Nationalism emphasizes prioritizing a nation's sovereignty, culture, and interests, often advocating strict immigration policies and economic protectionism to preserve identity and autonomy. Globalism promotes interconnectedness, supporting free trade, open borders, and international cooperation to address global challenges such as climate change and economic inequality. The tension between nationalism and globalism shapes political debates, influencing policies on security, economy, and cultural integration worldwide.
Table of Comparison
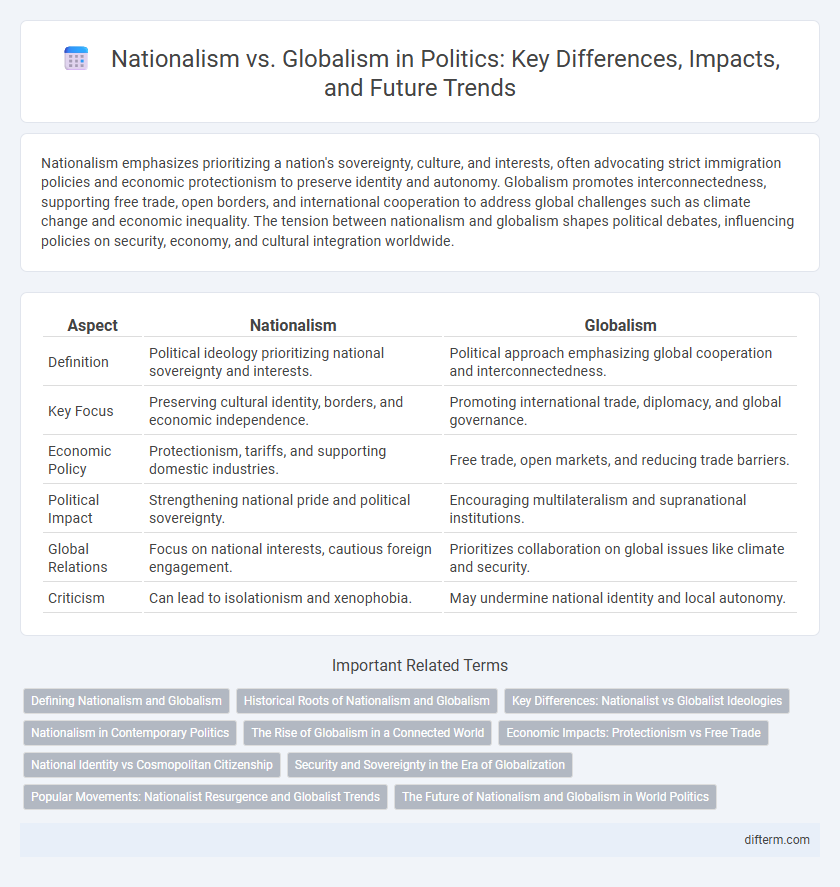
| Aspect | Nationalism | Globalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political ideology prioritizing national sovereignty and interests. | Political approach emphasizing global cooperation and interconnectedness. |
| Key Focus | Preserving cultural identity, borders, and economic independence. | Promoting international trade, diplomacy, and global governance. |
| Economic Policy | Protectionism, tariffs, and supporting domestic industries. | Free trade, open markets, and reducing trade barriers. |
| Political Impact | Strengthening national pride and political sovereignty. | Encouraging multilateralism and supranational institutions. |
| Global Relations | Focus on national interests, cautious foreign engagement. | Prioritizes collaboration on global issues like climate and security. |
| Criticism | Can lead to isolationism and xenophobia. | May undermine national identity and local autonomy. |
Defining Nationalism and Globalism
Nationalism emphasizes the sovereignty and interests of a specific nation, prioritizing cultural identity, economic independence, and political self-determination. Globalism advocates for interconnectedness, international cooperation, and the free exchange of goods, capital, and ideas across borders. The debate between nationalism and globalism centers on balancing national autonomy with global integration in political and economic policies.
