Prioritizing tasks using the Eat the Frog method ensures tackling the most challenging or important task first, reducing procrastination and boosting momentum. The Pareto Principle complements this by highlighting that 20% of efforts often generate 80% of results, allowing a focus on high-impact activities. Combining both approaches maximizes productivity by addressing key tasks early and concentrating on actions that yield the greatest outcomes.
Table of Comparison
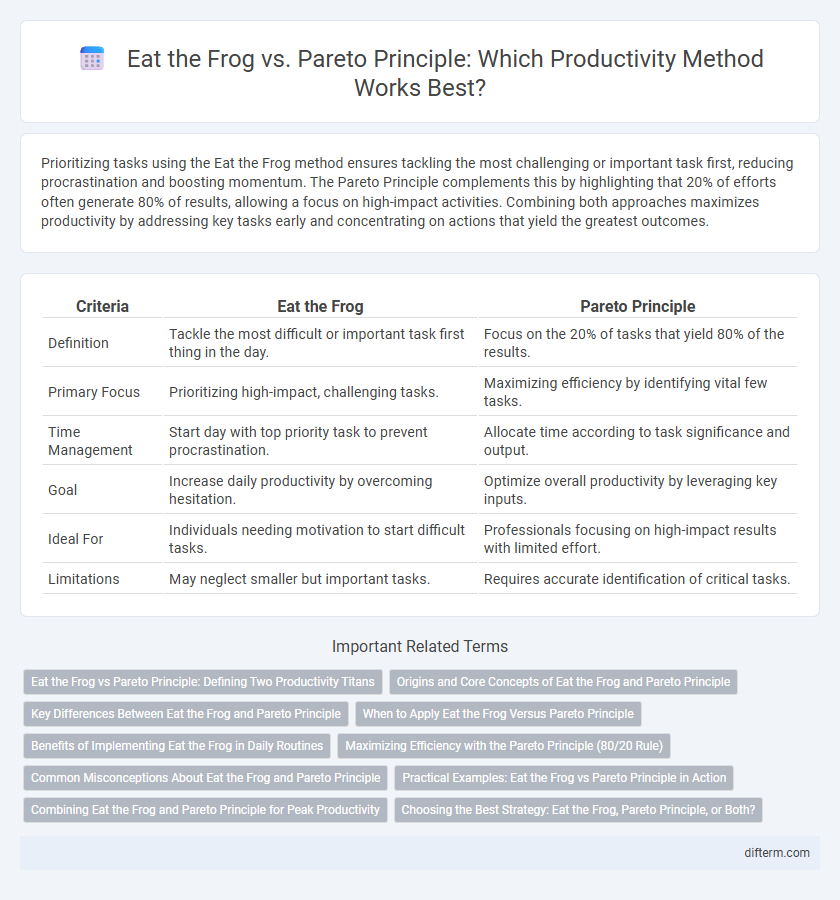
| Criteria | Eat the Frog | Pareto Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tackle the most difficult or important task first thing in the day. | Focus on the 20% of tasks that yield 80% of the results. |
| Primary Focus | Prioritizing high-impact, challenging tasks. | Maximizing efficiency by identifying vital few tasks. |
| Time Management | Start day with top priority task to prevent procrastination. | Allocate time according to task significance and output. |
| Goal | Increase daily productivity by overcoming hesitation. | Optimize overall productivity by leveraging key inputs. |
| Ideal For | Individuals needing motivation to start difficult tasks. | Professionals focusing on high-impact results with limited effort. |
| Limitations | May neglect smaller but important tasks. | Requires accurate identification of critical tasks. |
Eat the Frog vs Pareto Principle: Defining Two Productivity Titans
Eat the Frog emphasizes tackling the most challenging task first to drive significant momentum, while the Pareto Principle advocates focusing on the 20% of efforts that yield 80% of results for maximum efficiency. Both productivity strategies prioritize high-impact activities but differ in execution; Eat the Frog targets immediate action on daunting tasks, whereas Pareto guides resource allocation based on outcome analysis. Integrating these approaches can amplify workflow optimization by combining task prioritization with outcome-based focus.
