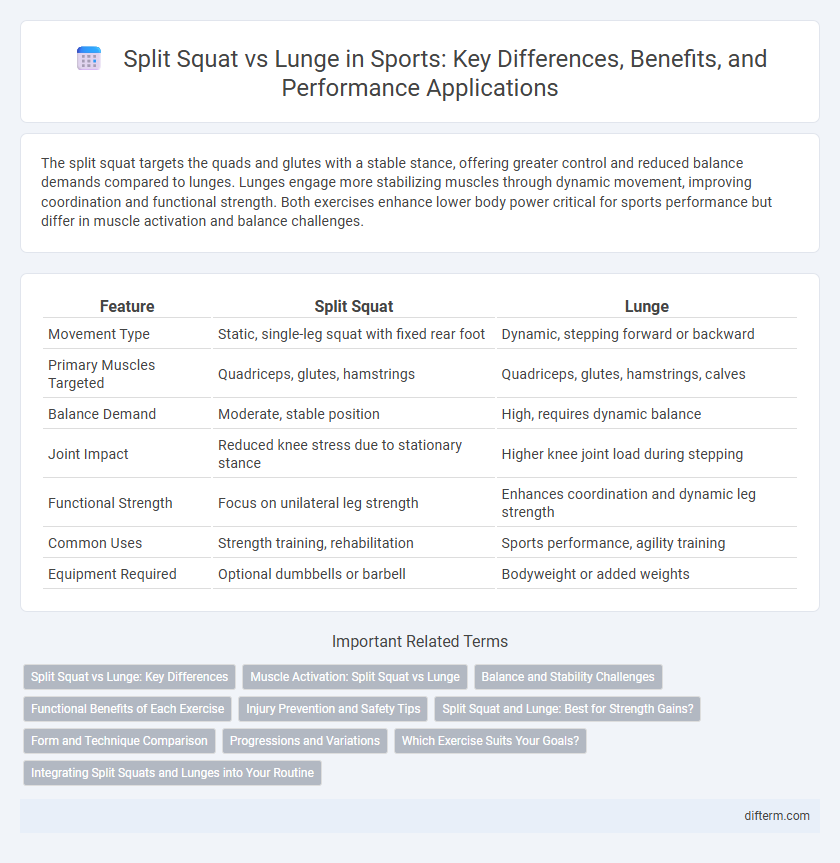
The split squat targets the quads and glutes with a stable stance, offering greater control and reduced balance demands compared to lunges. Lunges engage more stabilizing muscles through dynamic movement, improving coordination and functional strength. Both exercises enhance lower body power critical for sports performance but differ in muscle activation and balance challenges.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Split Squat | Lunge |
|---|---|---|
| Movement Type | Static, single-leg squat with fixed rear foot | Dynamic, stepping forward or backward |
| Primary Muscles Targeted | Quadriceps, glutes, hamstrings | Quadriceps, glutes, hamstrings, calves |
| Balance Demand | Moderate, stable position | High, requires dynamic balance |
| Joint Impact | Reduced knee stress due to stationary stance | Higher knee joint load during stepping |
| Functional Strength | Focus on unilateral leg strength | Enhances coordination and dynamic leg strength |
| Common Uses | Strength training, rehabilitation | Sports performance, agility training |
| Equipment Required | Optional dumbbells or barbell | Bodyweight or added weights |
Split Squat vs Lunge: Key Differences
The split squat isolates each leg by keeping the rear foot stationary, allowing for greater focus on unilateral leg strength and stability, while lunges involve stepping forward or backward, promoting dynamic balance and coordination. Split squats primarily target the quadriceps and glutes with less emphasis on hip flexors, whereas lunges engage hip flexors more due to the movement range. Both exercises improve lower body strength but differ in muscle activation patterns and joint mobility demands.
Muscle Activation: Split Squat vs Lunge
The split squat predominantly activates the quadriceps and gluteus maximus with enhanced stability demands on the hip abductors, while lunges engage a broader range of muscles including the hamstrings, glutes, and core for balance and propulsion. EMG studies reveal higher quadriceps activation during split squats, whereas lunges elicit greater hamstring and adductor muscle engagement due to the dynamic stepping motion. Incorporating both exercises optimizes lower body muscle activation by targeting complementary muscle groups essential for athletic performance and injury prevention.
Balance and Stability Challenges
Split squats enhance balance and stability by requiring a fixed rear foot position, which reduces forward momentum and isolates the quadriceps and gluteus medius for improved single-leg control. Lunges demand greater dynamic balance due to the forward or backward step, engaging core stabilizers and ankle proprioceptors to manage shifting weight and maintain posture. Studies show split squats promote joint stability in the knee, while lunges develop neuromuscular coordination by challenging multidirectional movement patterns.
Functional Benefits of Each Exercise
Split squats enhance unilateral leg strength by isolating each limb, improving balance and stability critical for athletic performance. Lunges promote dynamic movement patterns by engaging multiple muscle groups through a forward stepping motion, boosting coordination and agility. Both exercises contribute to injury prevention by strengthening stabilizer muscles and enhancing functional lower body mechanics.
Injury Prevention and Safety Tips
The split squat and lunge both enhance lower body strength while minimizing injury risk by promoting controlled movement and balanced muscle development. Maintaining proper knee alignment over the toes and avoiding excessive forward knee travel reduces strain on the joints and ligaments during these exercises. Incorporating adequate warm-up, focusing on form, and gradually increasing resistance further support injury prevention and optimize safety during split squats and lunges.
Split Squat and Lunge: Best for Strength Gains?
Split squats and lunges both effectively target the quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings for strength development, with split squats offering enhanced stability due to the fixed rear foot position. Lunges engage more dynamic balance and coordination, activating core muscles and improving functional strength through varied movement patterns. For maximal strength gains, split squats provide controlled, unilateral muscle engagement, making them ideal for isolating and progressively overloading specific leg muscles.
Form and Technique Comparison
The split squat emphasizes stability with both feet planted, requiring controlled descent and ascent to maintain knee alignment over the ankle, reducing injury risk. Lunges demand dynamic balance and forward momentum, engaging core muscles to stabilize the body while stepping, ensuring the front knee tracks in line with the toes. Proper technique in both exercises involves keeping the torso upright and avoiding knee valgus to maximize muscle engagement and joint safety.
Progressions and Variations
Split squat progressions typically involve increasing depth, adding weights such as dumbbells or barbells, and incorporating tempo changes to enhance muscle activation and stability. Lunge variations include forward, reverse, walking, and lateral lunges, which target different muscle groups and improve dynamic balance and coordination. Both exercises benefit from advanced modifications like plyometric lunges or Bulgarian split squats to boost power, agility, and unilateral leg strength in athletic training.
Which Exercise Suits Your Goals?
Split squats target the quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings with a stable base that enhances balance and strength, making them ideal for building unilateral lower body power. Lunges, offering dynamic movement patterns and greater range of motion, engage core stability and improve functional mobility, better suited for sports requiring agility and coordination. Choosing between split squats and lunges depends on whether your goals focus on strength development or dynamic, sport-specific movement enhancement.
Integrating Split Squats and Lunges into Your Routine
Integrating split squats and lunges into your workout routine enhances lower body strength, improves balance, and increases functional mobility by targeting the quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings. Split squats offer greater stability and unilateral leg strength, while lunges promote dynamic movement and coordination challenges. Combining both exercises optimizes muscle engagement, supports joint health, and accelerates athletic performance improvements.
split squat vs lunge Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com