Push communication involves sending information directly to recipients without requiring them to seek it out, ensuring messages are delivered promptly and widely. Pull communication relies on recipients accessing information at their convenience, often through centralized platforms or repositories, promoting self-directed engagement. Balancing push and pull communication strategies enhances overall information flow and user interaction in pet-related communication.
Table of Comparison
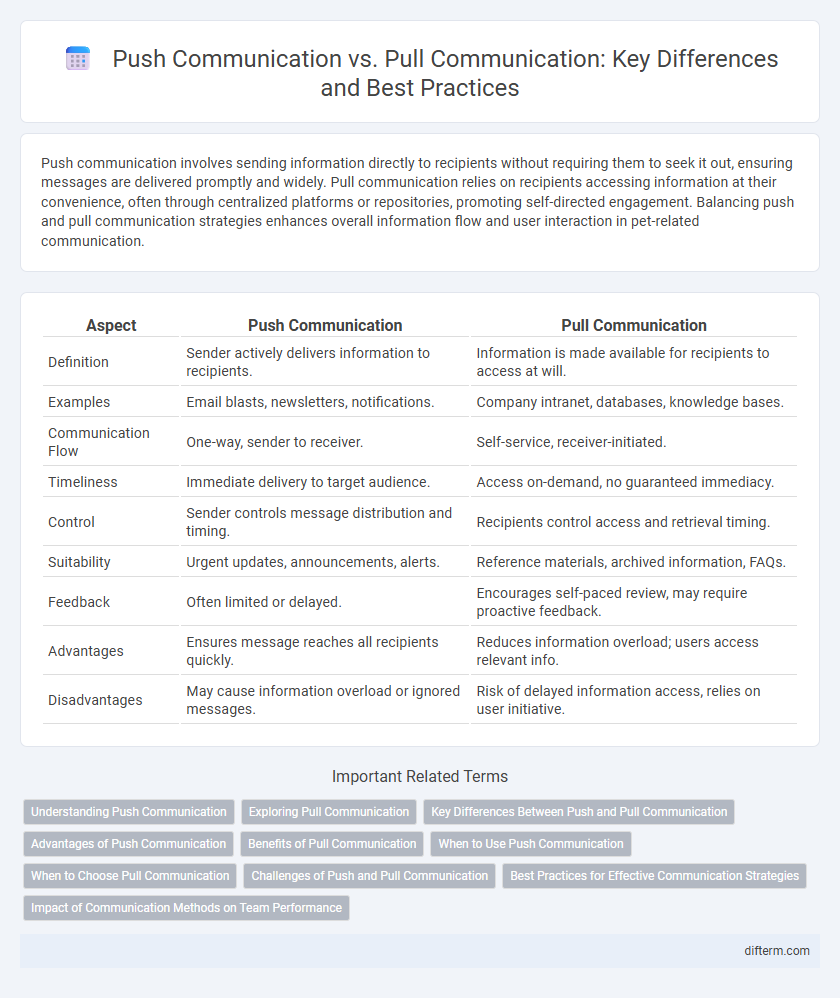
| Aspect | Push Communication | Pull Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sender actively delivers information to recipients. | Information is made available for recipients to access at will. |
| Examples | Email blasts, newsletters, notifications. | Company intranet, databases, knowledge bases. |
| Communication Flow | One-way, sender to receiver. | Self-service, receiver-initiated. |
| Timeliness | Immediate delivery to target audience. | Access on-demand, no guaranteed immediacy. |
| Control | Sender controls message distribution and timing. | Recipients control access and retrieval timing. |
| Suitability | Urgent updates, announcements, alerts. | Reference materials, archived information, FAQs. |
| Feedback | Often limited or delayed. | Encourages self-paced review, may require proactive feedback. |
| Advantages | Ensures message reaches all recipients quickly. | Reduces information overload; users access relevant info. |
| Disadvantages | May cause information overload or ignored messages. | Risk of delayed information access, relies on user initiative. |
Understanding Push Communication
Push communication involves delivering messages directly to recipients without requiring them to actively seek the information, ensuring critical updates reach the target audience promptly. Common examples include emails, memos, newsletters, and alerts, which push content to stakeholders to maintain alignment and avoid communication gaps. This method is essential in scenarios requiring immediate awareness or action, reducing delays caused by waiting for information retrieval.
Exploring Pull Communication
Pull communication allows recipients to access information at their convenience, enhancing flexibility and reducing information overload. This method is effective in environments where individuals need to retrieve detailed data or updates, such as intranets, knowledge bases, or shared digital repositories. By enabling selective information retrieval, pull communication supports personalized learning and timely decision-making.
Key Differences Between Push and Pull Communication
Push communication involves delivering information directly to recipients without requiring immediate feedback, typically through emails, memos, or announcements. Pull communication requires recipients to actively seek out information from sources such as intranet sites, databases, or knowledge repositories. The key differences lie in delivery method, control over information access, and the level of engagement required from the audience.
Advantages of Push Communication
Push communication ensures critical information reaches recipients directly and promptly, reducing the risk of message omission. This method is particularly beneficial for time-sensitive updates, compliance notifications, and urgent alerts, facilitating immediate action. By delivering messages proactively, push communication enhances accountability and streamlines workflow efficiency across teams.
Benefits of Pull Communication
Pull communication enables recipients to access information at their convenience, enhancing flexibility and reducing information overload. It promotes self-service and autonomy, allowing users to retrieve relevant content when needed, which improves engagement and retention. This method supports efficient knowledge management by centralizing resources and facilitating targeted information retrieval.
When to Use Push Communication
Push communication is effective when delivering urgent updates, instructions, or critical information that requires immediate attention from the recipients. It ensures that messages reach targeted individuals directly through emails, alerts, or memos, minimizing delays in response time. This method is ideal for time-sensitive situations, status reports, and formal notifications where confirmation of receipt is necessary.
When to Choose Pull Communication
Pull communication is ideal when recipients need to access detailed or complex information at their own pace, such as project documentation or training materials. It suits situations where the audience is large, diverse, or dispersed, allowing users to retrieve updates or data on demand. Organizations benefit from pull communication by reducing information overload and ensuring message accessibility without requiring immediate response.
Challenges of Push and Pull Communication
Push communication faces challenges such as information overload and message misinterpretation because recipients receive content without immediate context or feedback opportunities. Pull communication struggles with user engagement and timely access to critical information, as stakeholders must actively seek out updates, which can delay decision-making. Both methods require strategic management to balance effective information dissemination and responsiveness in diverse communication environments.
Best Practices for Effective Communication Strategies
Push communication delivers information directly to recipients through emails, notifications, or announcements, ensuring timely message dissemination. Pull communication allows individuals to access information at their convenience via portals, databases, or intranet sites, promoting autonomy and reduced information overload. Combining push and pull methods enhances engagement by balancing proactive updates with accessible resources tailored to audience needs.
Impact of Communication Methods on Team Performance
Push communication delivers information directly to team members, ensuring timely updates and reducing misunderstandings, which enhances coordination and accelerates decision-making. Pull communication allows team members to access information at their convenience, promoting autonomy and fostering deeper engagement with content. Balancing push and pull methods optimizes team performance by combining immediacy with flexibility, improving overall collaboration and productivity.
push communication vs pull communication Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com