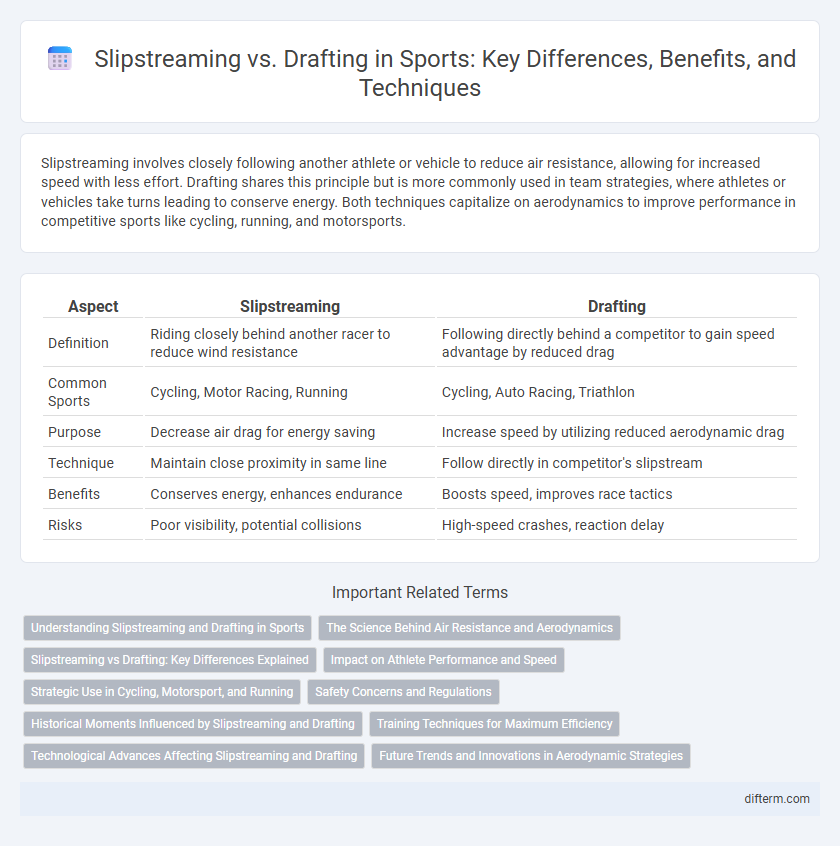
Slipstreaming involves closely following another athlete or vehicle to reduce air resistance, allowing for increased speed with less effort. Drafting shares this principle but is more commonly used in team strategies, where athletes or vehicles take turns leading to conserve energy. Both techniques capitalize on aerodynamics to improve performance in competitive sports like cycling, running, and motorsports.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Slipstreaming | Drafting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Riding closely behind another racer to reduce wind resistance | Following directly behind a competitor to gain speed advantage by reduced drag |
| Common Sports | Cycling, Motor Racing, Running | Cycling, Auto Racing, Triathlon |
| Purpose | Decrease air drag for energy saving | Increase speed by utilizing reduced aerodynamic drag |
| Technique | Maintain close proximity in same line | Follow directly in competitor's slipstream |
| Benefits | Conserves energy, enhances endurance | Boosts speed, improves race tactics |
| Risks | Poor visibility, potential collisions | High-speed crashes, reaction delay |
Understanding Slipstreaming and Drafting in Sports
Slipstreaming and drafting are aerodynamic techniques used by athletes and vehicles to reduce air resistance and conserve energy. In slipstreaming, a competitor closely follows the wake created by a leading athlete or vehicle, benefiting from reduced drag and increased speed. Drafting involves positioning behind a lead competitor to maintain pace and conserve stamina, commonly applied in cycling, motorsports, and running races to optimize performance and strategic advantage.
The Science Behind Air Resistance and Aerodynamics
Slipstreaming and drafting both exploit the science of air resistance and aerodynamics by positioning a vehicle or athlete directly behind another to reduce drag. By moving in the slipstream, the trailing entity encounters a zone of lowered air pressure created by the lead body, significantly decreasing aerodynamic drag and conserving energy. This reduction in wind resistance improves speed and efficiency, crucial in cycling, motorsports, and running competitions.
