Active user wheelchairs are designed for individuals who propel themselves, offering lightweight frames, customizable features, and enhanced maneuverability to support an independent lifestyle. Passive user wheelchairs, intended for users who rely on caregivers for movement, prioritize comfort, durability, and ease of handling during transport. Choosing the appropriate wheelchair enhances mobility, promoting user comfort and quality of life tailored to individual activity levels.
Table of Comparison
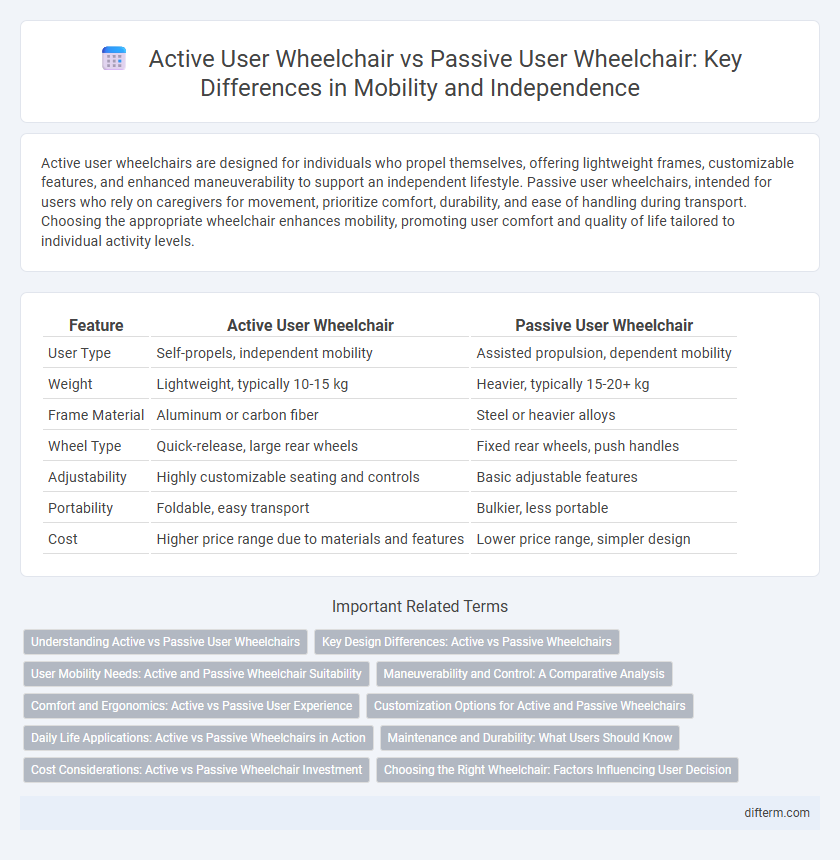
| Feature | Active User Wheelchair | Passive User Wheelchair |
|---|---|---|
| User Type | Self-propels, independent mobility | Assisted propulsion, dependent mobility |
| Weight | Lightweight, typically 10-15 kg | Heavier, typically 15-20+ kg |
| Frame Material | Aluminum or carbon fiber | Steel or heavier alloys |
| Wheel Type | Quick-release, large rear wheels | Fixed rear wheels, push handles |
| Adjustability | Highly customizable seating and controls | Basic adjustable features |
| Portability | Foldable, easy transport | Bulkier, less portable |
| Cost | Higher price range due to materials and features | Lower price range, simpler design |
Understanding Active vs Passive User Wheelchairs
Active user wheelchairs are designed for individuals who have the strength and dexterity to self-propel, featuring lightweight frames and customizable components to enhance mobility and independence. Passive user wheelchairs cater to users who rely on assistance for mobility, emphasizing comfort and support with features like reclinable backs and pressure-relief cushions. Understanding the differences between active and passive user wheelchairs helps in selecting the right mobility device tailored to the user's physical capability and lifestyle needs.
