Social pets often thrive in environments that embrace collectivism, where group harmony and shared responsibilities enhance their wellbeing and social interactions. In contrast, individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and independence, which may lead some pets to seek solitude or personalized care routines. Understanding the balance between collectivist social structures and individualistic tendencies helps optimize the companionship and care provided to social pets.
Table of Comparison
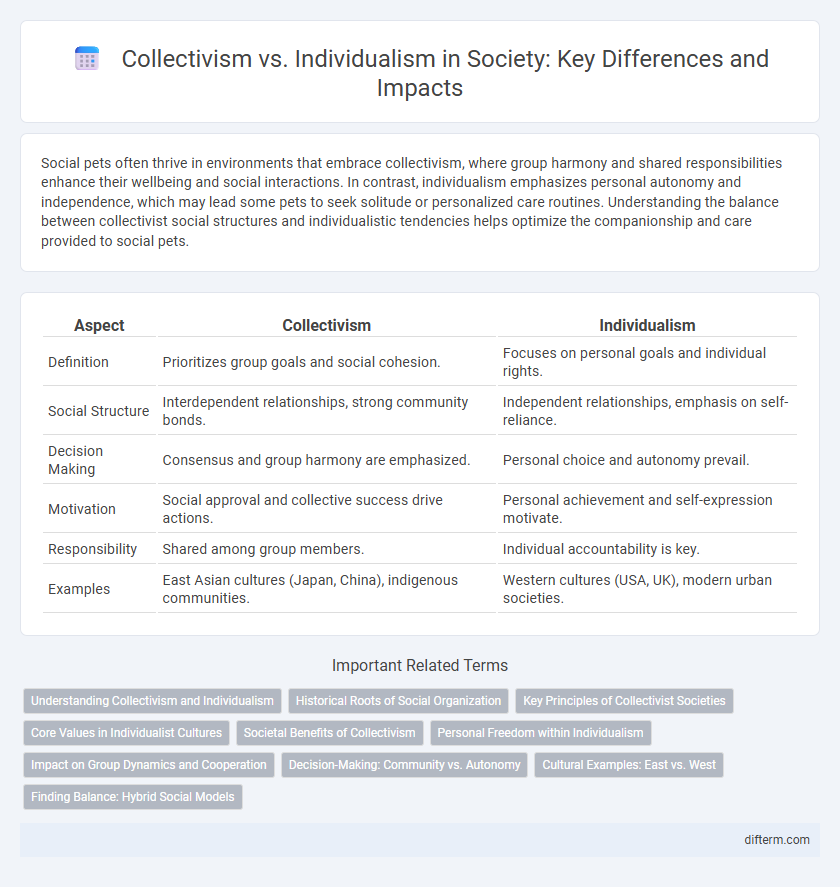
| Aspect | Collectivism | Individualism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prioritizes group goals and social cohesion. | Focuses on personal goals and individual rights. |
| Social Structure | Interdependent relationships, strong community bonds. | Independent relationships, emphasis on self-reliance. |
| Decision Making | Consensus and group harmony are emphasized. | Personal choice and autonomy prevail. |
| Motivation | Social approval and collective success drive actions. | Personal achievement and self-expression motivate. |
| Responsibility | Shared among group members. | Individual accountability is key. |
| Examples | East Asian cultures (Japan, China), indigenous communities. | Western cultures (USA, UK), modern urban societies. |
Understanding Collectivism and Individualism
Collectivism prioritizes group goals, social harmony, and interconnectedness, emphasizing the importance of community and shared responsibilities. Individualism centers on personal autonomy, self-expression, and individual rights, promoting independence and unique identity. Understanding these cultural orientations helps in analyzing social behaviors, communication styles, and societal structures across different cultures.
Historical Roots of Social Organization
Collectivism has deep historical roots in agricultural and tribal societies where survival depended on group cooperation and shared resources, reinforcing social bonds and mutual dependence. Individualism emerged prominently during the Enlightenment and Industrial Revolution, emphasizing personal freedom, self-reliance, and individual rights as societies transitioned toward urbanization and market economies. The historical evolution of social organization reflects a shift from community-centric norms to values prioritizing personal autonomy and individual achievement.
Key Principles of Collectivist Societies
Collectivist societies emphasize group harmony, interdependence, and social cohesion, where individuals prioritize communal goals over personal ambitions. Key principles include shared responsibility, strong family ties, and the importance of maintaining social roles and traditions to ensure collective well-being. These societies often foster cooperation, mutual support, and a sense of belonging that strengthens community resilience and identity.
Core Values in Individualist Cultures
Individualist cultures prioritize core values such as personal autonomy, self-reliance, and individual rights, emphasizing the importance of personal achievement and freedom. These societies encourage independent decision-making and value uniqueness, promoting a sense of identity derived from personal goals rather than group affiliation. The focus on self-expression and privacy reflects the central role that individualism plays in shaping social norms and interpersonal relationships.
Societal Benefits of Collectivism
Collectivism fosters social cohesion by emphasizing shared goals and mutual support, which enhances community resilience and reduces socioeconomic disparities. Societies with collectivist values often experience lower crime rates and improved public health outcomes due to stronger social networks and cooperation. This communal approach promotes resource sharing and collaborative problem-solving, leading to sustainable development and overall societal well-being.
Personal Freedom within Individualism
Personal freedom within individualism emphasizes autonomy and the right to pursue personal goals without undue interference from the collective or state. It fosters self-expression and accountability, encouraging innovation, creativity, and diverse perspectives. This principle supports individual rights as fundamental, influencing social policies that protect personal choice in areas like speech, lifestyle, and economic activity.
Impact on Group Dynamics and Cooperation
Collectivism fosters strong group cohesion and prioritizes shared goals, enhancing cooperation and trust among members. Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, which can lead to diverse perspectives but may challenge group consensus. The balance between these cultural orientations significantly shapes communication patterns, conflict resolution, and collaborative problem-solving within a group.
Decision-Making: Community vs. Autonomy
Collectivist societies prioritize community-driven decision-making, where group consensus and social harmony guide outcomes, emphasizing shared responsibility and collective well-being. In contrast, individualist cultures value personal autonomy, encouraging decisions based on individual preferences, self-interest, and independent judgment. These differences affect leadership styles, conflict resolution, and organizational dynamics, shaping how choices are made and implemented in social and professional contexts.
Cultural Examples: East vs. West
East Asian cultures such as Japan, China, and Korea emphasize collectivism, prioritizing group harmony, social roles, and community goals over individual desires. Western societies, including the United States and many European countries, promote individualism, valuing personal freedom, self-expression, and individual rights. These cultural orientations influence behavior, communication styles, and societal structures, reflecting deep-rooted philosophical traditions like Confucianism in the East and Enlightenment ideals in the West.
Finding Balance: Hybrid Social Models
Hybrid social models blend collectivism's emphasis on community support with individualism's focus on personal freedom, creating adaptable frameworks for diverse societies. These models prioritize cooperative networks alongside individual rights to foster social cohesion and innovation simultaneously. Emerging research highlights how balanced approaches enhance social resilience, economic stability, and cultural diversity in globalized contexts.
collectivism vs individualism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com