Acrylic paints dry faster than oil paints, allowing artists to layer colors quickly and work efficiently in a range of techniques. Oil paints offer richer textures and longer blending times, making them ideal for achieving detailed depth and subtle color transitions. Choosing between acrylic and oil depends on the artist's preferred style, drying time, and desired finish.
Table of Comparison
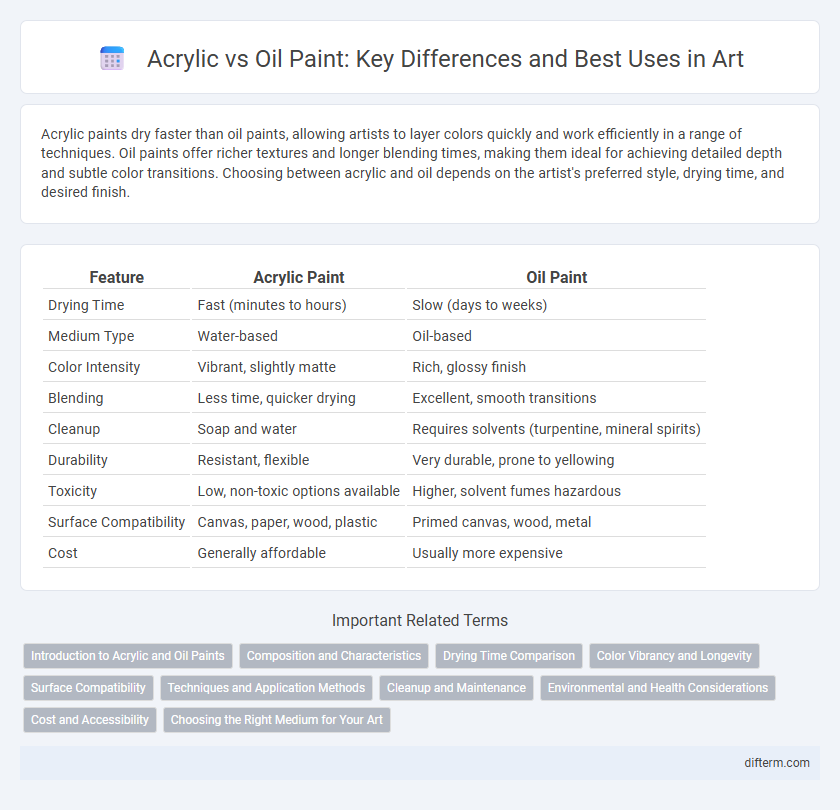
| Feature | Acrylic Paint | Oil Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Time | Fast (minutes to hours) | Slow (days to weeks) |
| Medium Type | Water-based | Oil-based |
| Color Intensity | Vibrant, slightly matte | Rich, glossy finish |
| Blending | Less time, quicker drying | Excellent, smooth transitions |
| Cleanup | Soap and water | Requires solvents (turpentine, mineral spirits) |
| Durability | Resistant, flexible | Very durable, prone to yellowing |
| Toxicity | Low, non-toxic options available | Higher, solvent fumes hazardous |
| Surface Compatibility | Canvas, paper, wood, plastic | Primed canvas, wood, metal |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Usually more expensive |
Introduction to Acrylic and Oil Paints
Acrylic paints consist of pigment suspended in an acrylic polymer emulsion, drying quickly to a flexible, water-resistant finish ideal for layering and mixed media techniques. Oil paints are made from pigments ground in drying oils like linseed, offering rich textures, vibrant colors, and extended drying times that allow for blending and subtle gradations. Both mediums provide unique advantages for artists, with acrylics favored for versatility and fast drying, while oils are prized for depth and color richness.
Composition and Characteristics
Acrylic paint is composed of pigment suspended in an acrylic polymer emulsion, drying quickly to a flexible, water-resistant finish, making it ideal for fast layering and vibrant color retention. Oil paint consists of pigment mixed with drying oils like linseed oil, which dry slowly and form a durable, glossy surface that allows for detailed blending and rich texture buildup. The molecular structure of acrylics enables rapid polymerization, while oils undergo oxidation, influencing drying time and finish characteristics.
Drying Time Comparison
Acrylic paints dry significantly faster than oil paints, with drying times ranging from 10 minutes to a few hours depending on thickness, while oil paints may take days to weeks to fully dry. This rapid drying time allows artists to work in layers quickly when using acrylics, enhancing productivity and enabling timely corrections. Oil paints' slow drying process offers extended blending opportunities, making them ideal for detailed, gradual color transitions and texture work.
Color Vibrancy and Longevity
Acrylic paints offer intense color vibrancy due to their fast-drying formula, preserving brightness without dulling over time. Oil paints provide deeper, richer hues with unparalleled blending capabilities, resulting in enhanced depth and texture in artworks. While acrylics resist yellowing and fading, oil paintings often gain character and longevity through natural oxidation and varnish application, sustaining color integrity for centuries.
Surface Compatibility
Acrylic paint adheres well to various surfaces including canvas, wood, paper, and fabric due to its fast-drying, flexible properties. Oil paint requires primed surfaces like gesso-coated canvas or specially prepared wood to prevent deterioration and ensure proper adhesion. Surface compatibility directly influences the durability and finish quality of both acrylic and oil artworks.
Techniques and Application Methods
Acrylic paint dries rapidly, allowing artists to layer colors quickly and utilize techniques such as glazing, impasto, and dry brushing with ease due to its fast-drying properties. Oil paint, known for its slow drying time, enables smoother blending, wet-on-wet application, and detailed textural work, making it ideal for techniques like glazing and scumbling. Mastering acrylic requires control over timing to exploit its versatility, while oil painting demands patience and skill in handling extended working times for rich, nuanced effects.
Cleanup and Maintenance
Acrylic paint offers easy cleanup with just soap and water, making it ideal for quick maintenance and minimal solvent use. Oil paint requires solvents like turpentine or mineral spirits for thorough brush cleaning, which can be more time-consuming and involves handling stronger chemicals. Proper disposal of oil paint solvents is crucial to avoid environmental hazards, whereas acrylic waste is generally less toxic and easier to manage.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Acrylic paints contain water-based polymers that emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to oil paints, making them a safer choice for indoor use and reducing environmental pollution. Oil paints rely on solvents like turpentine or mineral spirits for thinning and cleaning, which release toxic fumes harmful to both human health and the environment. Proper ventilation and the use of non-toxic mediums in oil painting can mitigate health risks, but acrylics remain the more eco-friendly and health-conscious option.
Cost and Accessibility
Acrylic paints are generally more affordable and widely accessible than oil paints, making them a popular choice for beginners and budget-conscious artists. Acrylics dry faster, reducing the need for extensive ventilation or specialized supplies, which can also lower overall costs. In contrast, oil paints often require additional mediums and cleaning materials, increasing the initial investment and complexity for artists.
Choosing the Right Medium for Your Art
Acrylic paint dries faster and offers versatility with its water-based composition, making it ideal for artists seeking quick layering and easy cleanup. Oil paint provides rich texture and depth due to its slow drying time, allowing for intricate blending and extended working periods. Consider the desired finish, drying time, and handling characteristics to select the medium that best supports your artistic vision and technique.
acrylic vs oil Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com