Key Design Differences: Active vs Passive Wheelchairs
Active user wheelchairs feature lightweight frames, customizable seating, and durable, high-performance wheels designed for increased maneuverability and prolonged use. Passive user wheelchairs prioritize comfort and stability with heavier, more robust frames and simplified controls, suited for occasional or assisted mobility. Key design differences include user-driven customization, weight distribution, and wheel configuration tailored to mobility independence versus support.
User Mobility Needs: Active and Passive Wheelchair Suitability
Active user wheelchairs are designed for individuals with higher mobility and physical strength, offering lightweight frames and enhanced maneuverability to support independent movement. Passive user wheelchairs prioritize comfort and support, featuring robust construction and customizable seating to accommodate users with limited upper body strength or who require assistance for mobility. Selecting the appropriate wheelchair depends on assessing the user's daily activity level, physical capabilities, and specific mobility needs to ensure optimal functionality and user satisfaction.
Maneuverability and Control: A Comparative Analysis
Active user wheelchairs offer superior maneuverability and control through lightweight frames, enhanced customizability, and advanced wheel designs, allowing users to navigate tight spaces and uneven terrain with greater precision. Passive user wheelchairs typically rely on caregivers for movement, limiting the user's control and responsiveness during navigation. Enhanced maneuverability in active wheelchairs supports greater independence and improves overall mobility outcomes by reducing effort and increasing user confidence.
Comfort and Ergonomics: Active vs Passive User Experience
Active user wheelchairs prioritize customizability and ergonomic design to support dynamic movement and reduce strain, often featuring adjustable seating and lightweight frames for enhanced comfort during prolonged use. Passive user wheelchairs emphasize stability and ease of use, with cushioned seating and supportive backrests that maximize comfort for users with limited mobility or those who rely on caregiver assistance. Both types incorporate ergonomic principles, but active models focus on enabling independence and agility, while passive models center on providing passive support and pressure relief.
Customization Options for Active and Passive Wheelchairs
Active user wheelchairs offer extensive customization options such as adjustable seat height, customizable backrests, and lightweight frames to enhance mobility and independence. Passive user wheelchairs prioritize comfort with features like padded seating, recline functions, and durable footrests tailored for longer sitting durations. Both wheelchair types can be optimized with accessories like anti-tip bars and specialized cushions to meet specific user needs and improve overall usability.
Daily Life Applications: Active vs Passive Wheelchairs in Action
Active wheelchairs offer enhanced maneuverability and customization, enabling users to independently navigate diverse environments and engage in dynamic daily activities. Passive wheelchairs prioritize comfort and support, often used by individuals requiring minimal physical effort, focusing on stability during routine tasks and transfers. Selecting between active and passive models directly impacts mobility, autonomy, and quality of life in everyday scenarios.
Maintenance and Durability: What Users Should Know
Active user wheelchairs require regular maintenance of components like bearings, tires, and brakes due to their frequent use and dynamic activities, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Passive user wheelchairs generally experience less wear, resulting in lower maintenance needs but may still require periodic checks to prevent deterioration from inactivity. Understanding these differences helps users select durable wheelchairs and adopt maintenance routines that extend lifespan and reliability.
Cost Considerations: Active vs Passive Wheelchair Investment
Active wheelchairs typically demand a higher initial investment due to advanced features like lightweight frames, enhanced maneuverability, and customizable components designed for daily, independent use. Passive wheelchairs generally have lower upfront costs, focusing on basic support and occasional use, making them more accessible but less adaptive to dynamic mobility needs. Evaluating long-term expenses such as maintenance, durability, and user lifestyle is crucial to optimizing cost effectiveness between active and passive wheelchair options.
Choosing the Right Wheelchair: Factors Influencing User Decision
Choosing the right wheelchair depends on user mobility, lifestyle, and physical capabilities. Active user wheelchairs prioritize lightweight materials, maneuverability, and customization to support independence and frequent use, while passive user wheelchairs focus on comfort, stability, and ease of use for limited mobility or assistance needs. Key factors influencing the decision include activity level, environment, and long-term health considerations.
active user wheelchair vs passive user wheelchair Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com