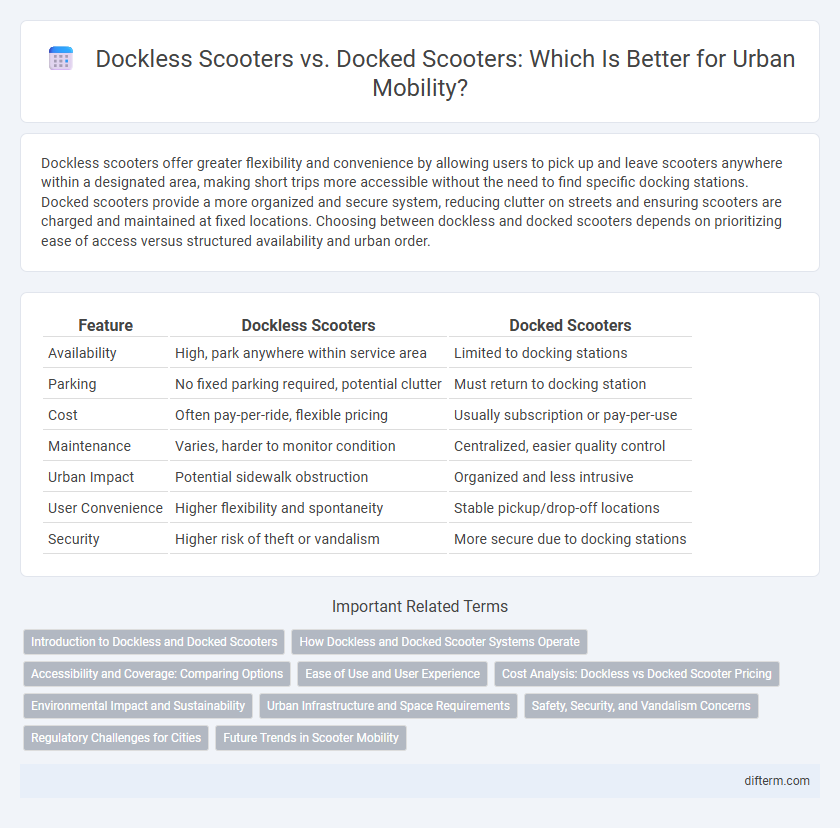
Dockless scooters offer greater flexibility and convenience by allowing users to pick up and leave scooters anywhere within a designated area, making short trips more accessible without the need to find specific docking stations. Docked scooters provide a more organized and secure system, reducing clutter on streets and ensuring scooters are charged and maintained at fixed locations. Choosing between dockless and docked scooters depends on prioritizing ease of access versus structured availability and urban order.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dockless Scooters | Docked Scooters |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | High, park anywhere within service area | Limited to docking stations |
| Parking | No fixed parking required, potential clutter | Must return to docking station |
| Cost | Often pay-per-ride, flexible pricing | Usually subscription or pay-per-use |
| Maintenance | Varies, harder to monitor condition | Centralized, easier quality control |
| Urban Impact | Potential sidewalk obstruction | Organized and less intrusive |
| User Convenience | Higher flexibility and spontaneity | Stable pickup/drop-off locations |
| Security | Higher risk of theft or vandalism | More secure due to docking stations |
Introduction to Dockless and Docked Scooters
Dockless scooters offer flexible, on-demand urban mobility without the need for fixed stations, enabling users to pick up and drop off scooters anywhere within service zones. Docked scooters require designated docking stations for parking and charging, providing organized and secure locations but less convenience in terms of accessibility. The choice between dockless and docked systems impacts city infrastructure, user behavior, and fleet management strategies in shared micro-mobility solutions.
How Dockless and Docked Scooter Systems Operate
Dockless scooter systems operate through GPS-enabled electric scooters that users can locate, unlock, and ride via mobile apps without designated parking stations, allowing flexible pick-up and drop-off locations across cities. Docked scooter systems require riders to pick up and return scooters to fixed docking stations, ensuring organized parking and reducing public space clutter but limiting scooter availability to station locations. Each system employs IoT connectivity and real-time data tracking to monitor scooter usage, battery status, and maintenance needs, optimizing fleet management and user experience.
