Monetization focuses on generating direct revenue from business pets by leveraging features such as subscription services, in-app purchases, and paid content. Commercialization involves broader strategies including marketing, brand partnerships, and market expansion to maximize the business pet's overall market presence. Understanding the balance between monetization and commercialization is essential for sustainable growth and long-term profitability.
Table of Comparison
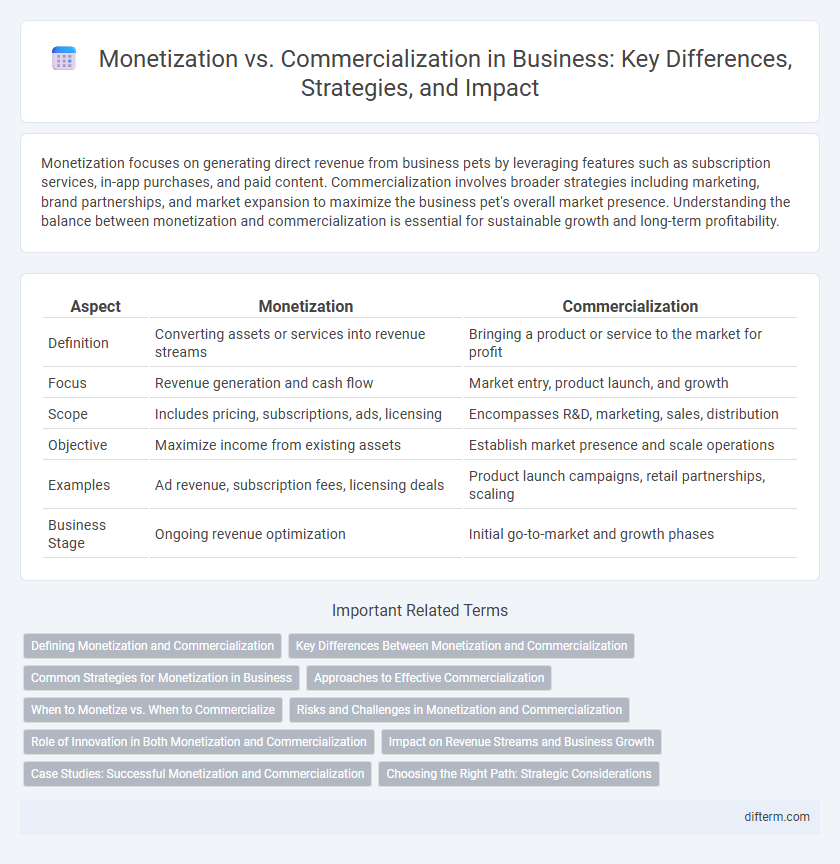
| Aspect | Monetization | Commercialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting assets or services into revenue streams | Bringing a product or service to the market for profit |
| Focus | Revenue generation and cash flow | Market entry, product launch, and growth |
| Scope | Includes pricing, subscriptions, ads, licensing | Encompasses R&D, marketing, sales, distribution |
| Objective | Maximize income from existing assets | Establish market presence and scale operations |
| Examples | Ad revenue, subscription fees, licensing deals | Product launch campaigns, retail partnerships, scaling |
| Business Stage | Ongoing revenue optimization | Initial go-to-market and growth phases |
Defining Monetization and Commercialization
Monetization refers to the process of converting a product, service, or asset into a source of revenue, typically through sales, subscriptions, or advertising. Commercialization encompasses broader activities beyond revenue generation, including market research, product development, distribution, and promotion to successfully launch and sustain a product in the marketplace. Businesses often focus on monetization strategies to directly earn income, while commercialization involves strategic planning to ensure long-term market viability and growth.
Key Differences Between Monetization and Commercialization
Monetization refers to the process of converting an asset or service into a revenue-generating stream, often through direct sales, subscription models, or advertising. Commercialization encompasses a broader strategy that includes product development, market entry, and scaling to achieve sustained market presence and profitability. Key differences lie in scope: monetization focuses on immediate revenue generation, while commercialization addresses long-term market integration and growth.
Common Strategies for Monetization in Business
Common strategies for monetization in business include subscription models, where customers pay recurring fees for ongoing access to products or services, and freemium approaches that offer basic features for free while charging for premium upgrades. Advertising revenue is another key method, especially for digital platforms leveraging user data to target ads effectively. Licensing and affiliate marketing also serve as effective channels by generating income through partnerships and third-party promotions.
Approaches to Effective Commercialization
Effective commercialization involves strategic market positioning, product differentiation, and building strong distribution channels to maximize reach and customer engagement. Emphasizing value creation through tailored marketing campaigns and customer feedback integration enhances brand recognition and competitive advantage. Leveraging partnerships and technology adoption further accelerates time-to-market and ensures scalable revenue streams in dynamic business environments.
When to Monetize vs. When to Commercialize
Monetize refers to generating revenue directly from a product or service, typically through sales, subscriptions, or advertisements, ideal when the market demand is clear and customer willingness to pay is established. Commercialize involves the broader process of bringing a product to market, including production scaling, marketing, and distribution, suited for early-stage products needing market validation and brand development. Businesses should monetize when customer acquisition and revenue streams are proven, while commercialization is essential during product launch phases requiring market penetration and infrastructure setup.
Risks and Challenges in Monetization and Commercialization
Monetization faces risks such as inconsistent revenue streams, market volatility, and customer acceptance challenges, which can undermine cash flow stability and business growth. Commercialization encounters obstacles including high upfront costs, regulatory compliance, and intense competitive pressure that can delay product launch and reduce profitability. Both processes demand strategic risk management to balance investment with potential returns while navigating market complexities.
Role of Innovation in Both Monetization and Commercialization
Innovation drives monetization by creating unique value propositions that convert products or services into revenue-generating assets. In commercialization, innovation navigates market entry strategies, optimizing product adoption and competitive positioning. Both processes rely on continuous innovation to sustain growth and capture market share effectively.
Impact on Revenue Streams and Business Growth
Monetization directly influences revenue streams by converting assets, products, or services into measurable income through sales, subscriptions, or advertising, creating immediate cash flow. Commercialization encompasses the broader process of bringing a product to market, including marketing, distribution, and customer engagement, which drives sustainable business growth by expanding market reach and brand presence. Effective monetization strategies enhance revenue generation while commercialization ensures long-term scalability and competitive advantage in the business landscape.
Case Studies: Successful Monetization and Commercialization
Case studies of successful monetization include Spotify's subscription model, which transformed free users into paying customers, generating consistent revenue streams through tiered service plans. On the commercialization side, Tesla's deployment of electric vehicles combined product innovation with aggressive market entry strategies, creating widespread market adoption and streamlining supply chain partnerships. Both approaches demonstrate how aligning business models with customer value propositions drives sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Choosing the Right Path: Strategic Considerations
Monetization focuses on generating revenue directly from products or services through pricing models, subscriptions, or advertising, while commercialization encompasses a broader strategy including product development, market entry, and scaling operations. Strategic considerations involve assessing market demand, competitive landscape, and long-term business goals to determine whether immediate revenue generation or sustainable growth offers greater value. Choosing the right path requires aligning monetization methods with commercialization efforts to optimize profitability and market positioning.
Monetization vs Commercialization Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com