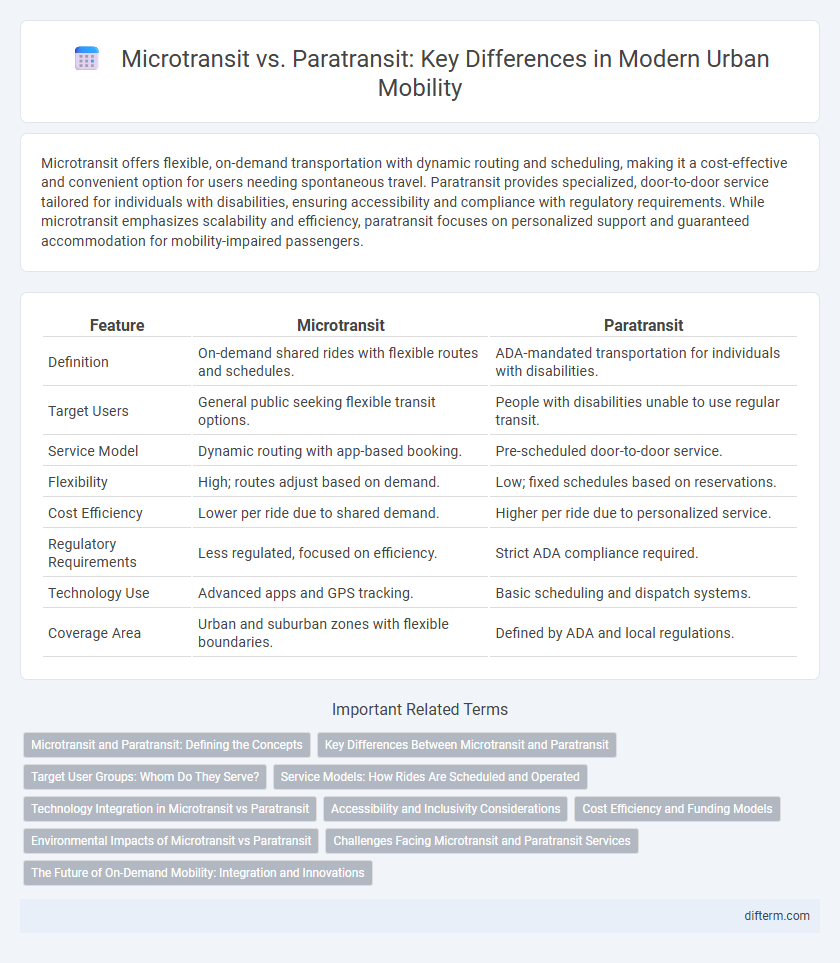
Microtransit offers flexible, on-demand transportation with dynamic routing and scheduling, making it a cost-effective and convenient option for users needing spontaneous travel. Paratransit provides specialized, door-to-door service tailored for individuals with disabilities, ensuring accessibility and compliance with regulatory requirements. While microtransit emphasizes scalability and efficiency, paratransit focuses on personalized support and guaranteed accommodation for mobility-impaired passengers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Microtransit | Paratransit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | On-demand shared rides with flexible routes and schedules. | ADA-mandated transportation for individuals with disabilities. |
| Target Users | General public seeking flexible transit options. | People with disabilities unable to use regular transit. |
| Service Model | Dynamic routing with app-based booking. | Pre-scheduled door-to-door service. |
| Flexibility | High; routes adjust based on demand. | Low; fixed schedules based on reservations. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower per ride due to shared demand. | Higher per ride due to personalized service. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Less regulated, focused on efficiency. | Strict ADA compliance required. |
| Technology Use | Advanced apps and GPS tracking. | Basic scheduling and dispatch systems. |
| Coverage Area | Urban and suburban zones with flexible boundaries. | Defined by ADA and local regulations. |
Microtransit and Paratransit: Defining the Concepts
Microtransit represents a flexible, on-demand transportation service using shared vehicles that operate within specific zones, often facilitated by digital platforms for efficient routing. Paratransit is a specialized transit service designed to accommodate individuals with disabilities or mobility impairments, providing door-to-door or curb-to-curb rides as mandated by the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). While microtransit emphasizes scalability and dynamic routing for general users, paratransit focuses on accessibility and compliance with regulatory requirements to serve vulnerable populations.