Accessibility and Coverage: Comparing Options
Dockless scooters provide greater accessibility by allowing users to pick up and drop off vehicles anywhere within a city, significantly expanding coverage areas beyond fixed docking stations. In contrast, docked scooters are limited to specific locations, which can restrict immediate availability but offer more reliable parking and reduce sidewalk clutter. Urban planners must balance the widespread reach of dockless options against the organized infrastructure of docked systems to optimize mobility for diverse user needs.
Ease of Use and User Experience
Dockless scooters offer greater ease of use by allowing riders to pick up and drop off vehicles anywhere within service zones, eliminating the need to locate designated docking stations. This flexibility enhances user experience by providing spontaneous and convenient mobility solutions tailored to urban environments. Conversely, docked scooters require users to find specific docking points, which can limit accessibility and slow trip initiation.
Cost Analysis: Dockless vs Docked Scooter Pricing
Dockless scooters typically incur higher per-ride costs due to increased maintenance and redistribution expenses, averaging $1 to $1.50 per ride plus $0.15 per minute, whereas docked scooters feature fixed station fees and lower operational costs, resulting in rides priced around $1 with minimal variable charges. Capital expenditure for dockless scooters includes frequent battery replacements and vandalism repair, whereas docked scooters require costly docking infrastructure but benefit from centralized management reducing long-term costs. Urban mobility studies highlight docked scooters as more cost-efficient in densely populated areas while dockless models offer flexible deployment but at elevated maintenance prices.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Dockless scooters reduce the need for physical docking infrastructure, minimizing urban space disruption and resource use but often face challenges in battery life and lifespan, affecting sustainability. Docked scooters require permanent stations, leading to increased material consumption and potential land use concerns while typically benefiting from centralized maintenance that extends vehicle durability. Evaluating environmental impact involves considering production emissions, lifecycle energy consumption, and end-of-life recycling processes for both docking models.
Urban Infrastructure and Space Requirements
Dockless scooters require minimal physical infrastructure, enabling flexible parking and reducing the need for fixed docking stations, which optimizes urban space use. Docked scooters depend on dedicated parking hubs that occupy sidewalk or curb space, potentially limiting pedestrian flow and requiring city planning adjustments. Urban infrastructure prioritizes dockless models for their adaptability in congested areas, while docked scooters offer organized storage that can ease clutter in densely populated zones.
Safety, Security, and Vandalism Concerns
Dockless scooters present greater safety risks due to unpredictable parking leading to pedestrian hazards and increased accidents, while docked scooters offer controlled access and designated parking zones that reduce sidewalk clutter and improve user compliance with traffic laws. Security challenges with dockless models include higher theft and vandalism rates because scooters are parked in public, unsecured areas, whereas docked scooters benefit from integrated locking systems and monitored stations that deter tampering. Vandalism is more prevalent among dockless scooters, often resulting in damaged equipment and costly repairs, whereas docked scooters experience less frequent abuse as docking stations provide physical barriers and surveillance deterrents.
Regulatory Challenges for Cities
Dockless scooters face significant regulatory challenges in cities due to issues like sidewalk clutter, inconsistent parking, and difficulties in enforcing safety standards compared to docked scooters. Cities struggle to implement uniform policies that address fleet management, user accountability, and clear geofencing without fixed docking stations. Effective regulation often requires advanced tracking technology and collaboration between municipalities and operators to balance accessibility with public safety.
Future Trends in Scooter Mobility
Dockless scooters continue to dominate urban mobility due to their convenience and accessibility, with cities integrating AI-powered fleet management to optimize distribution and reduce clutter. Advances in battery technology and IoT connectivity enable real-time tracking and predictive maintenance, enhancing user experience and operational efficiency. Emerging regulatory frameworks are expected to balance safety and innovation, fostering scalable growth for both dockless and docked scooter models in sustainable transportation ecosystems.
dockless scooters vs docked scooters Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com