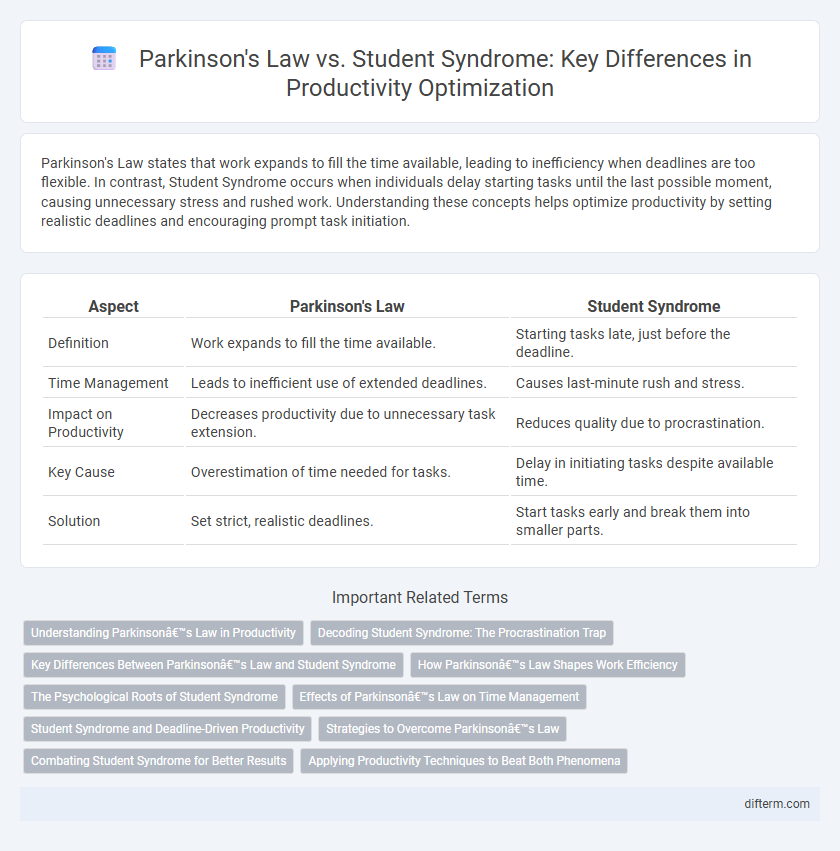
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, leading to inefficiency when deadlines are too flexible. In contrast, Student Syndrome occurs when individuals delay starting tasks until the last possible moment, causing unnecessary stress and rushed work. Understanding these concepts helps optimize productivity by setting realistic deadlines and encouraging prompt task initiation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Parkinson's Law | Student Syndrome |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Work expands to fill the time available. | Starting tasks late, just before the deadline. |
| Time Management | Leads to inefficient use of extended deadlines. | Causes last-minute rush and stress. |
| Impact on Productivity | Decreases productivity due to unnecessary task extension. | Reduces quality due to procrastination. |
| Key Cause | Overestimation of time needed for tasks. | Delay in initiating tasks despite available time. |
| Solution | Set strict, realistic deadlines. | Start tasks early and break them into smaller parts. |
Understanding Parkinson’s Law in Productivity
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, leading to inefficiencies and elongated deadlines. In contrast, Student Syndrome occurs when tasks are delayed until the last possible moment, resulting in rushed and subpar outcomes. Understanding Parkinson's Law helps optimize productivity by encouraging setting tighter, realistic deadlines to prevent unnecessary time consumption and improve time management.
Decoding Student Syndrome: The Procrastination Trap
Student Syndrome refers to the tendency to delay task initiation until the last possible moment, driven by a false sense of ample time that mirrors Parkinson's Law, which states work expands to fill the time available. This procrastination trap impairs productivity by compressing work into a stressful deadline crunch, resulting in rushed output and diminished quality. Understanding this cognitive bias helps in implementing time buffers and structured schedules to counteract ineffective time management and boost consistent productivity.
Key Differences Between Parkinson’s Law and Student Syndrome
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, leading to extended task completion when deadlines are loose, while Student Syndrome describes the tendency to delay work until the last possible moment, resulting in last-minute rushes. The key difference lies in time management behavior: Parkinson's Law emphasizes inefficiency caused by unnecessarily stretched deadlines, whereas Student Syndrome highlights procrastination and delayed task initiation. Understanding these contrasting patterns can help improve productivity by setting strict deadlines to counter Parkinson's Law and encouraging early task engagement to overcome Student Syndrome.
How Parkinson’s Law Shapes Work Efficiency
Parkinson's Law, which states that work expands to fill the time available, significantly influences work efficiency by encouraging time-bound task completion and reducing procrastination. Unlike Student Syndrome, where tasks are delayed until the last possible moment, Parkinson's Law promotes setting strict deadlines to optimize focus and streamline productivity. Understanding this principle enables individuals to allocate appropriate timeframes, improving workflow management and minimizing inefficiencies.
The Psychological Roots of Student Syndrome
Student Syndrome arises from procrastination fueled by the perception of ample time, causing individuals to delay task initiation until urgency peaks. The psychological roots of this behavior are linked to anxiety and motivation patterns, where the avoidance of early effort reduces immediate stress but ultimately hampers productivity. Understanding this syndrome highlights the contrast with Parkinson's Law, which states that work expands to fill the available time, revealing how time perception influences task management and completion.
Effects of Parkinson’s Law on Time Management
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, often leading to inefficient time use and procrastination. This results in tasks taking longer than necessary, reducing overall productivity and causing poor time management. Understanding this phenomenon helps individuals set stricter deadlines and improve focus to maximize efficiency.
Student Syndrome and Deadline-Driven Productivity
Student Syndrome describes the tendency to delay task initiation until the last possible moment before a deadline, resulting in heightened stress but often increased focus during the crunch period. This behavior contrasts with Parkinson's Law, which states that work expands to fill the time available, emphasizing how fixed deadlines drive urgency and productivity. Deadline-driven productivity leverages Student Syndrome by using tight deadlines to stimulate intense bursts of work, maximizing efficiency within limited time frames.
Strategies to Overcome Parkinson’s Law
Setting shorter, well-defined deadlines effectively counters Parkinson's Law by creating a sense of urgency that prevents tasks from dragging on unnecessarily. Breaking large projects into smaller, manageable chunks with specific goals enhances focus and accelerates completion, optimizing time use. Utilizing tools like time tracking and prioritization matrices helps maintain consistent productivity and reduces procrastination inherent in Parkinson's Law.
Combating Student Syndrome for Better Results
Combating Student Syndrome requires breaking tasks into smaller, manageable chunks with clearly defined deadlines to prevent last-minute rush and improve productivity. Implementing time-blocking techniques and setting intermediate milestones helps maintain consistent progress and reduces procrastination. Encouraging proactive planning and frequent self-assessment ensures timely task completion and better overall results.
Applying Productivity Techniques to Beat Both Phenomena
Applying productivity techniques like time blocking and setting clear deadlines combats Parkinson's Law by preventing tasks from expanding to fill available time, while breaking projects into smaller milestones helps mitigate Student Syndrome by encouraging steady progress before the final deadline. Techniques such as the Pomodoro Technique foster focused work intervals, enhancing concentration and reducing procrastination. Using tools like task prioritization frameworks ensures efficient workflow management, effectively beating both Parkinson's Law and Student Syndrome in productivity contexts.
parkinson’s law vs student syndrome Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com