Tight ends and wide receivers play crucial roles in football offenses, with tight ends serving as versatile players who can block and catch passes, while wide receivers specialize primarily in route running and receiving. Tight ends are generally bigger and stronger, making them effective in short-yardage and red-zone situations, whereas wide receivers rely on speed and agility to create separation and gain yardage downfield. Choosing between a tight end and a wide receiver depends on the team's offensive strategy and the type of plays being executed.
Table of Comparison
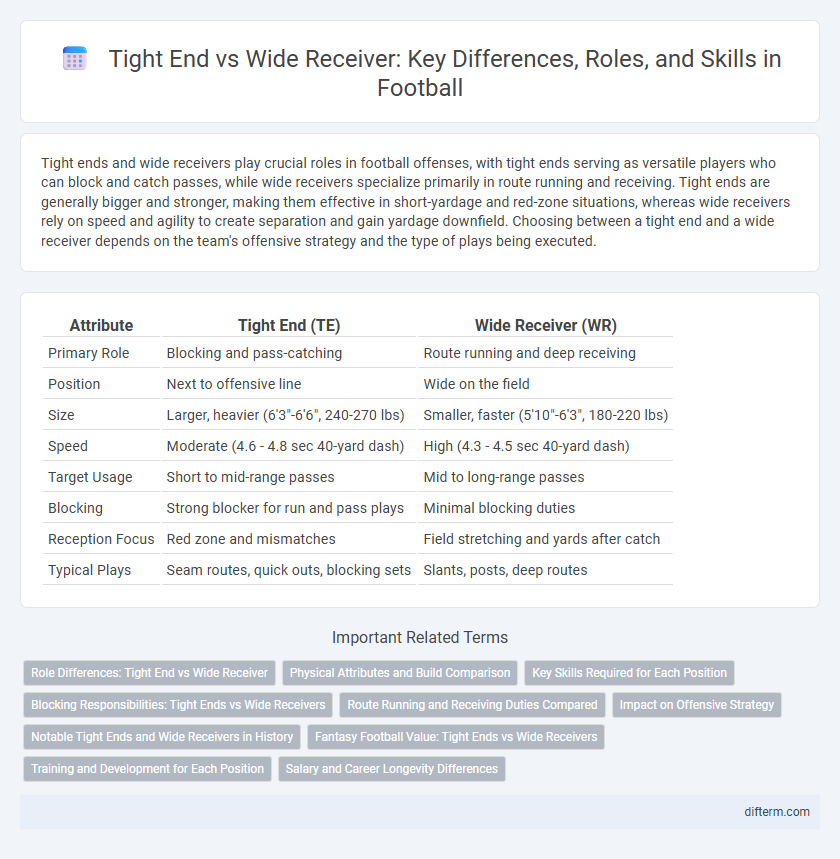
| Attribute | Tight End (TE) | Wide Receiver (WR) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Blocking and pass-catching | Route running and deep receiving |
| Position | Next to offensive line | Wide on the field |
| Size | Larger, heavier (6'3"-6'6", 240-270 lbs) | Smaller, faster (5'10"-6'3", 180-220 lbs) |
| Speed | Moderate (4.6 - 4.8 sec 40-yard dash) | High (4.3 - 4.5 sec 40-yard dash) |
| Target Usage | Short to mid-range passes | Mid to long-range passes |
| Blocking | Strong blocker for run and pass plays | Minimal blocking duties |
| Reception Focus | Red zone and mismatches | Field stretching and yards after catch |
| Typical Plays | Seam routes, quick outs, blocking sets | Slants, posts, deep routes |
Role Differences: Tight End vs Wide Receiver
Tight ends primarily serve as hybrid players, combining the roles of blockers and receivers, often positioned near the offensive line to support both running and passing plays. Wide receivers focus on route running and catching passes, leveraging speed and agility to create separation from defenders and stretch the field vertically. The tight end's dual-threat capability makes them crucial in short-yardage situations, while wide receivers excel in deep threat scenarios and spreading the defense.
