Choosing a pet often balances personal preference with ethical principles, where affection for certain animals may conflict with concerns about their welfare or environmental impact. Prioritizing principle over preference encourages adopting pets that align with responsible care and sustainability, such as rescued animals or species well-suited to the owner's lifestyle. This approach fosters a harmonious relationship that respects both the owner's desires and the broader ethical considerations of pet ownership.
Table of Comparison
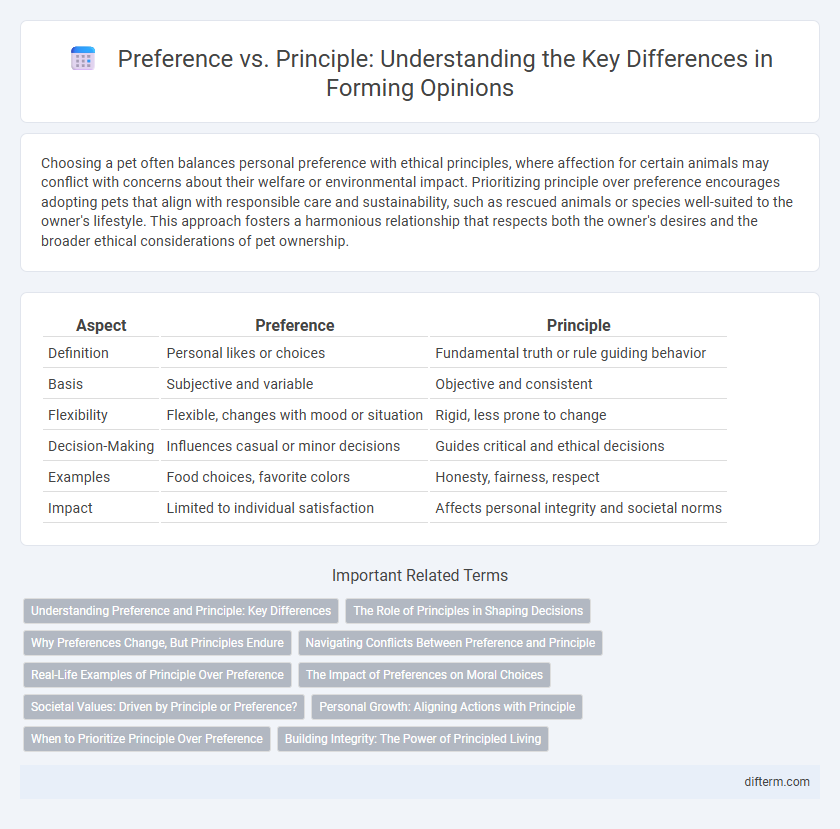
| Aspect | Preference | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal likes or choices | Fundamental truth or rule guiding behavior |
| Basis | Subjective and variable | Objective and consistent |
| Flexibility | Flexible, changes with mood or situation | Rigid, less prone to change |
| Decision-Making | Influences casual or minor decisions | Guides critical and ethical decisions |
| Examples | Food choices, favorite colors | Honesty, fairness, respect |
| Impact | Limited to individual satisfaction | Affects personal integrity and societal norms |
Understanding Preference and Principle: Key Differences
Understanding preference versus principle reveals key differences shaping decision-making processes. Preferences reflect individual desires influenced by personal tastes or circumstances, while principles represent core values or ethical standards guiding consistent behavior regardless of situation. Distinguishing between these concepts enhances clarity in evaluating choices and aligning actions with fundamental beliefs.
The Role of Principles in Shaping Decisions
Principles serve as foundational guides that anchor decision-making processes, ensuring consistency and integrity beyond fluctuating personal preferences. These core beliefs shape choices by providing a stable framework for evaluating options, particularly in complex or morally ambiguous situations. Prioritizing principles over preferences helps maintain ethical standards and fosters trustworthiness in both personal and professional contexts.
Why Preferences Change, But Principles Endure
Preferences often shift due to evolving experiences, changing environments, and new information influencing individual tastes and desires. Principles remain steadfast because they are rooted in core values and ethical frameworks that define a person's identity and guide consistent behavior. This stability in principles provides a reliable foundation amid the fluidity of personal preferences.
Navigating Conflicts Between Preference and Principle
Navigating conflicts between preference and principle requires prioritizing core values over personal desires to maintain integrity and consistency in decision-making. When preferences clash with established principles, grounding choices in ethical standards fosters trust and long-term respect. Balancing emotional inclinations with rational principles ensures disciplined actions that align with a coherent moral framework.
Real-Life Examples of Principle Over Preference
Choosing principle over preference often shapes profound real-life decisions, such as whistleblowers exposing corporate fraud despite personal risks, demonstrating unwavering commitment to ethical standards. In social movements, individuals prioritize justice and equality principles over comfort or social acceptance, profoundly impacting legal reforms and cultural shifts. These examples underscore how adhering to core values, rather than personal preferences, drives meaningful change and lasting integrity.
The Impact of Preferences on Moral Choices
Preferences shape moral choices by influencing the prioritization of values and outcomes, often leading individuals to favor decisions that align with their desires rather than universal ethical principles. This subjective impact can create variability in moral judgments, highlighting the tension between personal inclinations and objective moral standards. Understanding the role of preferences is essential for analyzing the complexity and diversity of ethical decision-making processes.
Societal Values: Driven by Principle or Preference?
Societal values shaped by principle provide a consistent moral framework that guides collective behavior and decision-making. Preference-based values tend to fluctuate with individual desires, risking fragmentation and undermining social cohesion. A principle-driven approach fosters long-term stability and shared understanding essential for harmonious communities.
Personal Growth: Aligning Actions with Principle
Personal growth thrives when actions consistently align with core principles, fostering integrity and self-awareness. Prioritizing principles over fleeting preferences cultivates resilience and long-term fulfillment. This alignment empowers individuals to navigate challenges with authenticity and purpose.
When to Prioritize Principle Over Preference
Prioritizing principle over preference ensures decisions align with core values and long-term integrity, preventing short-term desires from undermining ethical standards. In situations involving moral dilemmas or organizational policies, adhering to principle fosters trust and consistency, even when personal preferences conflict. Choosing principle solidifies a foundation of respect and accountability that transcends individual whims.
Building Integrity: The Power of Principled Living
Building integrity through principled living strengthens character by aligning actions with core values rather than fleeting preferences. Acting from principles fosters trust and consistency, creating a foundation for authentic relationships and long-term respect. Choosing principle over preference cultivates resilience and moral clarity in complex situations.
preference vs principle Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com