Intercultural communication involves interactions between individuals from different cultural backgrounds, emphasizing the exchange of diverse perspectives and customs. Intracultural communication occurs within the same cultural group, fostering shared understanding and reinforcing common norms and values. Both forms play crucial roles in enhancing effective communication and reducing misunderstandings in various social and professional settings.
Table of Comparison
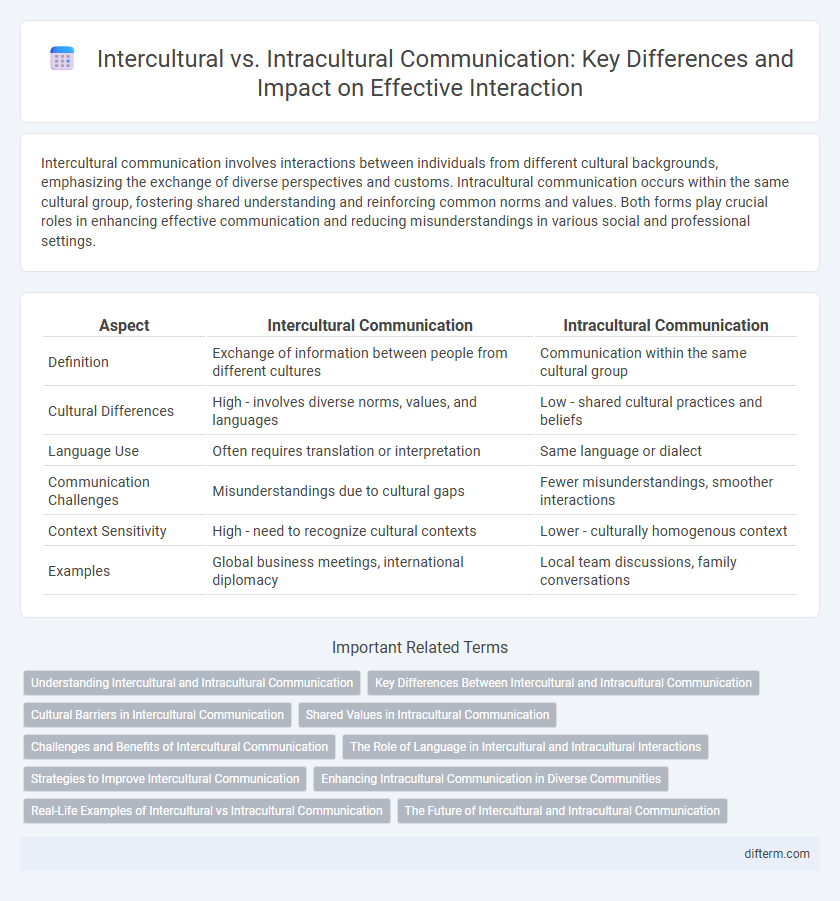
| Aspect | Intercultural Communication | Intracultural Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exchange of information between people from different cultures | Communication within the same cultural group |
| Cultural Differences | High - involves diverse norms, values, and languages | Low - shared cultural practices and beliefs |
| Language Use | Often requires translation or interpretation | Same language or dialect |
| Communication Challenges | Misunderstandings due to cultural gaps | Fewer misunderstandings, smoother interactions |
| Context Sensitivity | High - need to recognize cultural contexts | Lower - culturally homogenous context |
| Examples | Global business meetings, international diplomacy | Local team discussions, family conversations |
Understanding Intercultural and Intracultural Communication
Intercultural communication involves exchanges between individuals from different cultural backgrounds, emphasizing the importance of recognizing and respecting cultural diversity to avoid misunderstandings. Intracultural communication, in contrast, occurs within the same cultural group, where shared norms and values facilitate smoother interactions. Mastery of both communication types enhances global collaboration and reduces cultural barriers in personal and professional contexts.
Key Differences Between Intercultural and Intracultural Communication
Intercultural communication involves exchanging information between individuals from different cultural backgrounds, highlighting the variations in language, customs, and social norms. Intracultural communication occurs within the same cultural group, sharing common values, beliefs, and communication styles that enhance mutual understanding. Key differences include the presence of cultural barriers in intercultural communication versus the more seamless flow typical of intracultural interactions.
Cultural Barriers in Intercultural Communication
Cultural barriers in intercultural communication arise from differing values, beliefs, and communication styles between diverse cultural groups, often leading to misunderstandings and misinterpretations. These barriers include language differences, nonverbal misreads, and ethnocentrism, which hinder effective information exchange. Addressing these challenges requires cultural sensitivity, awareness, and adaptive communication strategies tailored to intercultural contexts.
Shared Values in Intracultural Communication
Shared values in intracultural communication create a strong foundation for mutual understanding and trust within a community, as members inherently recognize common beliefs and social norms. These shared cultural frameworks streamline communication by reducing misunderstandings and fostering a cohesive group identity. Such alignment enhances effective information exchange and collaborative problem-solving among individuals from the same cultural background.
Challenges and Benefits of Intercultural Communication
Intercultural communication involves interaction between people from different cultural backgrounds, presenting challenges such as language barriers, differing nonverbal cues, and contrasting cultural values. The benefits include enhanced creativity, broader perspectives, and improved problem-solving abilities stemming from diverse viewpoints. Effective intercultural communication fosters mutual respect and promotes global collaboration in increasingly interconnected societies.
The Role of Language in Intercultural and Intracultural Interactions
Language functions as a crucial tool in both intercultural and intracultural communication, shaping understanding and meaning within and between cultural groups. In intracultural interactions, shared linguistic norms and cultural references facilitate smooth communication and reinforce group identity. In contrast, intercultural communication often requires navigating language differences, cultural nuances, and varying communication styles that influence interpretation and interaction effectiveness.
Strategies to Improve Intercultural Communication
Effective strategies to improve intercultural communication include active listening, cultural awareness training, and employing empathy to understand different perspectives. Utilizing clear, simple language and avoiding idiomatic expressions reduce misunderstandings between diverse cultural groups. Incorporating feedback mechanisms and promoting open dialogue fosters mutual respect and enhances communication effectiveness across cultures.
Enhancing Intracultural Communication in Diverse Communities
Enhancing intracultural communication in diverse communities strengthens shared cultural norms, values, and language nuances that facilitate deeper mutual understanding and trust. Emphasizing common cultural frameworks minimizes misinterpretations and fosters collaborative problem-solving within groups. Effective intracultural dialogue supports social cohesion and empowers community members to address collective challenges more efficiently.
Real-Life Examples of Intercultural vs Intracultural Communication
Intercultural communication occurs when individuals from different cultural backgrounds, such as a Japanese businessperson negotiating with an American counterpart, must navigate varying social norms and communication styles, often leading to misunderstandings or enriched collaboration. Intracultural communication happens within the same cultural group, like a team of Italian colleagues discussing project strategies, sharing common cultural references and language nuances that facilitate smoother understanding. Real-life examples highlight that intercultural exchanges require heightened awareness of cultural differences, while intracultural interactions benefit from shared contextual knowledge.
The Future of Intercultural and Intracultural Communication
The future of intercultural communication emphasizes the integration of advanced technology and AI-driven translation tools to bridge language barriers and foster global collaboration. Intracultural communication will increasingly focus on deepening understanding within diverse subgroups, promoting cultural sensitivity and inclusivity in local contexts. Both forms of communication will evolve to support dynamic, real-time interactions that enhance empathy and reduce misunderstandings in an interconnected world.
intercultural vs intracultural Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com