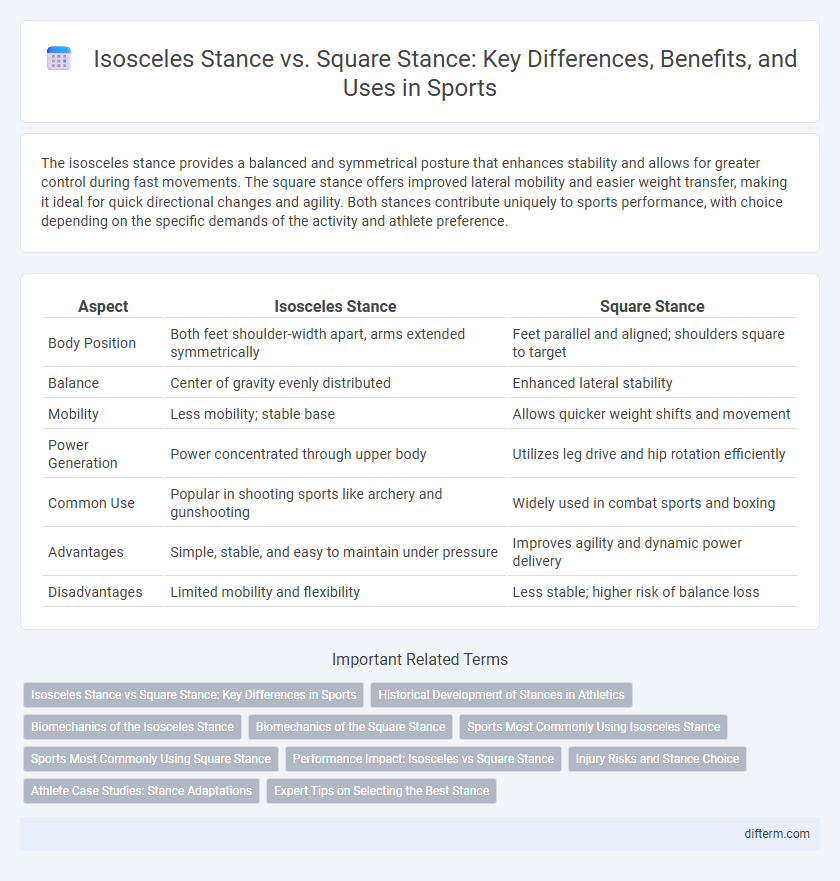
The isosceles stance provides a balanced and symmetrical posture that enhances stability and allows for greater control during fast movements. The square stance offers improved lateral mobility and easier weight transfer, making it ideal for quick directional changes and agility. Both stances contribute uniquely to sports performance, with choice depending on the specific demands of the activity and athlete preference.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Isosceles Stance | Square Stance |
|---|---|---|
| Body Position | Both feet shoulder-width apart, arms extended symmetrically | Feet parallel and aligned; shoulders square to target |
| Balance | Center of gravity evenly distributed | Enhanced lateral stability |
| Mobility | Less mobility; stable base | Allows quicker weight shifts and movement |
| Power Generation | Power concentrated through upper body | Utilizes leg drive and hip rotation efficiently |
| Common Use | Popular in shooting sports like archery and gunshooting | Widely used in combat sports and boxing |
| Advantages | Simple, stable, and easy to maintain under pressure | Improves agility and dynamic power delivery |
| Disadvantages | Limited mobility and flexibility | Less stable; higher risk of balance loss |
Isosceles Stance vs Square Stance: Key Differences in Sports
The isosceles stance in sports features both feet aligned evenly, providing balanced weight distribution and stability, while the square stance places feet parallel but staggered, enhancing power generation during movement. Athletes often prefer the isosceles stance for defensive sports like boxing due to its symmetrical posture, whereas the square stance is favored in activities like baseball and golf for improved rotational strength and follow-through. Understanding these key differences helps optimize performance by matching stance choice to specific sports demands and movement mechanics.
Historical Development of Stances in Athletics
The historical development of stances in athletics reveals that the isosceles stance, characterized by an equal distance between feet, gained prominence in sports like tennis due to its balance and power generation advantages. The square stance, with feet aligned parallel and shoulder-width apart, emerged earlier in track and field events for stability and linear force application. Over time, athletes adapted these stances based on biomechanical research and performance demands, influencing modern training techniques across various sports disciplines.
Biomechanics of the Isosceles Stance
The biomechanics of the isosceles stance in sports such as shooting or golf emphasize symmetrical weight distribution and balanced muscle engagement, enhancing stability and control. This stance allows for uniform shoulder alignment, reducing torque on the spine and promoting consistent force application. Compared to the square stance, the isosceles position optimizes joint angles to improve precision and reduce fatigue during repetitive movements.
Biomechanics of the Square Stance
The biomechanics of the square stance in sports emphasize balanced weight distribution across both feet, enhancing stability and power generation during movement. This stance aligns the hips and shoulders parallel to the target, promoting rotational efficiency and minimizing lateral torque. Athletes utilizing the square stance often experience improved force transfer and greater control in dynamic actions such as swinging or striking.
Sports Most Commonly Using Isosceles Stance
The isosceles stance is predominantly used in sports such as shooting and archery due to its balanced and symmetrical positioning, which enhances stability and accuracy. This stance allows athletes to distribute weight evenly across both feet, providing consistent control during precision-based activities. Its widespread adoption in competitive shooting sports like Olympic rifle events highlights its effectiveness in maximizing performance and minimizing body fatigue.
Sports Most Commonly Using Square Stance
Square stance is predominantly used in sports like boxing, baseball, and golf for its balance and power generation. This stance allows athletes to evenly distribute weight on both feet, enhancing stability during dynamic movements. In contrast, isosceles stance is more common in shooting sports, where symmetrical arm positioning aids precision.
Performance Impact: Isosceles vs Square Stance
The isosceles stance offers a balanced distribution of weight, enhancing stability and power in sports like boxing and tennis, improving overall performance during rapid directional changes. In contrast, the square stance allows for quicker lateral movements and better defensive positioning, favoring agility and reaction time. Athletes often choose between the two based on the specific demands of their sport, with the isosceles stance benefiting power-driven actions and the square stance optimizing speed and maneuverability.
Injury Risks and Stance Choice
Isosceles stance in sports like boxing offers balanced shoulder alignment, reducing strain on individual joints and lowering overall injury risk, while square stance increases torque on the knees and hips, potentially leading to ligament stress. Athletes prone to lower body injuries may benefit from isosceles stance due to its symmetrical weight distribution and improved defensive posture. However, stance choice should be tailored to the athlete's biomechanics and sport-specific demands to minimize injury and maximize performance.
Athlete Case Studies: Stance Adaptations
Athlete case studies reveal that the isosceles stance enhances defensive stability and balance in sports like boxing, offering increased front-line protection. Conversely, the square stance provides greater mobility and power generation, as observed in mixed martial arts fighters who adapt it for rapid offensive maneuvers. Performance data indicate that tailored stance adaptations correlate with improved reaction time and force output specific to each athlete's sport and strategy.
Expert Tips on Selecting the Best Stance
Expert tips for selecting the best stance in sports emphasize the isosceles stance for improved balance and symmetrical power distribution, ideal for activities requiring forward movement and rapid directional changes. The square stance offers enhanced stability and control, beneficial in sports demanding lateral movements and quick pivots. Athletes should assess their sport-specific demands and personal biomechanics to choose a stance that optimizes performance and reduces injury risk.
isosceles stance vs square stance Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com