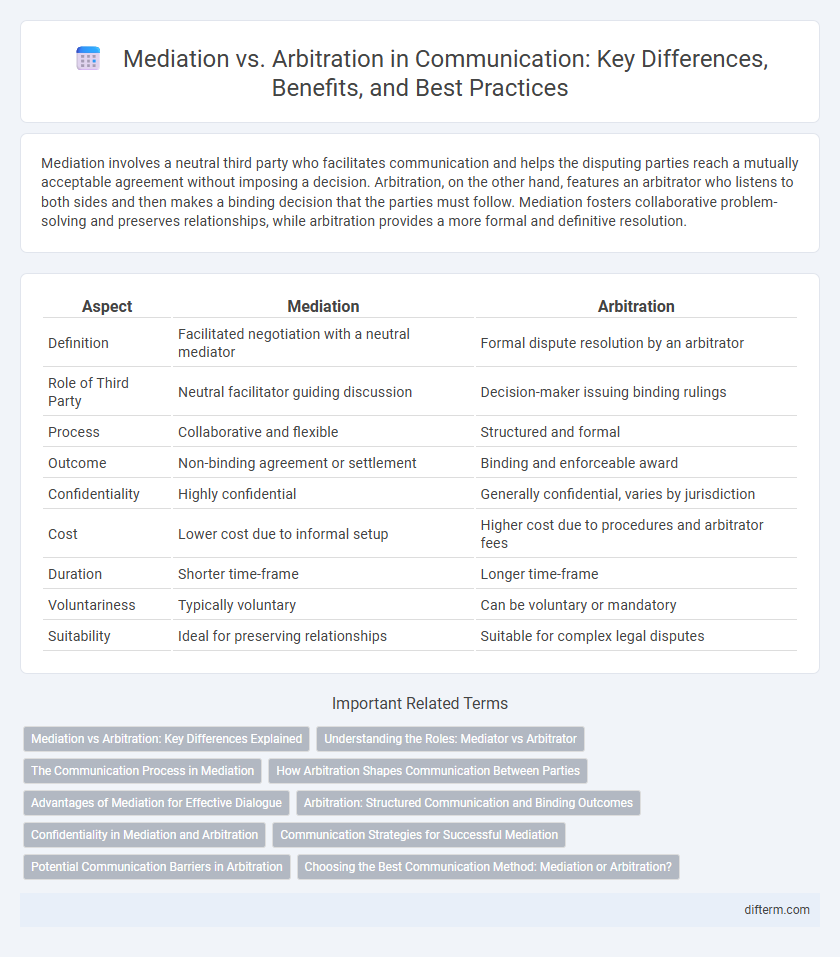
Mediation involves a neutral third party who facilitates communication and helps the disputing parties reach a mutually acceptable agreement without imposing a decision. Arbitration, on the other hand, features an arbitrator who listens to both sides and then makes a binding decision that the parties must follow. Mediation fosters collaborative problem-solving and preserves relationships, while arbitration provides a more formal and definitive resolution.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mediation | Arbitration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Facilitated negotiation with a neutral mediator | Formal dispute resolution by an arbitrator |
| Role of Third Party | Neutral facilitator guiding discussion | Decision-maker issuing binding rulings |
| Process | Collaborative and flexible | Structured and formal |
| Outcome | Non-binding agreement or settlement | Binding and enforceable award |
| Confidentiality | Highly confidential | Generally confidential, varies by jurisdiction |
| Cost | Lower cost due to informal setup | Higher cost due to procedures and arbitrator fees |
| Duration | Shorter time-frame | Longer time-frame |
| Voluntariness | Typically voluntary | Can be voluntary or mandatory |
| Suitability | Ideal for preserving relationships | Suitable for complex legal disputes |
Mediation vs Arbitration: Key Differences Explained
Mediation involves a neutral third party who facilitates open dialogue between disputing parties to help them reach a mutually acceptable agreement, emphasizing collaboration and voluntary resolution. Arbitration, by contrast, entrusts an arbitrator with the authority to make a binding decision after hearing arguments and reviewing evidence, resembling a private court process. Key differences include mediation's focus on consensus-building without enforceable rulings, whereas arbitration concludes with a legally binding judgment that resolves the dispute definitively.
