Visual communication in pets, such as body language and facial expressions, enables them to convey emotions and intentions effectively without sound. Auditory communication, including barking, meowing, or chirping, serves to alert, seek attention, or express needs in diverse situations. Understanding both forms enhances the human-animal bond and improves interaction accuracy.
Table of Comparison
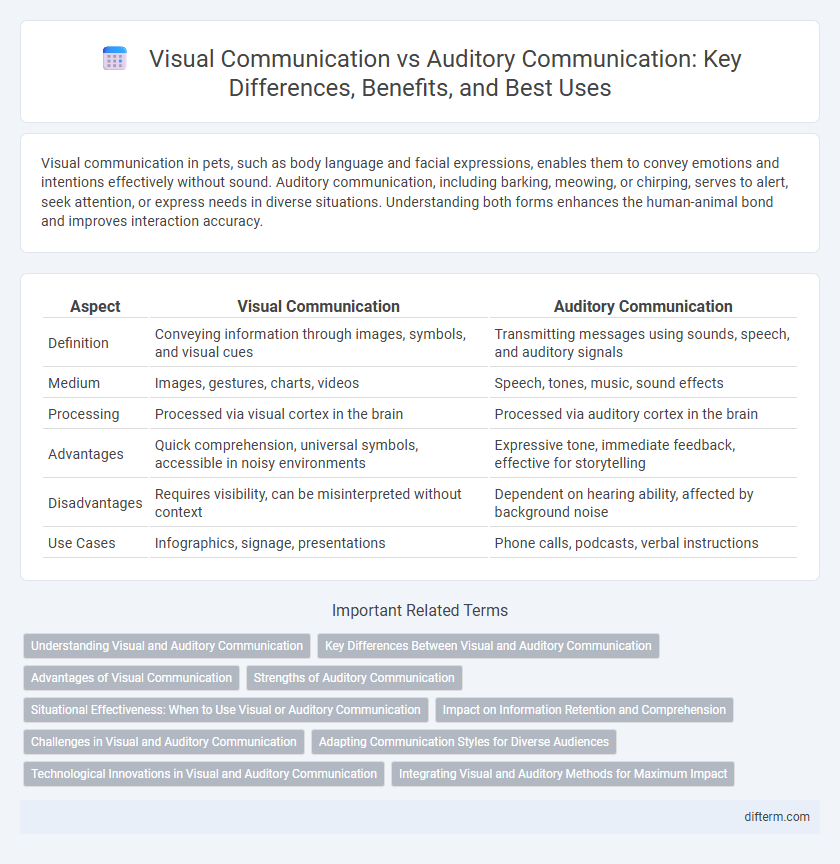
| Aspect | Visual Communication | Auditory Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conveying information through images, symbols, and visual cues | Transmitting messages using sounds, speech, and auditory signals |
| Medium | Images, gestures, charts, videos | Speech, tones, music, sound effects |
| Processing | Processed via visual cortex in the brain | Processed via auditory cortex in the brain |
| Advantages | Quick comprehension, universal symbols, accessible in noisy environments | Expressive tone, immediate feedback, effective for storytelling |
| Disadvantages | Requires visibility, can be misinterpreted without context | Dependent on hearing ability, affected by background noise |
| Use Cases | Infographics, signage, presentations | Phone calls, podcasts, verbal instructions |
Understanding Visual and Auditory Communication
Visual communication relies on images, symbols, and spatial arrangements to convey messages quickly and effectively, enhancing comprehension through visual cues. Auditory communication depends on sound, tone, and verbal expression, facilitating immediate feedback and emotional nuance. Understanding the strengths and limitations of both modalities is essential for optimizing message clarity and audience engagement in diverse communication environments.
Key Differences Between Visual and Auditory Communication
Visual communication relies on images, symbols, and body language to convey messages, making it highly effective for illustrating complex information quickly. Auditory communication depends on spoken words and sounds, which are essential for expressing tone, emotion, and immediate feedback in conversations. The key differences include the mode of transmission, with visual being primarily spatial and permanent, while auditory is temporal and transient, influencing how messages are perceived and retained.
Advantages of Visual Communication
Visual communication enhances information retention by leveraging images, charts, and symbols that the brain processes faster than text or speech. It transcends language barriers, enabling universal understanding through universally recognized icons and color codes. Visual aids also increase engagement and clarity, making complex data more accessible and easier to interpret during presentations or instructional settings.
Strengths of Auditory Communication
Auditory communication excels in conveying tone, emotion, and nuance, making it highly effective for personal interactions and storytelling. It allows for immediate feedback and clarification, enhancing understanding and engagement in conversations. Auditory signals can be perceived in low-visibility conditions, ensuring continuous communication in diverse environments.
Situational Effectiveness: When to Use Visual or Auditory Communication
Visual communication excels in complex or detailed information transfer where spatial or graphical representation enhances understanding, such as charts, diagrams, or written instructions. Auditory communication is more effective in dynamic or interactive situations requiring immediate feedback, tone, and emotional nuance, like conversations, presentations, or phone calls. Selecting the appropriate communication mode depends on factors like message complexity, audience preferences, and situational context to optimize clarity and engagement.
Impact on Information Retention and Comprehension
Visual communication enhances information retention by engaging multiple sensory pathways, making data easier to recall compared to auditory communication alone. Studies indicate that visual aids, such as charts and images, improve comprehension by clarifying complex concepts and reducing cognitive load. While auditory communication efficiently conveys tone and emotion, integrating visuals leads to higher overall accuracy in message interpretation and long-term memory retention.
Challenges in Visual and Auditory Communication
Visual communication faces challenges such as misinterpretation of images or symbols due to cultural differences and varying levels of visual literacy. Auditory communication struggles with factors like background noise, speech clarity, and listener attention span, which can distort the intended message. Both forms require careful consideration of the audience's context to ensure effective information transfer.
Adapting Communication Styles for Diverse Audiences
Visual communication leverages images, symbols, and spatial arrangements to convey messages effectively across language barriers, making it ideal for diverse audiences with varying literacy levels. Auditory communication, utilizing tone, pitch, and rhythm, engages listeners through vocal nuances that enhance understanding and emotional connection. Adapting communication styles by combining visual aids with clear auditory signals ensures inclusivity and maximizes message retention among heterogeneous groups.
Technological Innovations in Visual and Auditory Communication
Technological innovations in visual communication such as high-definition displays, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) have revolutionized how information is visually conveyed, enhancing user engagement and comprehension. In auditory communication, advancements like spatial audio, voice recognition, and AI-powered speech synthesis improve clarity, accessibility, and interactive experiences in real-time communication. Both technologies leverage machine learning algorithms and high-speed data processing to create immersive and dynamic communication environments, transforming professional and everyday interactions.
Integrating Visual and Auditory Methods for Maximum Impact
Integrating visual and auditory communication methods enhances message retention by engaging multiple cognitive pathways, resulting in stronger information processing and comprehension. Multimodal presentations combining images, videos, and sound facilitate deeper emotional connections and improved audience engagement compared to single-sensory approaches. Leveraging synchronized visual and auditory stimuli optimizes communication effectiveness in educational, marketing, and interpersonal contexts.
visual communication vs auditory communication Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com