Monthly goals create focused, achievable targets that drive consistent progress and maintain motivation through short-term accountability. Quarterly goals provide a broader perspective, enabling strategic planning and adjustments based on cumulative performance over time. Balancing monthly and quarterly goals enhances productivity by aligning immediate actions with long-term objectives.
Table of Comparison
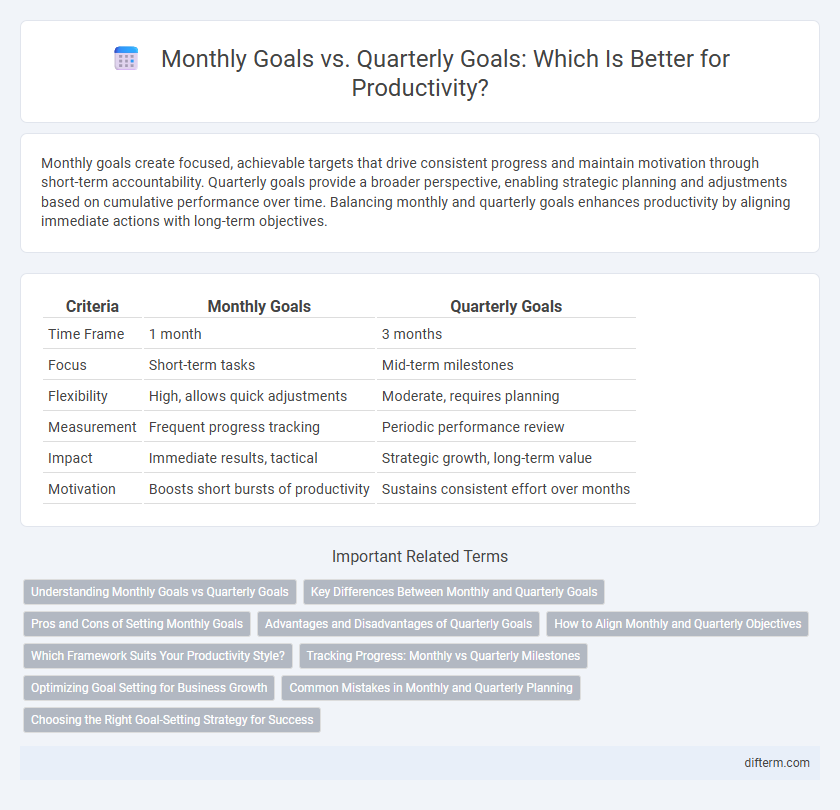
| Criteria | Monthly Goals | Quarterly Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Time Frame | 1 month | 3 months |
| Focus | Short-term tasks | Mid-term milestones |
| Flexibility | High, allows quick adjustments | Moderate, requires planning |
| Measurement | Frequent progress tracking | Periodic performance review |
| Impact | Immediate results, tactical | Strategic growth, long-term value |
| Motivation | Boosts short bursts of productivity | Sustains consistent effort over months |
Understanding Monthly Goals vs Quarterly Goals
Monthly goals provide specific, actionable targets that drive short-term productivity and allow for quick adjustments, while quarterly goals offer a broader perspective to align with long-term business priorities and strategic planning. Understanding monthly goals helps maintain consistent progress and immediate focus, whereas quarterly goals enable tracking of overarching achievements and resource allocation. Balancing both ensures steady momentum while adapting to evolving priorities within a productive workflow.
Key Differences Between Monthly and Quarterly Goals
Monthly goals offer short-term focus and allow quick adjustments to productivity strategies, enhancing immediate task completion rates. Quarterly goals provide a broader perspective, supporting long-term planning and alignment with strategic objectives for sustained growth. Key differences include time frame, flexibility, and impact on motivation, where monthly goals drive frequent momentum and quarterly goals foster comprehensive progress tracking.
Pros and Cons of Setting Monthly Goals
Setting monthly goals enhances focus by creating short-term targets that increase motivation and allow for swift adjustments. They promote consistent progress and accountability but may lead to a narrower perspective, potentially overlooking long-term objectives. Monthly goals can also induce pressure and frequent review demands, which might disrupt productivity if not managed effectively.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quarterly Goals
Quarterly goals provide a broader timeframe that encourages strategic thinking and allows for adjustment based on long-term trends, enhancing overall productivity alignment with company objectives. However, the extended period can lead to reduced urgency and delayed feedback, making it challenging to maintain consistent motivation and timely course corrections. Balancing quarterly goals with shorter benchmarks is essential to optimize progress tracking and sustained engagement.
How to Align Monthly and Quarterly Objectives
Aligning monthly and quarterly goals requires breaking down overarching quarterly objectives into specific, measurable monthly targets that drive progress incrementally. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) for each month, ensuring they directly contribute to achieving the larger quarterly outcomes and enable continuous performance tracking. Regularly review and adjust monthly plans based on progress data to maintain alignment and enhance productivity across both timeframes.
Which Framework Suits Your Productivity Style?
Monthly goals allow for quick adjustments and detailed tracking, ideal for individuals who thrive on frequent feedback and incremental progress. Quarterly goals provide a broader perspective, benefiting those who prefer strategic planning and longer-term focus without feeling overwhelmed by daily tasks. Choosing between monthly and quarterly frameworks depends on your productivity style, whether you value agility and constant momentum or sustained, big-picture growth.
Tracking Progress: Monthly vs Quarterly Milestones
Tracking progress through monthly goals enables more frequent assessments and timely adjustments, enhancing short-term productivity and immediate focus. Quarterly milestones provide a broader perspective, helping align tasks with long-term objectives and offering a comprehensive evaluation of overall performance. Combining both monthly and quarterly tracking methods ensures balanced goal setting, continuous motivation, and effective resource allocation.
Optimizing Goal Setting for Business Growth
Monthly goals provide clear, actionable milestones that drive immediate productivity and enable timely adjustments, while quarterly goals offer a broader strategic focus that aligns with long-term business objectives. Balancing these time frames enhances goal-setting by ensuring steady progress without losing sight of overarching growth targets. Integrating both cycles allows businesses to optimize resource allocation and measure performance effectively, fostering sustained growth and adaptability.
Common Mistakes in Monthly and Quarterly Planning
Setting overly ambitious monthly goals often leads to burnout and missed deadlines, while vague quarterly goals can result in lack of clear direction and measurable progress. Common mistakes include neglecting to align monthly tasks with broader quarterly objectives and failing to regularly review and adjust plans based on performance data. Effective productivity requires balancing short-term focus with long-term vision, ensuring goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Choosing the Right Goal-Setting Strategy for Success
Monthly goals provide short-term focus and quick feedback, enabling rapid adjustments that keep productivity aligned with immediate priorities. Quarterly goals encourage strategic thinking and long-term planning, fostering sustained progress toward larger objectives. Selecting the right goal-setting strategy depends on balancing the need for flexibility with the desire for comprehensive achievement tracking.
Monthly goals vs Quarterly goals Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com