and interference in the communication process, maintaining message integrity across diverse environments. Effective use of redundancy enhances comprehension and retention, particularly in complex or critical information exchanges.
The Role of Repetition in Effective Messaging
Repetition reinforces key messages, enhancing retention and comprehension in communication by embedding information deeper into the audience's memory. Strategic repetition, unlike redundancy, avoids unnecessary duplication and instead emphasizes critical points to strengthen persuasion and clarity. Effective messaging leverages repetition to create familiarity and trust, driving engagement and facilitating behavior change.
Positive and Negative Impacts of Redundancy
Redundancy in communication enhances message clarity by reinforcing key points, reducing misunderstanding, and supporting audience retention. However, excessive redundancy can lead to annoyance, disengagement, and reduced message impact, diluting the original intent. Balancing redundancy ensures effective communication without overwhelming or boring the audience.
Repetition as a Tool for Emphasis and Clarity
Repetition serves as an effective communication tool by reinforcing key messages, ensuring that important information is clearly understood and retained by the audience. Strategic repetition enhances clarity, making complex ideas more accessible and memorable through consistent reinforcement. This technique strengthens emphasis without overloading the message, facilitating better comprehension and engagement.
Avoiding Unnecessary Redundancy in Business Communication
Avoiding unnecessary redundancy in business communication ensures clarity and efficiency by eliminating repetitive information that does not add value. Clear, concise messages improve understanding and reduce the risk of misinterpretation among stakeholders. Effective communication prioritizes essential content, streamlining conversations and enhancing decision-making processes.
How Repetition Enhances Message Retention
Repetition reinforces key concepts by activating multiple neural pathways, making information more memorable and easier to retrieve. Strategic repetition within communication prevents message dilution and aids audience retention without causing redundancy overload. Utilizing varied phrasing and examples in repetition maximizes cognitive engagement and strengthens long-term impact.
Strategies to Balance Redundancy and Repetition
Effective communication strategies balance redundancy and repetition by tailoring messages to audience needs, ensuring clarity without overload. Utilizing varied phrasing and multimodal delivery reinforces key points while preventing listener fatigue. Incorporating feedback mechanisms helps adjust the frequency and depth of repeated information for optimal retention.
Best Practices for Clear and Concise Communication
Redundancy in communication involves unnecessary duplication of information that can clutter messages, while repetition strategically reinforces key points to enhance understanding and retention. Best practices for clear and concise communication emphasize eliminating redundant phrases and focusing on precise repetition to highlight critical ideas. Using targeted repetition in key messages aids clarity without overwhelming the audience or diluting the core content.
redundancy vs repetition Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com