Horizontal communication facilitates the seamless exchange of information among peers or colleagues at the same organizational level, enhancing collaboration and team cohesion. Diagonal communication bridges different departments and hierarchical levels, breaking down silos to promote efficiency and innovation across the organization. Both communication types are essential for a dynamic workplace, supporting diverse workflows and decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
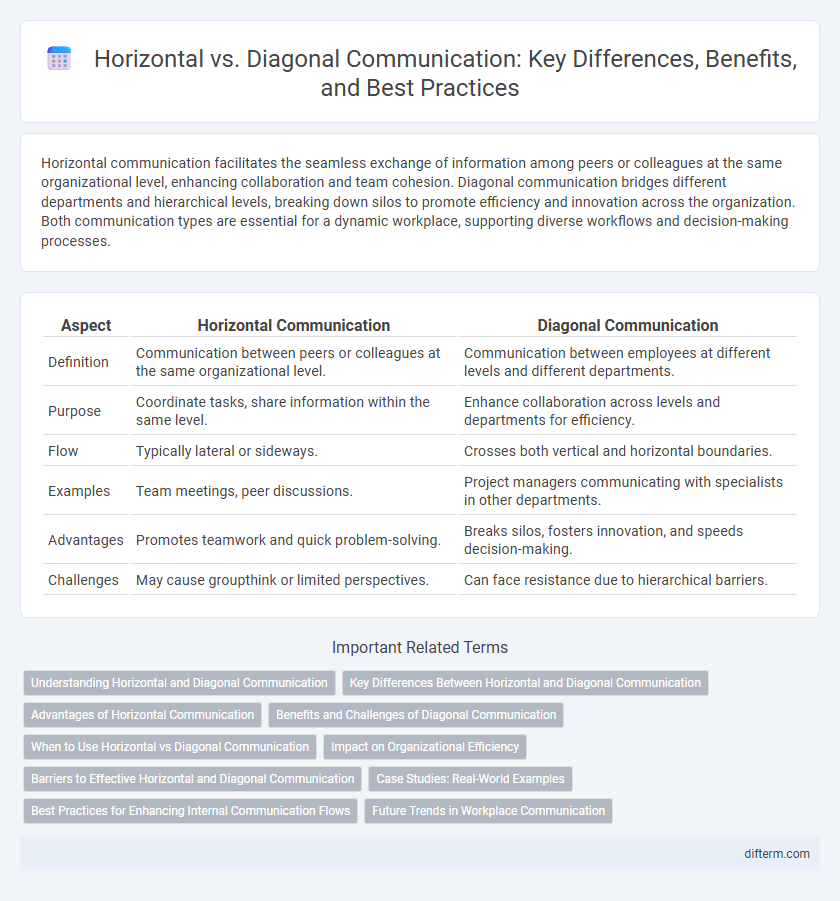
| Aspect | Horizontal Communication | Diagonal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication between peers or colleagues at the same organizational level. | Communication between employees at different levels and different departments. |
| Purpose | Coordinate tasks, share information within the same level. | Enhance collaboration across levels and departments for efficiency. |
| Flow | Typically lateral or sideways. | Crosses both vertical and horizontal boundaries. |
| Examples | Team meetings, peer discussions. | Project managers communicating with specialists in other departments. |
| Advantages | Promotes teamwork and quick problem-solving. | Breaks silos, fosters innovation, and speeds decision-making. |
| Challenges | May cause groupthink or limited perspectives. | Can face resistance due to hierarchical barriers. |
Understanding Horizontal and Diagonal Communication
Horizontal communication occurs between employees or departments at the same organizational level, facilitating collaboration and coordination on shared tasks. Diagonal communication cuts across different hierarchical levels and functional areas, enabling faster decision-making and problem-solving by connecting individuals who do not share a direct reporting line. Understanding these communication types enhances organizational efficiency by promoting appropriate information flow tailored to the context and objectives.
Key Differences Between Horizontal and Diagonal Communication
Horizontal communication occurs between peers or colleagues at the same organizational level, enhancing teamwork and collaboration with a focus on sharing information and solving problems within departments. Diagonal communication crosses both departmental and hierarchical boundaries, facilitating coordination and information flow between different levels and units, often improving organizational efficiency in complex projects. Key differences include the direction of information flow, with horizontal communication being lateral and diagonal communication cutting across layers, and their distinct roles in maintaining intra-departmental harmony versus fostering interdepartmental integration.
Advantages of Horizontal Communication
Horizontal communication promotes faster decision-making and improved coordination by facilitating direct interaction among employees at the same organizational level. It enhances teamwork and information sharing, leading to increased efficiency and innovation within departments. This communication style also reduces misunderstandings and conflicts by fostering a collaborative work environment.
Benefits and Challenges of Diagonal Communication
Diagonal communication enhances organizational flexibility by connecting employees across different departments and hierarchical levels, fostering innovation and quicker problem-solving. It breaks down silos, promoting diverse perspectives and improving coordination for complex projects, yet it can create confusion due to unclear communication channels and potential power dynamics. Effective diagonal communication requires transparent policies and strong interpersonal skills to manage conflicts and maintain message clarity.
When to Use Horizontal vs Diagonal Communication
Horizontal communication is most effective for coordinating tasks among colleagues within the same organizational level, facilitating quick decision-making and collaboration. Diagonal communication is beneficial when exchanging information or resolving issues across different departments and hierarchical levels, improving organizational efficiency. Choosing between these communication styles depends on the nature of the information flow and the organizational structure involved.
Impact on Organizational Efficiency
Horizontal communication enhances organizational efficiency by promoting collaboration and faster decision-making among peers within the same department. Diagonal communication breaks down silos by facilitating information flow between different levels and departments, leading to innovative problem-solving and streamlined workflows. Both communication types reduce misunderstandings and redundancies, directly improving overall productivity and employee engagement.
Barriers to Effective Horizontal and Diagonal Communication
Barriers to effective horizontal and diagonal communication include organizational silos, lack of trust, and unclear authority lines that hinder message flow between departments or hierarchical levels. Cultural differences and conflicting priorities often create misunderstandings and resistance to collaboration across peer and cross-functional teams. Technological limitations and inconsistent communication channels further disrupt the timely exchange of information essential for coordinated decision-making.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Case studies reveal that horizontal communication enhances team collaboration and problem-solving in companies like Google, where peer-to-peer information flow accelerates project development. In contrast, diagonal communication, exemplified by Toyota's cross-functional approach, breaks silos by connecting employees across different levels and departments, improving innovation. Real-world examples demonstrate that integrating both communication types optimizes organizational efficiency and responsiveness.
Best Practices for Enhancing Internal Communication Flows
Horizontal communication fosters collaboration by enabling peer-to-peer information exchange across departments, enhancing teamwork and problem-solving efficiency. Diagonal communication bridges gaps between different hierarchical levels and functional areas, promoting faster decision-making and innovation by combining diverse expertise. Best practices include establishing clear communication channels, encouraging transparency, and leveraging technology platforms to streamline information sharing and reduce misunderstandings.
Future Trends in Workplace Communication
Horizontal communication promotes seamless collaboration among peers, enhancing team agility and innovation, while diagonal communication bridges gaps between different organizational levels, fostering cross-functional problem-solving. Future trends emphasize digital platforms integrating AI-driven tools to facilitate real-time horizontal and diagonal interactions, breaking down silos and accelerating decision-making processes. Embracing these communication flows powered by advanced technologies will be crucial for adaptive, resilient workplace cultures in the evolving digital landscape.
horizontal vs diagonal communication Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com