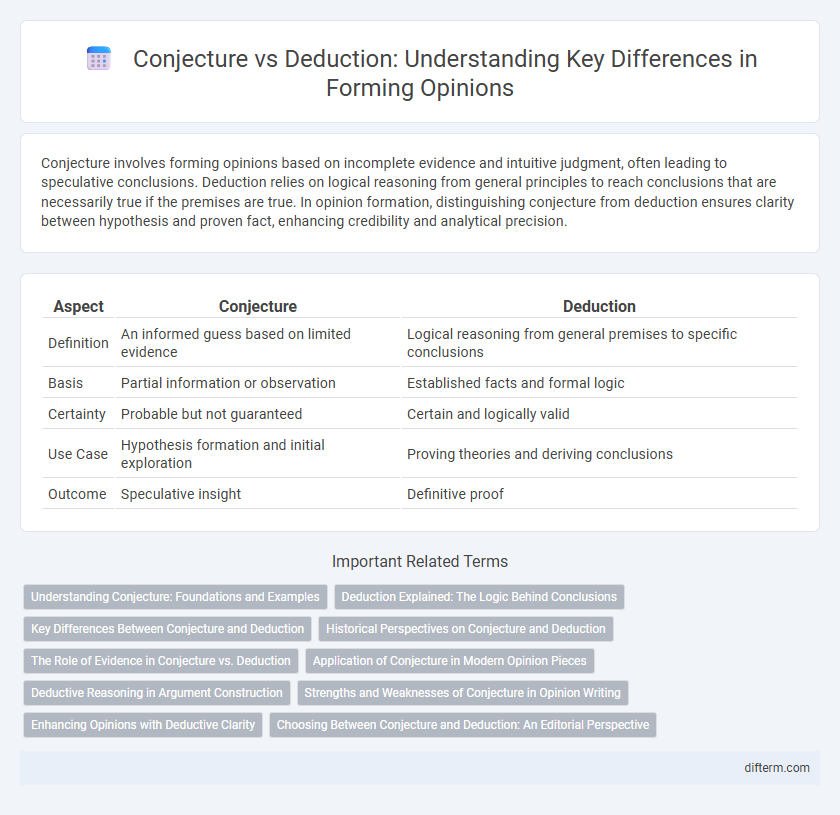
Conjecture involves forming opinions based on incomplete evidence and intuitive judgment, often leading to speculative conclusions. Deduction relies on logical reasoning from general principles to reach conclusions that are necessarily true if the premises are true. In opinion formation, distinguishing conjecture from deduction ensures clarity between hypothesis and proven fact, enhancing credibility and analytical precision.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Conjecture | Deduction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An informed guess based on limited evidence | Logical reasoning from general premises to specific conclusions |
| Basis | Partial information or observation | Established facts and formal logic |
| Certainty | Probable but not guaranteed | Certain and logically valid |
| Use Case | Hypothesis formation and initial exploration | Proving theories and deriving conclusions |
| Outcome | Speculative insight | Definitive proof |
Understanding Conjecture: Foundations and Examples
Conjecture serves as a preliminary hypothesis in the scientific and mathematical realms, grounded in observation yet lacking rigorous proof, exemplified by the famous Goldbach Conjecture which proposes that every even integer greater than two can be expressed as the sum of two prime numbers. This foundational aspect of conjecture stimulates further exploration and formal deduction, driving the advancement of knowledge by prompting mathematicians to seek definitive evidence. Understanding conjecture involves recognizing its role as a critical starting point that shapes inquiry and frames the path towards validated deductions.
Deduction Explained: The Logic Behind Conclusions
Deduction involves deriving conclusions from general premises through a logical, structured process that guarantees truth if the premises are accurate. This method prioritizes certainty and clarity, eliminating ambiguity common in conjecture, which relies on hypothesis and speculation. The strength of deduction lies in its ability to produce definitive outcomes based on established facts and logical rules.
Key Differences Between Conjecture and Deduction
Conjecture involves forming hypotheses based on incomplete evidence, relying heavily on intuition and guesswork, whereas deduction applies logical reasoning from established premises to arrive at certain conclusions. Deduction ensures certainty and validity through structured argumentation, while conjecture remains speculative and requires further proof. Understanding these key differences is crucial for distinguishing between exploratory ideas and definitive reasoning in critical thinking.
Historical Perspectives on Conjecture and Deduction
Historical perspectives reveal that conjecture served as a crucial heuristic tool in early scientific inquiry, allowing thinkers like Archimedes and Galileo to formulate hypotheses beyond empirical data. Deduction, rooted in Aristotelian logic, structured knowledge by moving from general premises to specific conclusions, establishing the foundation for formal proofs. The interplay between conjecture and deduction has shaped the evolution of scientific methods, balancing creativity with rigorous validation.
The Role of Evidence in Conjecture vs. Deduction
Evidence serves as the cornerstone in deduction by providing concrete support that guarantees the validity of conclusions drawn from premises. In conjecture, evidence plays a more tentative role, often serving as initial clues or partial observations that guide hypothesis formation without ensuring certainty. The distinction lies in deduction's reliance on definitive evidence to secure logical necessity, whereas conjecture embraces evidence as a flexible tool for exploration and theory generation.
Application of Conjecture in Modern Opinion Pieces
Conjecture plays a crucial role in modern opinion pieces by allowing writers to explore possibilities beyond established facts, fostering creative analysis and engaging readers with speculative insights. Opinion authors often employ conjecture to challenge conventional thinking and provoke discussion around complex social and political issues. This approach amplifies the dynamic nature of opinion journalism, where incomplete information requires thoughtful inference to shape persuasive arguments.
Deductive Reasoning in Argument Construction
Deductive reasoning strengthens argument construction by ensuring conclusions logically follow from established premises, reducing ambiguity and enhancing clarity. This method prioritizes validity and soundness, allowing arguments to stand firm when premises are true and the logical structure is correctly applied. Unlike conjecture, which relies on assumptions or hypothesis, deduction offers a systematic framework essential for rigorous analysis and evidence-based decision-making.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Conjecture in Opinion Writing
Conjecture in opinion writing allows for creative exploration and hypothesis generation, which can engage readers by presenting provocative ideas. However, its reliance on unproven assumptions can weaken arguments and reduce credibility when lacking supporting evidence. Balancing conjecture with factual information strengthens overall persuasiveness and reader trust.
Enhancing Opinions with Deductive Clarity
Enhancing opinions with deductive clarity involves grounding viewpoints in solid premises that logically lead to well-supported conclusions, avoiding the pitfalls of unverified conjectures. Deduction strengthens arguments by providing a clear, structured pathway from evidence to opinion, improving credibility and persuasive power. This approach ensures opinions are not merely speculative but are anchored in rational analysis, fostering more meaningful and impactful discourse.
Choosing Between Conjecture and Deduction: An Editorial Perspective
Choosing between conjecture and deduction involves weighing speculative intuition against logical certainty, where conjecture offers creative hypothesis generation, and deduction provides conclusive reasoning based on established premises. Editorial perspectives emphasize deduction's reliability for accurate conclusions, while acknowledging conjecture's role in driving innovative ideas when empirical evidence is limited. Prioritizing deduction ensures robustness in argumentation, whereas conjecture invites exploration beyond current knowledge boundaries.
conjecture vs deduction Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com