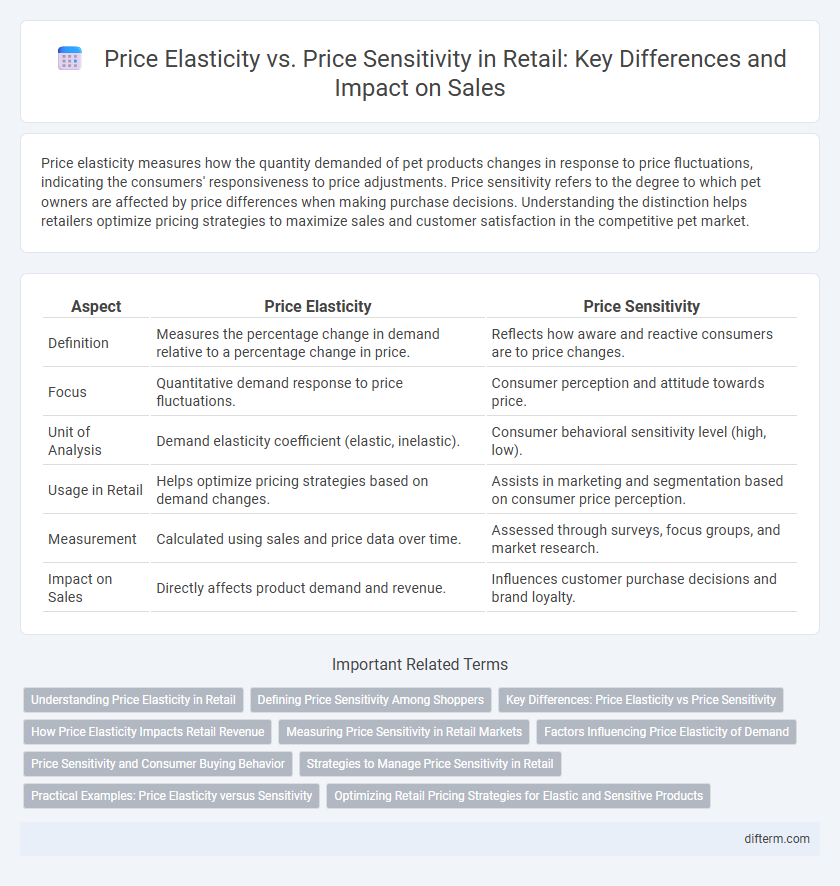
Price elasticity measures how the quantity demanded of pet products changes in response to price fluctuations, indicating the consumers' responsiveness to price adjustments. Price sensitivity refers to the degree to which pet owners are affected by price differences when making purchase decisions. Understanding the distinction helps retailers optimize pricing strategies to maximize sales and customer satisfaction in the competitive pet market.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Price Elasticity | Price Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures the percentage change in demand relative to a percentage change in price. | Reflects how aware and reactive consumers are to price changes. |
| Focus | Quantitative demand response to price fluctuations. | Consumer perception and attitude towards price. |
| Unit of Analysis | Demand elasticity coefficient (elastic, inelastic). | Consumer behavioral sensitivity level (high, low). |
| Usage in Retail | Helps optimize pricing strategies based on demand changes. | Assists in marketing and segmentation based on consumer price perception. |
| Measurement | Calculated using sales and price data over time. | Assessed through surveys, focus groups, and market research. |
| Impact on Sales | Directly affects product demand and revenue. | Influences customer purchase decisions and brand loyalty. |
Understanding Price Elasticity in Retail
Price elasticity in retail measures how consumer demand for products changes in response to price fluctuations, providing critical insights for pricing strategies. Unlike price sensitivity, which broadly captures consumer reactions to price changes, price elasticity quantifies this relationship using precise metrics such as the elasticity coefficient. Retailers leverage price elasticity data to optimize pricing, maximize revenue, and anticipate market trends effectively.
