Impasto creates texture and depth by applying thick layers of paint, making brushstrokes visible and enhancing the tactile quality of an artwork. Sfumato, on the other hand, blends colors and tones softly to produce smooth transitions and a smoky, atmospheric effect without harsh lines. Artists use impasto to emphasize structure and dynamism, while sfumato evokes subtlety and realism through delicate gradations.
Table of Comparison
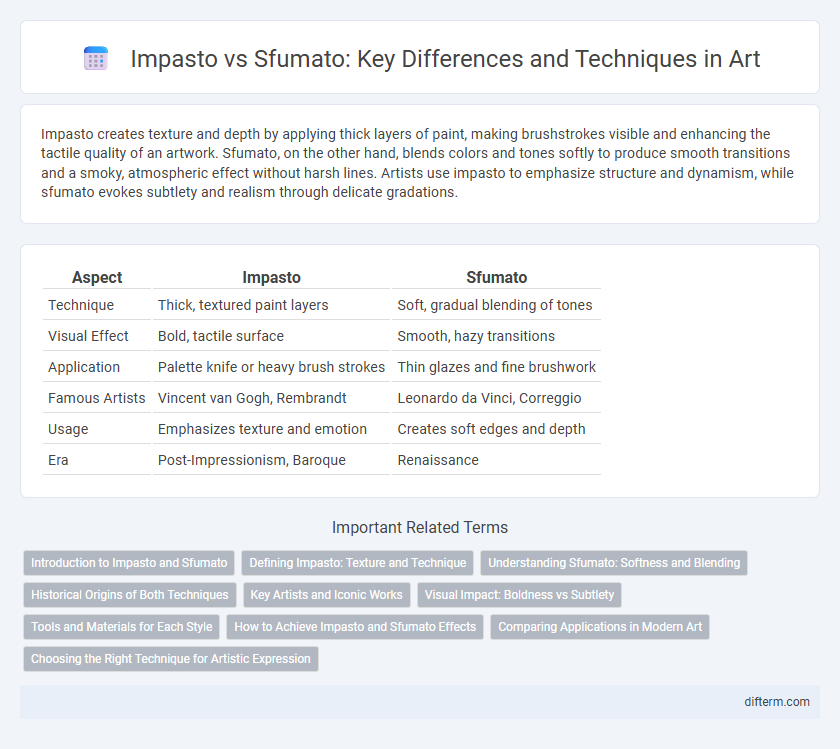
| Aspect | Impasto | Sfumato |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Thick, textured paint layers | Soft, gradual blending of tones |
| Visual Effect | Bold, tactile surface | Smooth, hazy transitions |
| Application | Palette knife or heavy brush strokes | Thin glazes and fine brushwork |
| Famous Artists | Vincent van Gogh, Rembrandt | Leonardo da Vinci, Correggio |
| Usage | Emphasizes texture and emotion | Creates soft edges and depth |
| Era | Post-Impressionism, Baroque | Renaissance |
Introduction to Impasto and Sfumato
Impasto is a painting technique characterized by thick, textured layers of paint applied with brush or palette knife, creating a three-dimensional surface that emphasizes light and shadow. Sfumato, pioneered by Leonardo da Vinci, involves the delicate blending of colors and tones to achieve soft transitions and a smoky, atmospheric effect without harsh lines. Both techniques enhance depth and emotion in artworks but differ fundamentally in texture and visual impact.
Defining Impasto: Texture and Technique
Impasto is a painting technique characterized by thick, textured layers of paint, often applied with a palette knife or brush to create a three-dimensional surface. This method enhances light reflection and shadow, adding dynamic depth and tactile richness to the artwork. Unlike sfumato, which emphasizes smooth transitions, impasto highlights the physicality of paint and the artist's gestures.
Understanding Sfumato: Softness and Blending
Sfumato is a Renaissance painting technique characterized by the delicate blending of colors and tones to create soft transitions without harsh lines, enhancing a lifelike depth and atmosphere. Unlike impasto, which emphasizes texture through thick paint application, sfumato relies on subtle gradations to mimic the natural diffusion of light and shadow. This technique achieves a smoky, hazy effect that enriches facial features and landscapes with a smooth, almost ethereal quality.
Historical Origins of Both Techniques
Impasto originated in the Renaissance period, primarily used by artists such as Titian to create texture and depth through thick layers of paint. Sfumato, pioneered by Leonardo da Vinci, emerged as a subtle blending technique to achieve soft transitions between colors and tones, enhancing realism. Both methods revolutionized oil painting practices, influencing centuries of artistic expression and visual storytelling.
Key Artists and Iconic Works
Impasto technique, characterized by thick, textured paint application, is exemplified by Vincent van Gogh's "Starry Night" and Rembrandt's self-portraits, where bold brushstrokes create vivid depth and emotional intensity. Sfumato, popularized by Leonardo da Vinci, particularly in "Mona Lisa" and "The Virgin of the Rocks," employs delicate blending of tones and colors to achieve soft transitions and realistic atmospheric effects. These techniques represent contrasting artistic approaches: impasto emphasizes tactile surface and dynamic expression, while sfumato masters subtle gradation and visual harmony.
Visual Impact: Boldness vs Subtlety
Impasto creates a bold visual impact through thick, textured layers of paint that capture and reflect light, emphasizing depth and movement in a tactile manner. Sfumato produces subtle transitions by blending colors and tones seamlessly, resulting in soft, hazy edges that enhance realism and atmospheric depth. The contrast between impasto's striking, raised surfaces and sfumato's smooth gradations highlights different artistic approaches to engaging viewers' emotional and sensory experiences.
Tools and Materials for Each Style
Impasto relies heavily on thick, textured oil paints applied with palette knives and stiff brushes to create a three-dimensional surface, often using heavy body acrylics or modeling paste for added volume. Sfumato requires delicate blending tools such as soft brushes and fine sponges, and utilizes thin layers of oil paints with solvent thinners like turpentine or mineral spirits to achieve smooth, smoky transitions. Canvas and primed wooden panels serve as common surfaces for both techniques, but the choice of materials directly impacts the tactile qualities and visual softness distinctive to each painting style.
How to Achieve Impasto and Sfumato Effects
Impasto is achieved by applying thick layers of paint with a palette knife or stiff brush, creating textured surfaces that catch light and add dimensionality to the artwork. Sfumato requires delicate blending of colors and tones using soft brushes or fingertips, allowing smooth transitions and soft edges without harsh lines, mimicking a smoky or hazy atmosphere. Mastering impasto involves building up paint layers for tactile depth while sfumato relies on subtle gradation and controlled glazing techniques to produce a seamless, atmospheric effect.
Comparing Applications in Modern Art
Impasto and sfumato represent contrasting techniques that shape modern art's texture and depth, with impasto emphasizing thick, textured paint application to create tactile surfaces, while sfumato employs delicate blending to achieve soft transitions and atmospheric effects. Contemporary artists utilize impasto to convey intense emotion and dynamic movement, whereas sfumato is favored for rendering subtle gradations and realistic portrayals, especially in portraiture. The choice between impasto and sfumato influences visual narrative and viewer engagement, reflecting diverse artistic intentions and evolving modern aesthetics.
Choosing the Right Technique for Artistic Expression
Impasto creates texture and dimensionality by layering thick paint, enhancing tactile and visual impact for expressive, bold artworks. Sfumato uses fine blending and soft transitions to achieve realistic depth and subtle atmospheric effects, ideal for delicate, nuanced compositions. Selecting between impasto and sfumato depends on whether the artist aims to emphasize texture and emotion or smooth tonal gradations for lifelike representation.
Impasto vs Sfumato Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com