A pinch hitter is a substitute batter who replaces another player during a specific at-bat, often used strategically to gain a hitting advantage in key moments. The designated hitter (DH) bats in place of the pitcher throughout the game without playing a defensive position. Understanding the distinct roles of pinch hitters and designated hitters is crucial for effective baseball team strategy and lineup management.
Table of Comparison
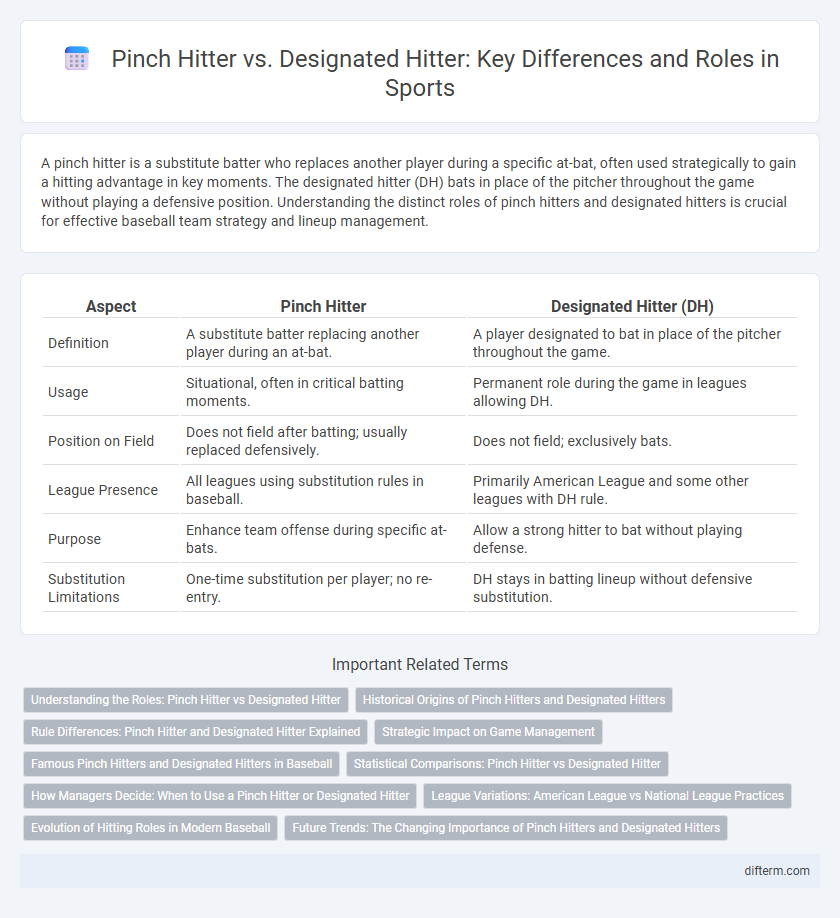
| Aspect | Pinch Hitter | Designated Hitter (DH) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A substitute batter replacing another player during an at-bat. | A player designated to bat in place of the pitcher throughout the game. |
| Usage | Situational, often in critical batting moments. | Permanent role during the game in leagues allowing DH. |
| Position on Field | Does not field after batting; usually replaced defensively. | Does not field; exclusively bats. |
| League Presence | All leagues using substitution rules in baseball. | Primarily American League and some other leagues with DH rule. |
| Purpose | Enhance team offense during specific at-bats. | Allow a strong hitter to bat without playing defense. |
| Substitution Limitations | One-time substitution per player; no re-entry. | DH stays in batting lineup without defensive substitution. |
Understanding the Roles: Pinch Hitter vs Designated Hitter
A pinch hitter is a substitute batter who enters the game to bat in place of another player, typically in crucial situations to leverage better hitting skills, while a designated hitter (DH) is a player who bats in place of the pitcher throughout the game without playing a defensive position. The pinch hitter role is situational and flexible, often leading to strategic advantages during late innings, whereas the designated hitter provides consistent offensive strength by occupying a permanent batting spot. Understanding these roles highlights their impact on team strategy, influencing lineup decisions and game outcomes in leagues like MLB's American League where the DH rule is implemented.
