Realpolitik emphasizes pragmatic and strategic decision-making based on power dynamics and national interests, often prioritizing practical outcomes over moral considerations. Idealism advocates for foreign policies grounded in ethical principles and international cooperation, aiming to promote justice and human rights globally. The tension between realpolitik and idealism shapes the complex landscape of global diplomacy and policy formulation.
Table of Comparison
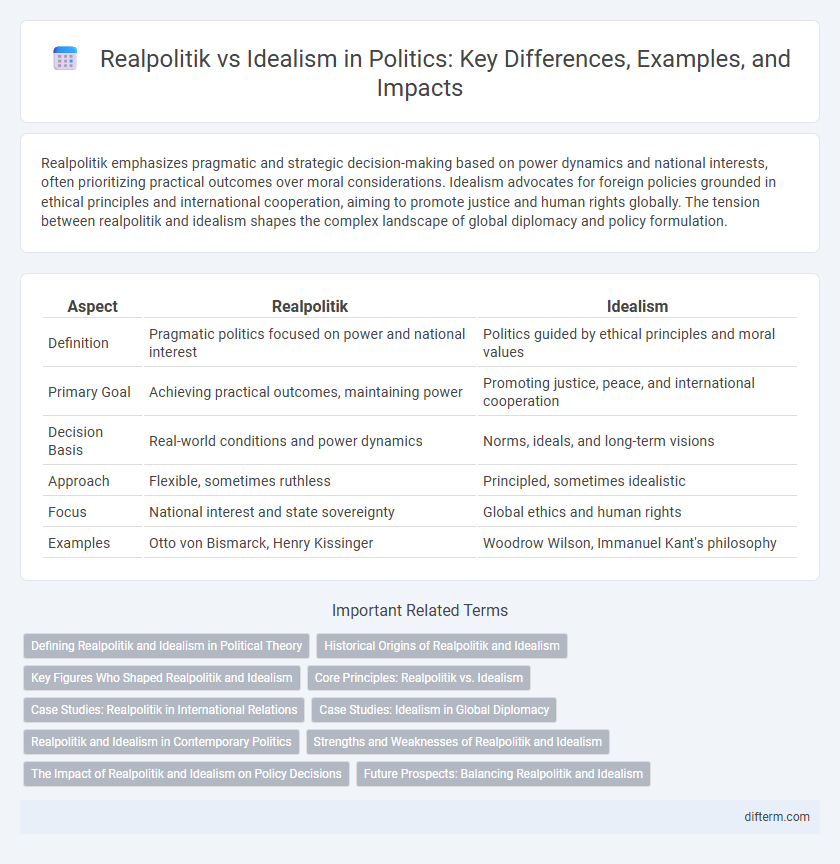
| Aspect | Realpolitik | Idealism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pragmatic politics focused on power and national interest | Politics guided by ethical principles and moral values |
| Primary Goal | Achieving practical outcomes, maintaining power | Promoting justice, peace, and international cooperation |
| Decision Basis | Real-world conditions and power dynamics | Norms, ideals, and long-term visions |
| Approach | Flexible, sometimes ruthless | Principled, sometimes idealistic |
| Focus | National interest and state sovereignty | Global ethics and human rights |
| Examples | Otto von Bismarck, Henry Kissinger | Woodrow Wilson, Immanuel Kant's philosophy |
Defining Realpolitik and Idealism in Political Theory
Realpolitik in political theory emphasizes pragmatic, power-centered decision-making driven by national interest and practical considerations rather than moral or ideological goals. Idealism advocates for politics guided by ethical principles, human rights, and the pursuit of justice, often prioritizing international cooperation and moral values over strategic gains. The contrast between Realpolitik and idealism shapes policy approaches in diplomacy, conflict resolution, and governance worldwide.