Physical Attributes and Build Comparison
Tight ends typically possess a larger, more muscular build, averaging around 6'4" to 6'6" in height and 240 to 260 pounds, optimized for blocking and short-yardage receptions. Wide receivers are generally leaner and faster, measuring between 5'10" to 6'3" and weighing 180 to 210 pounds, designed for agility and long-distance route running. The contrast in physical attributes underscores the tight end's dual role in both blocking and receiving versus the wide receiver's primary focus on speed and catching.
Key Skills Required for Each Position
Tight ends require a blend of blocking strength and reliable receiving skills to support both the offensive line and the passing game effectively. Wide receivers prioritize speed, precise route running, and exceptional catching ability to create separation and make critical receptions downfield. Both positions demand strong hands and spatial awareness, but tight ends often engage more in physical contact at the line of scrimmage.
Blocking Responsibilities: Tight Ends vs Wide Receivers
Tight ends have significantly greater blocking responsibilities compared to wide receivers, as they often line up close to the offensive line and are key in run blocking and pass protection schemes. Wide receivers primarily focus on route running and catching passes, with blocking generally limited to downfield blocks during passing plays. The dual role of tight ends as both blockers and receivers makes them essential for balanced offensive strategies in football.
Route Running and Receiving Duties Compared
Tight ends and wide receivers differ significantly in route running and receiving duties, with tight ends often running shorter, more physical routes such as curls, seams, and flats to create mismatches against linebackers or safeties. Wide receivers specialize in precise route running across the field, executing complex patterns like slants, posts, and deep fades to exploit defensive backs in man or zone coverage. Receiving duties for tight ends emphasize blocking responsibilities and securing contested catches in traffic, while wide receivers prioritize speed, separation, and yard-after-catch opportunities.
Impact on Offensive Strategy
Tight ends provide a versatile threat by combining blocking prowess with receiving skills, influencing offensive strategies that prioritize both run support and short-to-intermediate passing plays. Wide receivers stretch defenses vertically and horizontally, creating space and exploiting coverage mismatches to boost explosive passing attacks. Teams often adjust formations and play-calling to leverage tight ends in red zone efficiency and use wide receivers to open up the field for dynamic yardage gains.
Notable Tight Ends and Wide Receivers in History
Notable tight ends such as Tony Gonzalez and Rob Gronkowski revolutionized the position with their blend of size, athleticism, and receiving skills, becoming pivotal offensive weapons in NFL history. Legendary wide receivers like Jerry Rice and Randy Moss set unparalleled records in receptions, yards, and touchdowns, defining the role with exceptional speed and route-running precision. Both positions have produced Hall of Famers whose impact eternally shapes professional football's offensive strategies.
Fantasy Football Value: Tight Ends vs Wide Receivers
Tight ends often provide more consistent fantasy football value due to their dual role in blocking and receiving, especially in red-zone situations where touchdowns are critical. Wide receivers typically offer higher upside with greater target volume and yardage, making them key for PPR (points per reception) leagues. Evaluating matchup strength and offensive scheme is essential when deciding between a tight end and wide receiver for weekly fantasy lineups.
Training and Development for Each Position
Tight ends prioritize strength and blocking technique training to excel in both receiving and run support roles, while wide receivers focus on speed, agility drills, and route-running precision to maximize separation from defenders. Tight end development often includes enhanced physical conditioning to withstand inline blocking demands, whereas wide receiver training emphasizes hand-eye coordination and explosive acceleration for deep pass threats. Position-specific skill drills and film study are crucial for both roles to master playbook reads and adjust to defensive coverages effectively.
Salary and Career Longevity Differences
Tight ends generally earn higher average salaries than wide receivers due to their versatility in both blocking and receiving, which makes them valuable assets in offensive schemes. Career longevity for tight ends tends to be longer, as their blocking responsibilities reduce the exposure to high-speed collisions compared to wide receivers who often face intense coverage and sprinting demands. Statistical analysis shows tight ends can have careers lasting 8 to 10 years on average, while wide receivers commonly average around 6 to 8 years in the NFL.
tight end vs wide receiver Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com