Opinions are personal beliefs shaped by individual experiences and open to change, while stereotypes are oversimplified, fixed ideas about a group that ignore individual differences. Forming opinions requires critical thinking and empathy, whereas relying on stereotypes perpetuates misunderstandings and biases. Challenging stereotypes allows for more nuanced and authentic perspectives, fostering mutual respect and deeper connections.
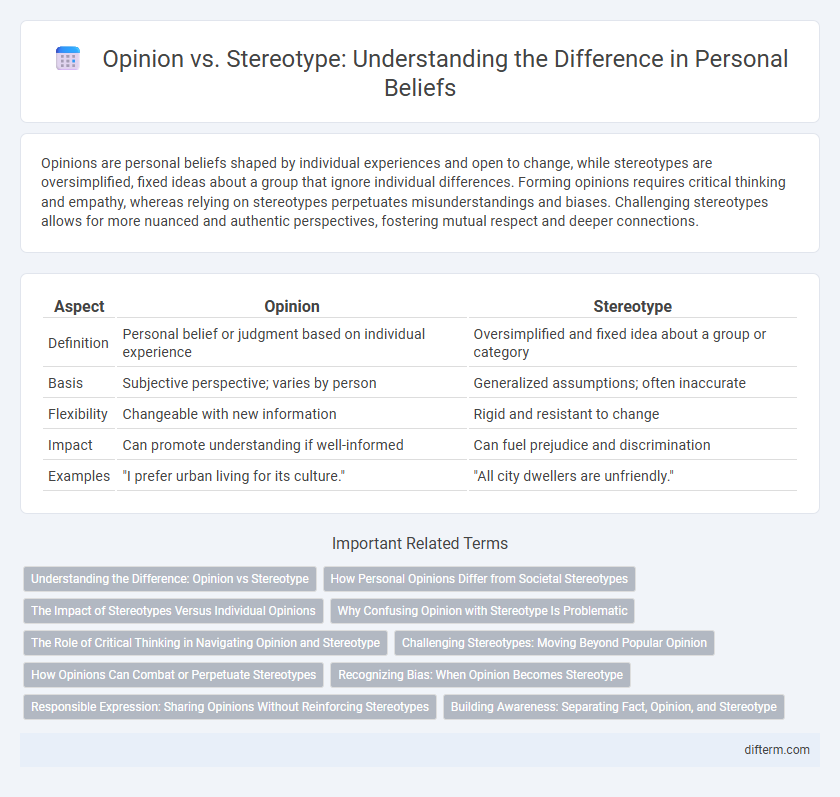
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Opinion | Stereotype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal belief or judgment based on individual experience | Oversimplified and fixed idea about a group or category |
| Basis | Subjective perspective; varies by person | Generalized assumptions; often inaccurate |
| Flexibility | Changeable with new information | Rigid and resistant to change |
| Impact | Can promote understanding if well-informed | Can fuel prejudice and discrimination |
| Examples | "I prefer urban living for its culture." | "All city dwellers are unfriendly." |
Understanding the Difference: Opinion vs Stereotype
Opinions are personal beliefs shaped by individual experiences and evidence, reflecting subjective viewpoints. Stereotypes are generalized and often oversimplified assumptions about groups, lacking nuanced understanding. Recognizing the difference fosters critical thinking and reduces prejudiced judgments in social interactions.
How Personal Opinions Differ from Societal Stereotypes
Personal opinions are subjective beliefs shaped by individual experiences and values, whereas societal stereotypes are widely held, oversimplified generalizations about groups. Unlike stereotypes, opinions allow for nuance and change based on new information or perspectives. Understanding the distinction helps promote critical thinking and reduces prejudice.
The Impact of Stereotypes Versus Individual Opinions
Stereotypes often lead to generalized and oversimplified judgments about groups, limiting personal understanding and fostering prejudice. Individual opinions, grounded in personal experience and critical thinking, allow for more nuanced and authentic perspectives that challenge stereotypes. The impact of stereotypes can reinforce social biases, whereas valuing individual opinions encourages empathy and promotes social harmony.
Why Confusing Opinion with Stereotype Is Problematic
Confusing opinion with stereotype undermines critical thinking by reinforcing unfounded generalizations instead of fostering nuanced understanding. Stereotypes often rely on oversimplified, biased assumptions that distort reality, whereas opinions should be based on evidence and individual judgment. This conflation perpetuates misinformation and social division, hindering constructive dialogue and informed decision-making.
The Role of Critical Thinking in Navigating Opinion and Stereotype
Critical thinking allows individuals to analyze opinions by evaluating evidence and reasoning rather than accepting stereotypes based on generalized beliefs. It fosters open-mindedness and reduces biases, enabling more accurate and nuanced judgments about social groups. Developing critical thinking skills strengthens the ability to differentiate between subjective viewpoints and unfair stereotypes, promoting informed decision-making and empathy.
Challenging Stereotypes: Moving Beyond Popular Opinion
Opinions reflect individual perspectives shaped by experience, while stereotypes are oversimplified ideas that ignore complexity and diversity. Challenging stereotypes requires critical thinking and exposure to diverse viewpoints to dismantle harmful generalizations. Moving beyond popular opinion fosters empathy and promotes a more nuanced understanding of people and cultures.
How Opinions Can Combat or Perpetuate Stereotypes
Opinions shaped by critical thinking and diverse experiences can effectively challenge stereotypes by promoting nuanced understanding and empathy. When opinions rely on generalized assumptions rather than factual evidence, they risk reinforcing harmful stereotypes and biases. Cultivating informed opinions through exposure to varied perspectives is key to dismantling stereotypical thinking and fostering social inclusivity.
Recognizing Bias: When Opinion Becomes Stereotype
Recognizing bias is crucial in distinguishing opinion from stereotype, as opinions are personal beliefs while stereotypes are oversimplified generalizations about groups. Opinion becomes stereotype when subjective views transform into rigid assumptions, often ignoring individual diversity and perpetuating prejudice. Understanding this transition helps challenge biases and promotes more nuanced, respectful perspectives.
Responsible Expression: Sharing Opinions Without Reinforcing Stereotypes
Responsible expression demands distinguishing personal opinions from harmful stereotypes, ensuring that individual viewpoints do not perpetuate generalized biases. Emphasizing evidence-based insights and nuanced perspectives helps prevent the reinforcement of misleading stereotypes in public discourse. Clear, respectful communication fosters understanding while maintaining the integrity of diverse experiences and identities.
Building Awareness: Separating Fact, Opinion, and Stereotype
Distinguishing between opinion, fact, and stereotype is essential for building awareness and fostering critical thinking. Opinions reflect personal beliefs and emotions, while facts are objective and verifiable, and stereotypes involve oversimplified generalizations about groups. Developing the ability to separate these elements enhances informed decision-making and reduces bias in communication.
opinion vs stereotype Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com