Historical Origins of Realpolitik and Idealism
The origins of realpolitik trace back to 19th-century Europe, particularly through the works of statesmen like Otto von Bismarck, who emphasized pragmatic power politics and state interests over ideology. Idealism in politics emerged earlier with Enlightenment thinkers such as Immanuel Kant, advocating for moral principles, international cooperation, and the promotion of human rights. These contrasting historical foundations reflect realpolitik's focus on practical statecraft versus idealism's emphasis on ethical values in global affairs.
Key Figures Who Shaped Realpolitik and Idealism
Otto von Bismarck exemplified Realpolitik through his pragmatic approach to unifying Germany by prioritizing power and practical interests over ideological goals. In contrast, Woodrow Wilson championed Idealism, advocating for democracy and international cooperation via the League of Nations to promote global peace. These figures significantly influenced political strategies by embodying the tension between practical power politics and principled idealism in modern statecraft.
Core Principles: Realpolitik vs. Idealism
Realpolitik emphasizes pragmatic and strategic decision-making based on national interest and power dynamics, often prioritizing stability and practical outcomes over moral considerations. Idealism advocates for policies guided by ethical values, justice, and the promotion of human rights, aiming for global cooperation and long-term peace. The core principles of Realpolitik prioritize realism and adaptability, while Idealism focuses on normative goals and principled diplomacy.
Case Studies: Realpolitik in International Relations
Realpolitik in international relations is exemplified by the 19th-century Concert of Europe, where major powers prioritized national interest and balance of power over ideological goals to maintain stability. The pragmatic diplomacy of Otto von Bismarck during German unification leveraged alliances and realpolitik tactics to consolidate power without pursuing broad ideological objectives. In contrast to idealism, which emphasizes moral principles, realpolitik emphasizes practical considerations such as security, economic advantage, and geopolitical influence in statecraft.
Case Studies: Idealism in Global Diplomacy
Idealism in global diplomacy emphasizes international cooperation, human rights, and ethical governance, as seen in the formation of the United Nations and the diplomatic efforts to establish the Paris Agreement on climate change. These case studies highlight how idealism fosters multilateralism, conflict resolution, and sustainable development despite challenges posed by competing national interests. The success of idealistic diplomacy often depends on the willingness of states to prioritize collective global benefits over short-term realpolitik strategies.
Realpolitik and Idealism in Contemporary Politics
Realpolitik dominates contemporary politics through pragmatic decision-making based on national interest, power dynamics, and strategic alliances, often prioritizing security and economic gains over moral considerations. Idealism persists in advocating for international cooperation, human rights, and ethical governance yet frequently faces challenges when geopolitical realities demand compromise. The tension between Realpolitik and Idealism shapes foreign policy frameworks, influencing diplomatic negotiations, conflict resolution, and global governance strategies worldwide.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Realpolitik and Idealism
Realpolitik emphasizes pragmatic, power-based decision-making, enabling swift and realistic responses to geopolitical complexities, but often sacrifices ethical considerations and long-term values. Idealism prioritizes moral principles and human rights, fostering international cooperation and promoting peace, yet it can lead to impractical policies and vulnerability to exploitation. Balancing Realpolitik's strategic strength with Idealism's ethical vision remains a persistent challenge in effective political leadership.
The Impact of Realpolitik and Idealism on Policy Decisions
Realpolitik prioritizes pragmatic, power-driven decisions that often emphasize national interests and security over moral or ideological considerations in policymaking. Idealism influences policy decisions by promoting values such as justice, human rights, and international cooperation, aiming for long-term global stability and ethical outcomes. The tension between Realpolitik and idealism shapes diplomatic strategies, where balancing pragmatic power dynamics with principled goals determines the effectiveness and ethical stance of national policies.
Future Prospects: Balancing Realpolitik and Idealism
Future prospects in politics hinge on integrating Realpolitik's pragmatic power dynamics with idealism's vision for ethical governance. Policymakers must navigate immediate strategic interests while fostering long-term goals of justice and human rights to ensure sustainable international relations. Balancing these approaches strengthens diplomatic resilience and advances global stability amid complex geopolitical challenges.
realpolitik vs idealism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com