Understanding the Roles: Mediator vs Arbitrator
Mediators facilitate communication between disputing parties to help them reach a mutually acceptable agreement without imposing decisions, emphasizing collaboration and understanding. Arbitrators act as neutral decision-makers who review evidence and arguments before issuing a binding resolution, prioritizing a definitive outcome over consensus. Understanding these distinct roles is essential in selecting the appropriate dispute resolution method based on the desired level of control and finality.
The Communication Process in Mediation
The communication process in mediation centers on active listening, open dialogue, and mutual understanding to facilitate a voluntary resolution between disputing parties. Mediators employ techniques such as reframing, summarizing, and questioning to clarify issues and uncover underlying interests, promoting constructive communication. This process contrasts with arbitration, where communication is more formal and limited, as the arbitrator renders a binding decision without facilitating ongoing dialogue.
How Arbitration Shapes Communication Between Parties
Arbitration structures communication by enforcing formal procedures and limiting direct dialogue between parties, which can reduce emotional exchanges and focus on factual evidence. The arbitrator acts as a neutral facilitator, guiding discussions and making binding decisions, thereby minimizing misinterpretations and fostering clearer, more concise exchanges. These controlled interactions often enhance efficiency but can restrict collaborative problem-solving compared to mediation.
Advantages of Mediation for Effective Dialogue
Mediation promotes open communication by creating a neutral environment where parties can express their concerns freely, enhancing mutual understanding and collaboration. The flexible and informal structure of mediation encourages creative problem-solving and fosters trust without the pressure of legal constraints. This approach often leads to more sustainable agreements, preserving relationships and reducing future conflicts.
Arbitration: Structured Communication and Binding Outcomes
Arbitration ensures structured communication through formal procedures that promote clarity and efficiency in dispute resolution. Unlike mediation, arbitration results in binding outcomes enforced by law, providing parties with definitive resolutions. This authoritative process minimizes ambiguity and fosters accountability in contractual and legal conflicts.
Confidentiality in Mediation and Arbitration
Confidentiality in mediation ensures that all discussions and disclosures remain private, fostering an open and honest dialogue between parties without fear of information being used against them later. Arbitration confidentiality is more limited, as arbitration proceedings and outcomes may be disclosed or used in future legal actions depending on jurisdiction and agreement terms. Maintaining confidentiality in mediation supports trust and resolution, while in arbitration, parties must carefully review confidentiality clauses to protect sensitive information.
Communication Strategies for Successful Mediation
Successful mediation hinges on effective communication strategies such as active listening, empathy, and clear articulation of interests to build trust and understanding between parties. Unlike arbitration, which relies on authoritative decision-making, mediation encourages open dialogue and collaborative problem-solving, fostering mutual agreement. Employing techniques like reframing negative statements and asking open-ended questions enhances the mediator's ability to guide discussions toward constructive outcomes.
Potential Communication Barriers in Arbitration
Arbitration often faces potential communication barriers such as limited interaction between parties, which can hinder the clarity and depth of information exchange. The formal structure and strict procedural rules in arbitration may restrict open dialogue, leading to misunderstandings or incomplete disclosure. These communication challenges can impact the effectiveness of dispute resolution compared to more flexible methods like mediation.
Choosing the Best Communication Method: Mediation or Arbitration?
Mediation emphasizes collaborative dialogue where a neutral mediator facilitates understanding and mutually acceptable solutions, making it ideal for preserving relationships and resolving conflicts amicably. Arbitration involves a binding decision by an arbitrator or panel, offering a more structured and decisive outcome suited for disputes requiring a clear resolution. Evaluating factors such as the desired level of control, confidentiality, cost, and time efficiency helps determine whether mediation or arbitration best fits the communication needs of the parties involved.
mediation vs arbitration Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com