Eco-tourism prioritizes experiencing natural environments with minimal impact, promoting conservation and local culture appreciation. Sustainable tourism integrates broader practices, including economic viability, social equity, and environmental protection, ensuring long-term benefits for both destinations and communities. Travelers seeking responsible pet-friendly adventures can support initiatives that combine eco-tourism principles with sustainable tourism goals.
Table of Comparison
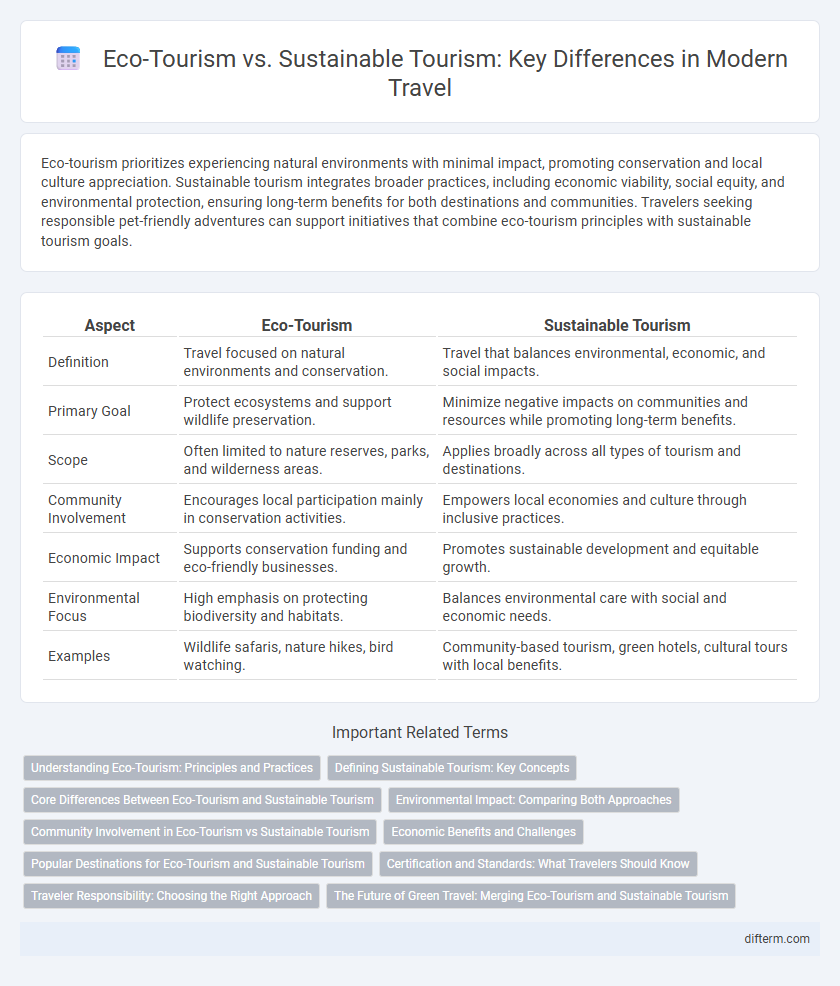
| Aspect | Eco-Tourism | Sustainable Tourism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Travel focused on natural environments and conservation. | Travel that balances environmental, economic, and social impacts. |
| Primary Goal | Protect ecosystems and support wildlife preservation. | Minimize negative impacts on communities and resources while promoting long-term benefits. |
| Scope | Often limited to nature reserves, parks, and wilderness areas. | Applies broadly across all types of tourism and destinations. |
| Community Involvement | Encourages local participation mainly in conservation activities. | Empowers local economies and culture through inclusive practices. |
| Economic Impact | Supports conservation funding and eco-friendly businesses. | Promotes sustainable development and equitable growth. |
| Environmental Focus | High emphasis on protecting biodiversity and habitats. | Balances environmental care with social and economic needs. |
| Examples | Wildlife safaris, nature hikes, bird watching. | Community-based tourism, green hotels, cultural tours with local benefits. |
Understanding Eco-Tourism: Principles and Practices
Eco-tourism emphasizes responsible travel to natural areas, prioritizing conservation, minimizing environmental impact, and supporting local communities. It involves activities such as wildlife observation, habitat preservation, and cultural immersion that foster environmental awareness and respect for indigenous cultures. Sustainable tourism broadens this scope by integrating economic viability and social equity, ensuring travel benefits ecosystems, local economies, and future generations without depleting natural resources.