Historical Origins of Pinch Hitters and Designated Hitters
The pinch hitter originated in the early days of baseball as a strategic substitution to improve batting outcomes during critical game moments, with documented uses dating back to the late 19th century. The designated hitter (DH) was introduced in the American League in 1973 to boost offensive production by allowing a player to bat in place of the pitcher without defensive responsibilities. These innovations reflect evolving approaches to lineup optimization and game strategy within professional baseball history.
Rule Differences: Pinch Hitter and Designated Hitter Explained
A pinch hitter substitutes for another batter during a specific at-bat and must take over that player's spot defensively if the substitution remains. The designated hitter (DH) bats in place of the pitcher without entering the game defensively, a rule primarily used in the American League and some other leagues. Unlike the pinch hitter, the DH cannot be replaced by the original pitcher or switch to a defensive position once the game starts.
Strategic Impact on Game Management
A pinch hitter offers strategic flexibility by allowing managers to replace a weak batter with a stronger hitter in crucial situations, directly impacting run production and game momentum. The designated hitter, however, provides consistent offensive strength by letting teams keep their best hitter in the lineup without sacrificing defensive positions, thus enhancing lineup stability and scoring potential. Utilizing a pinch hitter often signals tactical adjustments during high-pressure moments, while the designated hitter role supports sustained offensive pressure throughout the game.
Famous Pinch Hitters and Designated Hitters in Baseball
Famous pinch hitters like Lenny Harris hold the MLB record with 212 career pinch hits, showcasing their clutch ability off the bench, while iconic designated hitters such as David Ortiz revolutionized the role by combining power and consistency in the Boston Red Sox lineup. Pinch hitters excel in high-pressure moments to change game momentum, whereas designated hitters contribute regular offensive production without defensive duties in the American League. Players like Matt Stairs and Edgar Martinez exemplify these roles, with Martinez's .312 career batting average highlighting the strategic advantage of designated hitters.
Statistical Comparisons: Pinch Hitter vs Designated Hitter
Pinch hitters generally have lower overall batting averages compared to designated hitters due to limited at-bats and high-pressure situations, with MLB career averages around .230 versus .270 for designated hitters. Designated hitters accumulate more plate appearances, contributing to higher on-base percentages and slugging percentages, often exceeding .350 OBP and .450 SLG, while pinch hitters tend to record below .320 OBP and .400 SLG. Statistical analysis shows designated hitters significantly impact run production over a full season, whereas pinch hitters' contributions are situational and sporadic, reflected in fewer RBIs and home runs per game.
How Managers Decide: When to Use a Pinch Hitter or Designated Hitter
Managers decide to use a pinch hitter primarily in critical game situations requiring a stronger batter to replace a weaker hitter, often late in the game or during strategic matchups. The designated hitter (DH) remains constant in the lineup, designed to bat in place of the pitcher in leagues that allow it, providing consistent offensive strength. Strategic use of a pinch hitter depends on the opposing pitcher's handedness, player fatigue, and game context, while the designated hitter offers long-term lineup stability and offensive production.
League Variations: American League vs National League Practices
In Major League Baseball, the American League employs the designated hitter (DH) rule, allowing a player to bat in place of the pitcher without affecting defensive positions. Conversely, the National League traditionally relies on pinch hitters, substituting batters during the game while pitchers remain active defensively. This distinction influences strategic decisions, affecting game pace and player specialization across the two leagues.
Evolution of Hitting Roles in Modern Baseball
Pinch hitters and designated hitters represent key evolutions in modern baseball's offensive strategy. The designated hitter role, introduced in the American League in 1973, revolutionized lineups by allowing a player to bat in place of the pitcher, increasing offensive production. Pinch hitters, used strategically for situational advantages, have evolved alongside analytics to optimize matchups and maximize run-scoring opportunities.
Future Trends: The Changing Importance of Pinch Hitters and Designated Hitters
The evolving strategies in Major League Baseball emphasize the growing prominence of designated hitters, driven by rule changes such as the universal DH rule adopted in the 2022 season. Pinch hitters are becoming more specialized, often utilized in high-leverage situations demanding precise matchups and situational hitting expertise. Data analytics and player versatility continue to influence roster construction, gradually shifting the role dynamics between pinch hitters and designated hitters in modern baseball.
Pinch hitter vs Designated hitter Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com