Watercolour paints offer a translucent quality that enhances luminosity and layering effects, making them ideal for delicate washes and subtle gradients. Gouache, on the other hand, provides an opaque finish with vibrant, solid colors that are perfect for bold illustrations and graphic artworks. Artists often choose watercolour for its fluidity and softness, while gouache is favored for its versatility and ability to create matte, richly pigmented textures.
Table of Comparison
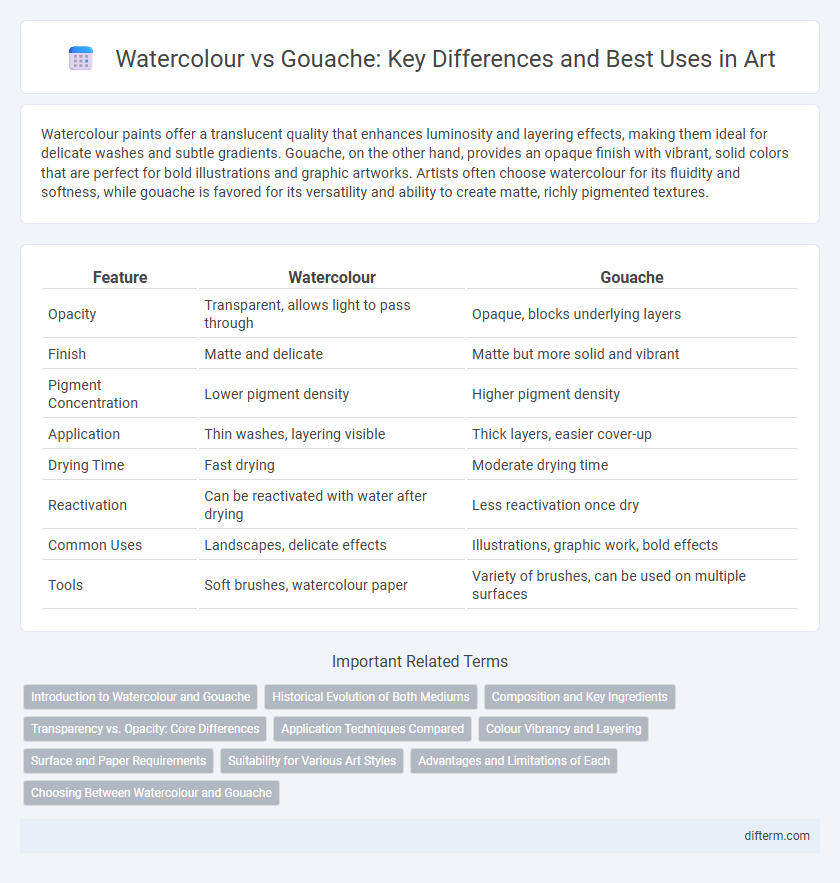
| Feature | Watercolour | Gouache |
|---|---|---|
| Opacity | Transparent, allows light to pass through | Opaque, blocks underlying layers |
| Finish | Matte and delicate | Matte but more solid and vibrant |
| Pigment Concentration | Lower pigment density | Higher pigment density |
| Application | Thin washes, layering visible | Thick layers, easier cover-up |
| Drying Time | Fast drying | Moderate drying time |
| Reactivation | Can be reactivated with water after drying | Less reactivation once dry |
| Common Uses | Landscapes, delicate effects | Illustrations, graphic work, bold effects |
| Tools | Soft brushes, watercolour paper | Variety of brushes, can be used on multiple surfaces |
Introduction to Watercolour and Gouache
Watercolour and gouache are both water-based paints prized for their vibrant hues and versatility in fine art. Watercolour is renowned for its transparency and ability to create delicate washes, ideal for capturing light and subtle gradients. Gouache, while similar in texture, offers an opaque finish with richer pigmentation, making it preferred for bold, matte illustrations and graphic work.
Historical Evolution of Both Mediums
Watercolour painting originated in ancient Egypt and China, with its widespread European use developing during the Renaissance for delicate washes and detailed botanical illustrations. Gouache emerged in the Middle Ages as a more opaque medium favored by manuscript illuminators, later gaining popularity among commercial artists in the 20th century for its vivid, matte finish. Both mediums evolved through technological advancements in pigments and binders, shaping their distinct roles in artistic techniques and styles.
Composition and Key Ingredients
Watercolour relies on transparent pigments suspended in a water-soluble binder, enabling light to pass through and reflect off the paper for luminous effects, ideal for delicate compositions. Gouache incorporates a higher pigment concentration with an inert white pigment like chalk, resulting in an opaque finish that allows artists to layer and modify compositions with greater opacity and solid color blocks. Both mediums offer distinct compositional techniques: watercolour emphasizes fluidity and layering of translucent washes, while gouache supports bold, flat areas and reworkability due to its opacity.
Transparency vs. Opacity: Core Differences
Watercolour paint is renowned for its transparency, allowing light to pass through the pigment and reflect off the paper, creating luminous and delicate washes. Gouache, by contrast, is highly opaque due to its higher pigment concentration and added white pigment, enabling solid, matte finishes and strong color coverage. This core difference in transparency versus opacity fundamentally influences their application techniques and visual effects in art.
Application Techniques Compared
Watercolour techniques emphasize layering translucent washes to create luminosity and subtle gradients, relying on water dilution for softness and blending. Gouache application uses thicker, more opaque strokes that allow for solid color blocking and reworking areas without transparency, offering matte finishes. Artists often combine these methods to exploit watercolour's fluidity and gouache's coverage in mixed media works.
Colour Vibrancy and Layering
Watercolour offers translucent layers that create delicate, luminous effects ideal for subtle gradients, while gouache provides rich, opaque colour vibrancy allowing for bold, solid coverage and easy reworking. The layering in watercolour requires careful planning to maintain brightness without muddying, whereas gouache allows for more versatile layering with strong opacity that can cover underlying layers completely. Artists seeking intense colour saturation and flexibility in corrections often prefer gouache, whereas those valuing lightness and fluidity gravitate towards watercolour.
Surface and Paper Requirements
Watercolour requires textured, absorbent paper with high cotton content to allow delicate pigment dispersion and layering. Gouache, being more opaque and heavier, works best on thicker, less absorbent surfaces that can support its dense pigment without warping. Both media benefit from cold-pressed or rough paper, but gouache demands a sturdier substrate to handle reworking and multiple paint layers.
Suitability for Various Art Styles
Watercolour suits delicate, transparent washes and fluid techniques ideal for landscapes and botanical illustrations, offering subtle color gradations. Gouache provides opaque, vibrant colors that work well for graphic, illustrative styles and bold, textured applications, enabling precise layering and corrections. Artists choose watercolour for its luminosity and softness, while gouache excels in producing matte finishes with strong visual impact.
Advantages and Limitations of Each
Watercolour offers translucency and subtle layering, enabling artists to create luminous, delicate effects with ease, but it can be challenging to correct mistakes due to its fast drying and transparency. Gouache provides rich, opaque coverage and vibrant colors, making it ideal for bold, graphic work and easy revision, though it may lack the lightness and fluidity typical of watercolour. Both mediums require different approaches in technique and handling, with watercolour favoring spontaneity and gouache allowing for greater control and texture.
Choosing Between Watercolour and Gouache
Choosing between watercolour and gouache hinges on the desired opacity and texture in artwork. Watercolour offers translucent layers ideal for delicate washes and light effects, while gouache provides vibrant, opaque coverage suited for bold, solid colors and graphic styles. Artists should consider the final visual impact, drying time, and layering techniques when selecting between these two versatile paint mediums.
watercolour vs gouache Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com