Mastering the forehand and backhand strokes is essential for excelling in sports like tennis and badminton. The forehand typically offers more power and control, while the backhand provides versatility and reach for difficult shots. Developing a balanced technique for both enhances overall performance and gameplay strategy.
Table of Comparison
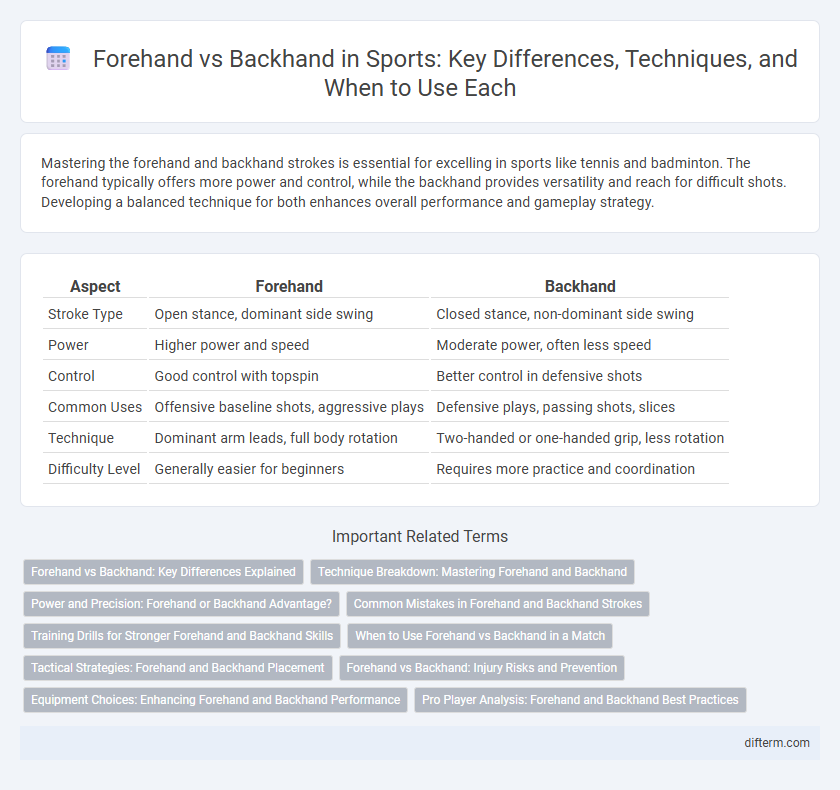
| Aspect | Forehand | Backhand |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke Type | Open stance, dominant side swing | Closed stance, non-dominant side swing |
| Power | Higher power and speed | Moderate power, often less speed |
| Control | Good control with topspin | Better control in defensive shots |
| Common Uses | Offensive baseline shots, aggressive plays | Defensive plays, passing shots, slices |
| Technique | Dominant arm leads, full body rotation | Two-handed or one-handed grip, less rotation |
| Difficulty Level | Generally easier for beginners | Requires more practice and coordination |
Forehand vs Backhand: Key Differences Explained
Forehand shots generate more power and are typically easier to master due to the natural swinging motion, allowing players to cover a wider area of the court effectively. Backhand strokes, whether one-handed or two-handed, offer greater control and versatility in shot placement, making them essential for returning challenging balls and executing precise angles. Understanding the biomechanical differences and tactical applications between forehand and backhand techniques enhances overall gameplay and strategic performance in tennis and other racket sports.
Technique Breakdown: Mastering Forehand and Backhand
Mastering forehand and backhand techniques relies on precise body positioning, grip, and swing mechanics tailored to each stroke's unique demands. The forehand typically emphasizes open stance and wrist acceleration for power, while the backhand requires strong core rotation and controlled follow-through for accuracy. Consistent practice of footwork, timing, and racket angle adjustments enhances stroke effectiveness and overall game performance.
Power and Precision: Forehand or Backhand Advantage?
Forehand strokes generally generate more power due to the natural biomechanics and stronger muscle groups involved, making them ideal for aggressive baseline play. Backhands, particularly one-handed techniques, offer superior precision and control, allowing for accurate placements and spin variations. Players often develop a strategic balance, using forehands to dominate rallies and backhands to execute precise shots in critical situations.
Common Mistakes in Forehand and Backhand Strokes
Common mistakes in forehand strokes include improper grip, leading to reduced control and power, and poor body rotation, which limits stroke effectiveness. In backhand strokes, players often struggle with incorrect racquet positioning and lack of follow-through, causing weak and inaccurate shots. Consistent practice focusing on wrist stability and shoulder alignment helps correct these errors and enhances overall performance.
Training Drills for Stronger Forehand and Backhand Skills
Training drills for stronger forehand and backhand skills include shadow swings, focusing on proper grip and body rotation to enhance muscle memory. Incorporating multi-ball drills improves footwork and timing, enabling players to react quickly and maintain powerful strokes under pressure. Consistent practice with resistance bands or weighted racquets builds arm strength and endurance, crucial for sustained performance during matches.
When to Use Forehand vs Backhand in a Match
The forehand is most effective for powerful, aggressive shots on the dominant side, ideal for controlling rallies and dictating pace during baseline exchanges. The backhand is crucial for reaching wide balls, handling defensive play, and executing precise angles when the forehand is out of position. Choosing between forehand and backhand depends on ball placement, player stance, and match strategy to maximize shot effectiveness and court coverage.
Tactical Strategies: Forehand and Backhand Placement
Forehand placement often targets wide angles to exploit an opponent's weaker backhand side, creating open court space and opportunities to dictate play. Backhand placement typically emphasizes consistency and depth, aiming to neutralize aggressive shots and force errors. Effective tactical strategies integrate precise forehand attacks with reliable backhand defense to maintain control during rallies.
Forehand vs Backhand: Injury Risks and Prevention
Forehand strokes in tennis typically involve more natural body movement, reducing the risk of injuries such as tennis elbow compared to backhand strokes, which often place extra strain on the wrist and elbow. Strengthening forearm muscles and maintaining proper technique are crucial for minimizing injury risks during both forehand and backhand shots. Preventative measures include targeted exercises, adequate warm-ups, and using equipment like shock-absorbing grips to protect against repetitive strain injuries.
Equipment Choices: Enhancing Forehand and Backhand Performance
Selecting the appropriate racket for forehand and backhand shots significantly influences stroke effectiveness, with factors such as grip size, string tension, and racket weight tailored to enhance control and power. Players often prefer a lighter racket with a larger sweet spot for forehand strokes to maximize speed and spin, while a slightly heavier racket may provide stability and precision during backhand swings. Customizing string type and tension further optimizes responsiveness, allowing athletes to adapt their equipment to their specific biomechanical strengths in both forehand and backhand techniques.
Pro Player Analysis: Forehand and Backhand Best Practices
Pro players consistently demonstrate that a powerful, well-timed forehand generates higher winners and aggressive point construction, emphasized by strong racket head speed and optimal body rotation. Backhand strokes, whether one-handed or two-handed, prioritize precision, control, and versatility, allowing for effective defensive play and seamless transition to offense. Detailed analysis shows top athletes integrate footwork, split-step timing, and grip adjustments to maximize the efficiency and consistency of both forehand and backhand techniques.
forehand vs backhand Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com