Defining Sustainable Tourism: Key Concepts
Sustainable tourism focuses on minimizing environmental impact while promoting economic viability and cultural preservation within travel destinations. It integrates responsible resource management, community engagement, and long-term benefits for local populations. Unlike general eco-tourism, sustainable tourism encompasses broader social and economic dimensions alongside environmental stewardship.
Core Differences Between Eco-Tourism and Sustainable Tourism
Eco-tourism emphasizes responsible travel to natural areas, aiming to conserve the environment and improve local communities' well-being through minimal impact visits. Sustainable tourism, broader in scope, incorporates environmental, economic, and social dimensions to ensure long-term benefits for destinations, including local culture preservation and resource management. Key differences lie in eco-tourism's focus on nature conservation and education, while sustainable tourism targets a holistic approach to tourism development and sustainability.
Environmental Impact: Comparing Both Approaches
Eco-tourism emphasizes minimal environmental impact by promoting responsible travel to natural areas, conserving biodiversity, and educating visitors about ecological preservation. Sustainable tourism adopts a broader approach, integrating environmental, economic, and social dimensions to ensure long-term benefits for local communities and ecosystems. Both strategies aim to reduce carbon footprints, protect wildlife habitats, and support resource conservation, but sustainable tourism incorporates systemic planning beyond just environmental concerns.
Community Involvement in Eco-Tourism vs Sustainable Tourism
Eco-tourism emphasizes direct community involvement by engaging local populations in conservation efforts and offering authentic cultural exchanges that promote environmental awareness. Sustainable tourism integrates community input to balance ecological protection with economic growth, ensuring long-term benefits without compromising natural or social resources. Both approaches prioritize local empowerment but eco-tourism centers specifically on ecological education and low-impact travel experiences.
Economic Benefits and Challenges
Eco-tourism generates economic benefits by promoting local employment and supporting small-scale businesses, enhancing community income through responsible travel practices. Sustainable tourism ensures long-term economic growth by balancing environmental preservation with infrastructure development, reducing resource depletion and operational costs. Challenges include managing fluctuating tourist demands and investing in eco-friendly technologies, which may require significant upfront capital and continuous community engagement.
Popular Destinations for Eco-Tourism and Sustainable Tourism
Costa Rica's Monteverde Cloud Forest and Kenya's Maasai Mara are popular destinations for eco-tourism, offering rich biodiversity and community-led conservation projects. In comparison, sustainable tourism destinations like Norway's fjords and New Zealand's South Island focus on minimizing environmental impact while supporting local economy and culture. Both eco-tourism and sustainable tourism prioritize preserving natural habitats and cultural heritage, but sustainable tourism emphasizes long-term resource management and local stakeholder engagement.
Certification and Standards: What Travelers Should Know
Certification and standards in eco-tourism typically emphasize environmental conservation and minimal ecological impact, with labels such as Green Globe and Rainforest Alliance guiding travelers towards responsible operators. Sustainable tourism certifications cover a broader scope, including social, economic, and cultural aspects, exemplified by standards like GSTC (Global Sustainable Tourism Council) criteria. Travelers should prioritize certifications verified by recognized bodies to ensure genuine commitment to eco-friendly practices and support meaningful community benefits.
Traveler Responsibility: Choosing the Right Approach
Travelers play a crucial role in promoting eco-tourism by minimizing environmental impact through responsible activities such as wildlife observation and supporting local conservation efforts. Sustainable tourism expands this responsibility by encouraging choices that benefit local communities economically and culturally while preserving natural resources for future generations. Selecting between eco-tourism and sustainable tourism depends on prioritizing either direct environmental conservation or a broader commitment to overall community well-being and resource management.
The Future of Green Travel: Merging Eco-Tourism and Sustainable Tourism
The future of green travel lies in merging eco-tourism and sustainable tourism to create holistic experiences that minimize environmental impact while supporting local communities. Eco-tourism emphasizes conservation and wildlife protection, whereas sustainable tourism integrates broader social, economic, and environmental goals for long-term viability. Combining these approaches fosters responsible travel practices that preserve natural resources and promote cultural heritage for future generations.
eco-tourism vs sustainable tourism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com