Slipstreaming vs Drafting: Key Differences Explained
Slipstreaming involves closely following another athlete or vehicle to reduce air resistance and conserve energy, while drafting specifically refers to positioning directly behind another competitor to gain aerodynamic advantage. The key difference lies in slipstreaming's broader application of reduced drag zones around a lead entity, whereas drafting is more precise, focusing on the turbulent wake immediately behind. Both techniques enhance performance by minimizing wind resistance but differ in tactical execution and spatial positioning in sports like cycling, racing, and swimming.
Impact on Athlete Performance and Speed
Slipstreaming and drafting both reduce aerodynamic drag by positioning athletes closely behind competitors, significantly enhancing speed and energy efficiency. Slipstreaming offers a more dynamic approach by maintaining close proximity in fluid environments, optimizing airflow to maximize velocity with lower energy expenditure. Drafting, commonly used in cycling and running, strategically conserves stamina and delays fatigue, resulting in improved overall athlete performance during endurance events.
Strategic Use in Cycling, Motorsport, and Running
Slipstreaming and drafting are strategic techniques used in cycling, motorsport, and running to reduce aerodynamic drag and conserve energy by positioning closely behind a leading competitor. Cyclists often exploit slipstreaming during races like the Tour de France to maintain higher speeds with less effort, while motorsport drivers use drafting to slingshot past opponents on tracks like NASCAR circuits. Runners, especially in middle- and long-distance events, adopt drafting to decrease wind resistance and improve endurance, maximizing racing efficiency.
Safety Concerns and Regulations
Slipstreaming and drafting both reduce air resistance to boost speed, but drafting poses higher safety risks due to closer proximity and reduced driver visibility. Racing regulations often limit drafting distances and enforce penalties to prevent collisions and pile-ups, ensuring safer competition on tracks. Strict adherence to these rules combined with driver skill minimizes accidents linked to slipstreaming and drafting maneuvers.
Historical Moments Influenced by Slipstreaming and Drafting
Slipstreaming and drafting have shaped iconic sports moments, such as the 1979 Daytona 500, where Richard Petty used drafting to outpace competitors in NASCAR's most prestigious race. In cycling, Eddy Merckx expertly utilized slipstreaming during the 1974 Tour de France to conserve energy and launch decisive attacks, cementing his legacy. These techniques remain fundamental in motorsports and cycling, influencing race strategies and outcomes over decades.
Training Techniques for Maximum Efficiency
Slipstreaming and drafting are advanced training techniques in sports like cycling and motorsports, used to reduce aerodynamic drag and conserve energy. Athletes practice positioning closely behind a lead competitor, optimizing body posture and maintaining precise distance to maximize the slipstream effect. Consistent training in these methods improves speed, endurance, and overall race efficiency through enhanced energy management.
Technological Advances Affecting Slipstreaming and Drafting
Advancements in aerodynamic technology and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) have significantly enhanced slipstreaming and drafting techniques in sports like cycling and motorsports. Modern race vehicles utilize optimized body shapes and active aero components to maximize the reduction of air resistance within a slipstream, improving speed and energy efficiency. Real-time telemetry and wind tunnel testing enable teams to fine-tune drafting strategies, increasing competitive performance through precise manipulation of airflow dynamics.
Future Trends and Innovations in Aerodynamic Strategies
Slipstreaming and drafting techniques are evolving with advancements in computational fluid dynamics and real-time telemetry, enabling athletes to optimize aerodynamic positioning dynamically during competition. Innovations like adaptive aerodynamics and smart wearable sensors are set to enhance airflow management, reducing drag and maximizing speed more efficiently than traditional methods. Future trends emphasize integrating AI-driven performance analytics to personalize slipstreaming strategies, revolutionizing competitive racing across cycling, motorsports, and track events.
Slipstreaming vs Drafting Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com