Defining Price Sensitivity Among Shoppers
Price sensitivity among shoppers refers to the degree to which consumers alter their purchasing behavior in response to price changes, reflecting their willingness to pay different prices. Unlike price elasticity, which measures the percentage change in quantity demanded relative to price changes at a market level, price sensitivity emphasizes individual consumer responses and perceptions of value. Retailers analyze price sensitivity to optimize pricing strategies, improve promotions, and tailor offers that resonate with target segments.
Key Differences: Price Elasticity vs Price Sensitivity
Price elasticity measures the percentage change in quantity demanded relative to price changes, indicating how demand varies with price fluctuations in retail products. Price sensitivity refers to consumer responsiveness to price changes, capturing the subjective perception of price impact on purchasing decisions. Key differences include that price elasticity quantifies demand variability through economic formulas, while price sensitivity reflects behavioral tendencies influenced by psychological and situational factors in retail markets.
How Price Elasticity Impacts Retail Revenue
Price elasticity measures how consumer demand for retail products changes in response to price variations, directly influencing revenue generation. High price elasticity means small price adjustments lead to significant shifts in sales volume, requiring retailers to carefully optimize pricing strategies to maximize profits. Understanding price sensitivity helps retailers predict customer reactions and balance competitive pricing with sustainable revenue growth.
Measuring Price Sensitivity in Retail Markets
Measuring price sensitivity in retail markets involves analyzing consumer responses to changes in product prices, often through demand elasticity metrics such as price elasticity of demand, which quantifies the percentage change in quantity demanded relative to a price change. Retailers utilize data from sales patterns, competitor pricing, and consumer surveys to identify price thresholds that significantly affect purchase behavior. Leveraging advanced analytics and predictive models helps optimize pricing strategies to balance profitability and volume by accurately capturing variations in price sensitivity across different customer segments.
Factors Influencing Price Elasticity of Demand
Price elasticity of demand in retail is influenced by factors such as availability of substitutes, necessity level of the product, and proportion of income spent on the item. Products with many alternatives typically exhibit higher price elasticity, causing demand to fluctuate significantly with price changes. Essential goods and items representing a small fraction of consumer income tend to show lower elasticity, resulting in more stable demand despite price variations.
Price Sensitivity and Consumer Buying Behavior
Price sensitivity in retail reflects how changes in product prices influence consumer buying behavior, with highly price-sensitive customers likely to reduce purchases or switch brands when prices rise. Unlike price elasticity, which measures the percentage change in quantity demanded relative to price changes, price sensitivity captures the psychological and emotional factors impacting purchasing decisions. Understanding consumer price sensitivity enables retailers to optimize pricing strategies, promotions, and product positioning to maximize sales and customer loyalty.
Strategies to Manage Price Sensitivity in Retail
Retailers can manage price sensitivity by implementing dynamic pricing strategies that adjust prices based on real-time demand and competitor actions. Personalized promotions and loyalty programs enhance perceived value, reducing consumers' sensitivity to price changes. Leveraging data analytics enables accurate identification of price elasticity, allowing retailers to optimize pricing without sacrificing sales volume.
Practical Examples: Price Elasticity versus Sensitivity
Price elasticity measures how much the quantity demanded of a product changes in response to a price change, such as a 10% price drop leading to a 20% increase in sales of seasonal clothing. Price sensitivity reflects consumers' willingness to pay varying prices based on perceived value, seen when shoppers choose premium brands during holiday sales despite higher costs. In retail, understanding price elasticity helps optimize pricing strategies, while gauging price sensitivity aids in tailoring promotions to customer segments.
Optimizing Retail Pricing Strategies for Elastic and Sensitive Products
Retail pricing strategies require a deep understanding of price elasticity and price sensitivity to optimize revenue and enhance customer satisfaction. Price elasticity measures how much demand changes in response to price adjustments, while price sensitivity reflects how consumers perceive price changes based on personal value. Tailoring pricing tactics for elastic products involves small price shifts to maximize sales volume, whereas sensitive products benefit from careful pricing to maintain perceived value without deterring buyers.
Price elasticity vs Price sensitivity Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com