Origins and Core Concepts of Eat the Frog and Pareto Principle
Eat the Frog, popularized by Brian Tracy, is based on Mark Twain's advice to tackle the most challenging task first to boost productivity. The Pareto Principle, formulated by Vilfredo Pareto, asserts that 80% of results come from 20% of efforts, emphasizing prioritization of high-impact tasks. Both concepts originate from different fields but converge on optimizing time management by focusing on critical activities that yield the greatest outcomes.
Key Differences Between Eat the Frog and Pareto Principle
Eat the Frog emphasizes tackling the most challenging and important task first each day, maximizing focus and overcoming procrastination. The Pareto Principle highlights that 80% of results come from 20% of efforts, encouraging prioritization of high-impact tasks but not necessarily in chronological order. Unlike Eat the Frog's task sequencing, Pareto focuses on identifying and allocating time to the most productive activities overall.
When to Apply Eat the Frog Versus Pareto Principle
Eat the Frog is most effective when tackling high-priority, challenging tasks that significantly impact daily productivity, especially at the start of the day. The Pareto Principle excels in broader time management, helping identify the 20% of activities that yield 80% of results for strategic resource allocation. Applying Eat the Frog suits immediate action on critical tasks, while the Pareto Principle guides long-term prioritization and productivity improvements.
Benefits of Implementing Eat the Frog in Daily Routines
Implementing Eat the Frog in daily routines enhances productivity by prioritizing the most challenging tasks first, reducing procrastination and building momentum throughout the day. This method fosters a sense of accomplishment early, boosting motivation and focus for subsequent activities. Unlike the Pareto Principle's broad focus on the 20% of tasks yielding 80% of results, Eat the Frog delivers immediate clarity and actionable steps to tackle high-impact tasks effectively.
Maximizing Efficiency with the Pareto Principle (80/20 Rule)
Focusing on the Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of results come from 20% of efforts, maximizes productivity by identifying and prioritizing high-impact tasks. Unlike the Eat the Frog method that emphasizes tackling the hardest task first, the 80/20 rule directs attention to activities that yield the greatest returns, ensuring efficient use of time and resources. Leveraging this principle enables individuals to streamline efforts, reduce wasted energy, and significantly boost overall efficiency in both personal and professional settings.
Common Misconceptions About Eat the Frog and Pareto Principle
Many people mistakenly believe Eat the Frog requires tackling the hardest task first every time, overlooking its flexibility in prioritizing based on impact. The Pareto Principle is often misunderstood as a rigid 80/20 rule, while it actually highlights that a small percentage of efforts typically yield most results but may vary in exact ratios. Both concepts emphasize prioritization but differ: Eat the Frog focuses on sequencing tasks to overcome procrastination, whereas Pareto identifies key tasks driving most outcomes.
Practical Examples: Eat the Frog vs Pareto Principle in Action
Prioritizing tasks by "eating the frog" means tackling the most challenging or important task first to boost productivity and reduce procrastination. The Pareto Principle, or 80/20 rule, focuses on identifying and completing the 20% of tasks that yield 80% of the results, optimizing effort for maximum impact. For example, a project manager using the frog approach might start the day by resolving the biggest project hurdle, while applying Pareto would involve allocating time to critical client meetings and key deliverables that drive most project success.
Combining Eat the Frog and Pareto Principle for Peak Productivity
Combining Eat the Frog and the Pareto Principle maximizes productivity by prioritizing the most impactful tasks first, addressing the critical 20% that drives 80% of results. Starting the day by tackling the biggest, most challenging task (the frog) clears mental clutter and boosts momentum for smaller, high-value activities. This blend ensures focused effort on essential goals, reducing procrastination and amplifying overall efficiency.
Choosing the Best Strategy: Eat the Frog, Pareto Principle, or Both?
Choosing the best productivity strategy depends on task prioritization and desired outcomes. The Eat the Frog method emphasizes tackling the most challenging or important task first to boost momentum and reduce procrastination, while the Pareto Principle focuses on identifying the 20% of tasks that yield 80% of results for maximum efficiency. Combining both approaches allows optimal focus by addressing critical tasks early while ensuring efforts target high-impact activities, enhancing overall productivity.
Eat the frog vs Pareto principle Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com