Historical Roots of Nationalism and Globalism
Nationalism traces its origins to the 18th and 19th centuries, fueled by the Enlightenment and the rise of the nation-state concept in Europe. Globalism emerged after World War II, propelled by the formation of international institutions like the United Nations and economic bodies such as the International Monetary Fund and World Bank. These historical developments reflect contrasting responses to sovereignty, identity, and economic interdependence in global politics.
Key Differences: Nationalist vs Globalist Ideologies
Nationalist ideologies emphasize sovereignty, cultural identity, and prioritizing domestic interests, often advocating for strict immigration controls and protectionist economic policies. Globalist perspectives promote international cooperation, open borders, and free trade, emphasizing interconnectedness and collective problem-solving across nations. The core difference lies in nationalism's focus on preserving state autonomy versus globalism's aim to integrate economies and governance for shared benefits.
Nationalism in Contemporary Politics
Nationalism in contemporary politics emphasizes the prioritization of national sovereignty, cultural identity, and economic independence. Movements in Europe and Asia demonstrate a resurgence of nationalist rhetoric advocating stricter immigration controls and protectionist trade policies. Political parties leveraging nationalist sentiments often challenge global institutions and promote policies that assert state autonomy over international cooperation.
The Rise of Globalism in a Connected World
Globalism has surged as an influential force in politics, driven by technological advancements and the integration of economies worldwide. This interconnectedness fosters multinational cooperation, promoting shared policies on climate change, trade, and security. The rise of globalism challenges traditional nationalism by emphasizing collective progress over sovereign interests, reshaping international relations in the 21st century.
Economic Impacts: Protectionism vs Free Trade
Nationalism-driven economic policies often favor protectionism through tariffs and trade barriers to safeguard domestic industries, leading to reduced imports and potential short-term job preservation. Conversely, globalism supports free trade agreements that lower tariffs and increase market access, enhancing economic efficiency and consumer choice but sometimes causing domestic job displacement. The tension between these approaches influences economic growth, trade balances, and geopolitical relationships, with protectionism risking retaliatory measures and globalism promoting interdependence.
National Identity vs Cosmopolitan Citizenship
National identity emphasizes the shared history, culture, and values that bind a community or nation-state, fostering social cohesion and loyalty within defined borders. Cosmopolitan citizenship advocates for a global sense of belonging, transcending national boundaries to promote inclusivity, human rights, and cooperation across diverse populations. The tension between nationalism and globalism centers on balancing sovereign self-determination with universal responsibilities in an interconnected world.
Security and Sovereignty in the Era of Globalization
Nationalism emphasizes the protection of state sovereignty and prioritizes national security through strict border controls and independent defense policies, asserting the primacy of local governance over external influence. Globalism advocates for cooperative security frameworks and multilateral alliances to address transnational threats such as terrorism, cyberattacks, and climate change, promoting shared sovereignty for collective stability. The tension between these paradigms shapes current political debates on balancing national autonomy with international collaboration in safeguarding security.
Popular Movements: Nationalist Resurgence and Globalist Trends
Popular movements worldwide reveal a dynamic tension between nationalist resurgence and globalist trends, as grassroots groups increasingly demand sovereignty and cultural preservation amidst expanding international cooperation. Nationalist movements emphasize border security, economic protectionism, and national identity, while globalist trends advocate for transnational governance, free trade, and multicultural integration. This polarization impacts policy-making, electoral outcomes, and international relations, shaping the future of political landscapes with competing visions of sovereignty and globalization.
The Future of Nationalism and Globalism in World Politics
Nationalism will continue to influence state sovereignty and identity politics as countries prioritize domestic interests and cultural preservation. Globalism drives international cooperation, economic integration, and transnational policy frameworks to address shared challenges like climate change and security. The future of world politics depends on balancing national interests with global collaboration to ensure stability and sustainable development.
nationalism vs globalism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com