Monochronic communication emphasizes strict scheduling, punctuality, and a linear approach to tasks, favoring clarity and structured interactions. Polychronic communication allows for multitasking, flexible timing, and relational focus, often prioritizing people over strict adherence to schedules. Understanding these cultural differences enhances effective communication in diverse environments, reducing misunderstandings and fostering collaboration.
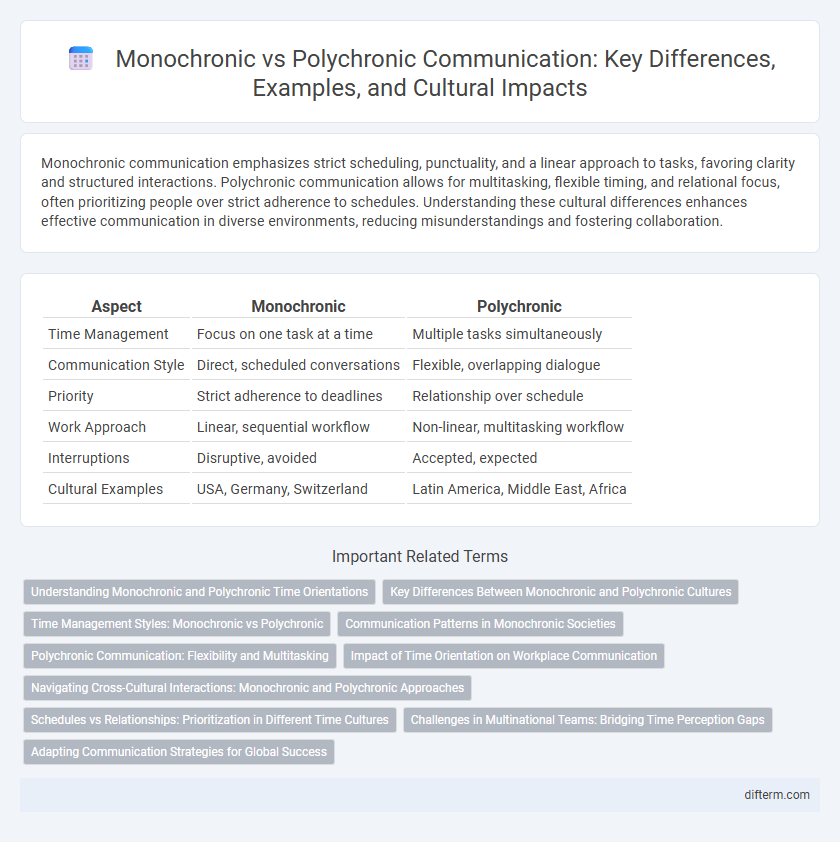
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Monochronic | Polychronic |
|---|---|---|
| Time Management | Focus on one task at a time | Multiple tasks simultaneously |
| Communication Style | Direct, scheduled conversations | Flexible, overlapping dialogue |
| Priority | Strict adherence to deadlines | Relationship over schedule |
| Work Approach | Linear, sequential workflow | Non-linear, multitasking workflow |
| Interruptions | Disruptive, avoided | Accepted, expected |
| Cultural Examples | USA, Germany, Switzerland | Latin America, Middle East, Africa |
Understanding Monochronic and Polychronic Time Orientations
Monochronic time orientation emphasizes linear scheduling, punctuality, and completing one task at a time, which is common in Western cultures like the United States and Germany. Polychronic time orientation involves multitasking, flexible scheduling, and valuing relationships over strict adherence to time, often seen in Latin American and Middle Eastern cultures. Understanding these differences enhances cross-cultural communication by aligning expectations around time management and social interactions.
Key Differences Between Monochronic and Polychronic Cultures
Monochronic cultures prioritize schedules, punctuality, and linear task completion, emphasizing individual focus and strict time management. Polychronic cultures value multitasking, flexible time perception, and relational interactions, often placing human relationships above rigid adherence to schedules. Understanding these key differences enhances cross-cultural communication by aligning expectations around time use and interpersonal priorities.
Time Management Styles: Monochronic vs Polychronic
Monochronic time management prioritizes focusing on one task at a time, valuing schedules and punctuality, which enhances productivity in structured environments. Polychronic time management embraces multitasking and flexible scheduling, emphasizing relationships and adaptability over strict adherence to time. Understanding these contrasting styles aids effective communication by aligning expectations and improving collaboration across cultural contexts.
Communication Patterns in Monochronic Societies
Communication patterns in monochronic societies emphasize punctuality, directness, and structured interactions, where speakers value clear, concise messaging and adherence to schedules. Conversations tend to follow a linear flow, with speakers focusing on one topic at a time to avoid misunderstandings and ensure efficient information exchange. These societies prefer formal communication channels and expect participants to respect conversational turn-taking and time constraints during meetings.
Polychronic Communication: Flexibility and Multitasking
Polychronic communication emphasizes flexibility and multitasking, allowing individuals to engage in multiple conversations or tasks simultaneously without strict adherence to schedules. This style fosters adaptability in dynamic environments, where relationships and social interactions take precedence over rigid time management. Embracing polychronic communication enhances collaborative efforts and responsiveness in culturally diverse workplaces.
Impact of Time Orientation on Workplace Communication
Monochronic time orientation emphasizes strict scheduling and linear task completion, which promotes clear deadlines and efficient, focused communication in the workplace. Polychronic orientation values multitasking and fluid time management, fostering flexible interactions but potentially leading to misunderstandings or perceived disorganization. Understanding these differences improves cross-cultural communication, enhances team collaboration, and reduces conflict related to time expectations in diverse work environments.
Navigating Cross-Cultural Interactions: Monochronic and Polychronic Approaches
Navigating cross-cultural interactions requires understanding monochronic cultures that value punctuality, linear task completion, and strict scheduling versus polychronic cultures that prioritize relationships, multitasking, and flexible time management. Effective communication hinges on adapting to these differing temporal orientations to avoid misunderstandings and foster collaboration. Recognizing the monochronic emphasis on deadlines alongside the polychronic focus on social harmony enhances cross-cultural competence in global business and personal exchanges.
Schedules vs Relationships: Prioritization in Different Time Cultures
Monochronic cultures prioritize schedules, valuing strict adherence to timelines and punctuality in communication, ensuring tasks are completed sequentially. Polychronic cultures emphasize relationships, often multitasking and prioritizing interpersonal connections over rigid schedules. Understanding these differences improves cross-cultural communication by respecting time management preferences and fostering stronger connections.
Challenges in Multinational Teams: Bridging Time Perception Gaps
Monochronic time orientation emphasizes strict adherence to schedules and linear task completion, while polychronic cultures prioritize multitasking and flexible time management, leading to misunderstandings in multinational teams. These divergent perceptions of time often cause conflicts in deadline expectations, meeting punctuality, and prioritization of tasks, which can hinder team collaboration and productivity. Successful communication requires awareness of these cultural differences and implementing strategies such as setting clear timelines, allowing flexibility, and fostering mutual respect to bridge time perception gaps.
Adapting Communication Strategies for Global Success
Adapting communication strategies requires understanding the differences between monochronic and polychronic time orientations, where monochronic cultures prioritize schedules and punctuality while polychronic cultures emphasize relationships and multitasking. Effective global communication demands flexibility in approach, aligning message timing and interaction style with the cultural context to build trust and clarity. Leveraging cultural awareness of monochronic and polychronic behaviors enhances collaboration, reduces misunderstandings, and drives international business success.
monochronic vs polychronic Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com