Key Differences Between Microtransit and Paratransit
Microtransit offers flexible, on-demand shared rides along dynamically routed paths, primarily serving the general public in urban and suburban areas. Paratransit provides specialized, door-to-door transportation tailored to individuals with disabilities or mobility challenges, often requiring advance booking and adherence to ADA standards. Key differences include eligibility criteria, service areas, scheduling flexibility, and the nature of rider assistance provided.
Target User Groups: Whom Do They Serve?
Microtransit primarily serves urban commuters seeking flexible, on-demand shared rides within city areas, targeting individuals who prefer alternatives to fixed-route public transit. Paratransit is designed to assist people with disabilities or mobility impairments who are unable to use regular public transportation, offering door-to-door, personalized service to meet specific accessibility needs. These distinct target user groups highlight the tailored nature of microtransit and paratransit services in addressing diverse mobility challenges.
Service Models: How Rides Are Scheduled and Operated
Microtransit operates through dynamic, app-based scheduling systems that match multiple passengers traveling in similar directions, optimizing routes in real-time to increase efficiency. Paratransit services rely on advance reservations, often requiring passengers to book rides at least 24 hours ahead, accommodating specific accessibility needs. The on-demand flexibility of microtransit contrasts with the fixed, eligibility-based model of paratransit, influencing operational costs and service scalability.
Technology Integration in Microtransit vs Paratransit
Microtransit leverages advanced technologies such as real-time tracking, dynamic routing algorithms, and mobile app integrations to enhance service flexibility and efficiency. Paratransit systems often rely on legacy scheduling software with limited real-time adaptability, restricting responsiveness to rider needs. Integration of AI-driven dispatch and on-demand booking platforms in microtransit significantly improves user experience and operational scalability compared to traditional paratransit services.
Accessibility and Inclusivity Considerations
Microtransit services enhance accessibility by offering flexible, on-demand routes that adapt to diverse rider needs, improving transit options for individuals with varying mobility challenges. Paratransit prioritizes inclusivity by providing specialized, door-to-door transportation designed specifically for people with disabilities, ensuring compliance with ADA standards. Integrating both solutions can optimize coverage and accessibility, addressing the full spectrum of mobility requirements in urban and suburban settings.
Cost Efficiency and Funding Models
Microtransit offers superior cost efficiency compared to traditional paratransit by using dynamic routing and shared rides, reducing per-passenger expenses and optimizing vehicle utilization. Paratransit services often require higher funding levels due to fixed routes, specialized vehicles, and labor-intensive scheduling, resulting in increased operating costs. Funding models for microtransit leverage flexible public-private partnerships and scalable fare structures, whereas paratransit relies heavily on government subsidies and mandated service requirements.
Environmental Impacts of Microtransit vs Paratransit
Microtransit systems generally offer lower environmental impacts compared to paratransit by utilizing dynamic routing and smaller, fuel-efficient vehicles that reduce emissions and congestion. Paratransit services often rely on larger, less fuel-efficient vehicles making fixed trips, which can result in higher carbon footprints per passenger. Studies indicate microtransit can decrease greenhouse gas emissions by up to 20% through optimized ride-sharing and reduced idle time.
Challenges Facing Microtransit and Paratransit Services
Microtransit faces challenges such as route optimization and balancing demand with limited vehicle capacity, impacting efficiency and service coverage. Paratransit struggles with maintaining timely and accessible transportation for individuals with disabilities while managing higher operational costs and regulatory compliance. Both services must address funding constraints and the integration of technology to enhance user experience and operational effectiveness.
The Future of On-Demand Mobility: Integration and Innovations
Microtransit and paratransit are converging towards integrated platforms that leverage real-time data, AI routing algorithms, and mobile app interfaces to enhance accessibility and efficiency. The future of on-demand mobility focuses on seamless user experiences that combine flexible, shared rides with tailored services for persons with disabilities, supported by autonomous vehicle technology and IoT connectivity. Innovations such as dynamic scheduling, multimodal trip planning, and adaptive service zones aim to reduce wait times and operational costs while promoting inclusive urban transportation networks.
microtransit vs paratransit Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com