Native advertising seamlessly integrates promotional content within the user experience, enhancing engagement by matching the platform's design and tone. Programmatic advertising uses automated technology and data-driven targeting to deliver ads at scale, optimizing reach and efficiency across multiple channels. Understanding these approaches helps marketers balance relevance and precision to maximize campaign performance.
Table of Comparison
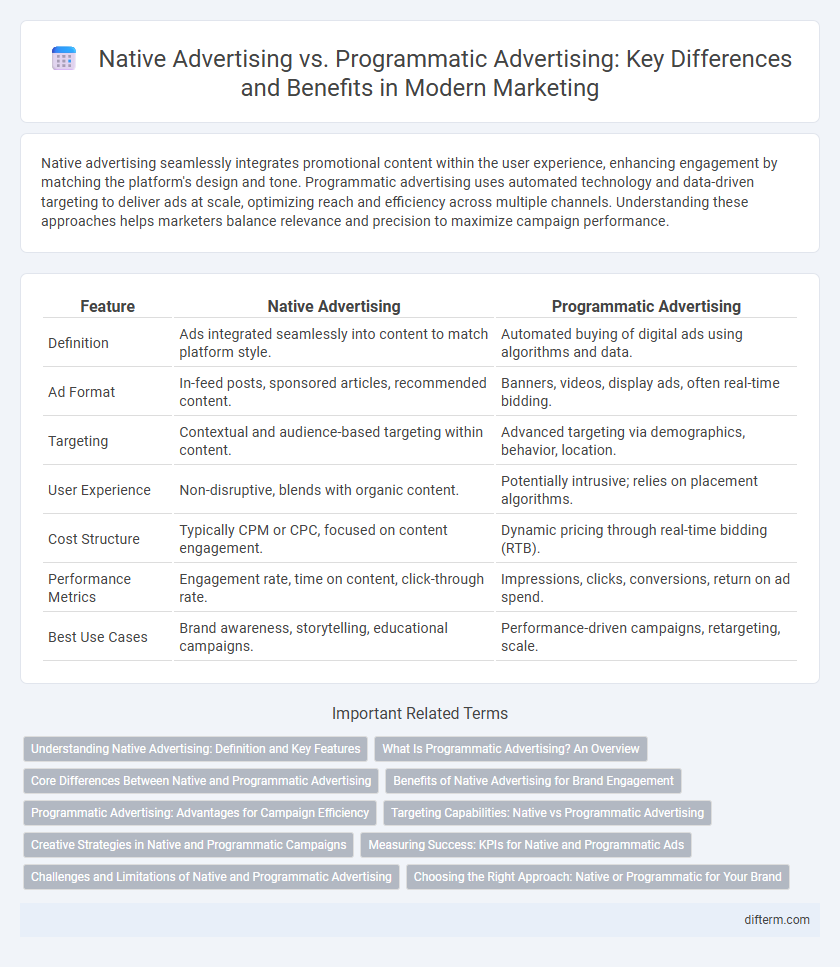
| Feature | Native Advertising | Programmatic Advertising |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ads integrated seamlessly into content to match platform style. | Automated buying of digital ads using algorithms and data. |
| Ad Format | In-feed posts, sponsored articles, recommended content. | Banners, videos, display ads, often real-time bidding. |
| Targeting | Contextual and audience-based targeting within content. | Advanced targeting via demographics, behavior, location. |
| User Experience | Non-disruptive, blends with organic content. | Potentially intrusive; relies on placement algorithms. |
| Cost Structure | Typically CPM or CPC, focused on content engagement. | Dynamic pricing through real-time bidding (RTB). |
| Performance Metrics | Engagement rate, time on content, click-through rate. | Impressions, clicks, conversions, return on ad spend. |
| Best Use Cases | Brand awareness, storytelling, educational campaigns. | Performance-driven campaigns, retargeting, scale. |
Understanding Native Advertising: Definition and Key Features
Native advertising integrates promotional content seamlessly within a platform's natural content flow, enhancing user engagement by matching the form and function of the surrounding media. Key features include non-disruptive placement, contextual relevance, and a design that mirrors the user experience, fostering higher trust and click-through rates compared to traditional ads. This form of advertising prioritizes subtlety and value, making it an essential strategy for brands aiming to build authentic connections with their target audience while avoiding ad fatigue.
What Is Programmatic Advertising? An Overview
Programmatic advertising is an automated digital marketing strategy that uses software and algorithms to buy and optimize ad placements in real-time. It leverages data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to target specific audiences across multiple channels, increasing efficiency and campaign performance. This approach contrasts with native advertising by prioritizing precision targeting and automated bidding rather than seamless content integration.
Core Differences Between Native and Programmatic Advertising
Native advertising integrates seamlessly with the platform's content, delivering personalized ads that match the user experience, while programmatic advertising utilizes automated technology and algorithms to buy and optimize ad placements across multiple channels in real-time. Native ads prioritize user engagement by blending with editorial content, focusing on relevance and subtlety, whereas programmatic ads emphasize scale, efficiency, and targeting precision using data-driven audience segmentation. Core differences include the execution format--native works as in-feed content, and programmatic spans display, video, and social ads--and the buying process, where native often involves direct negotiation and programmatic relies on automated auctions.
Benefits of Native Advertising for Brand Engagement
Native advertising enhances brand engagement by seamlessly integrating promotional content into the user experience, increasing relevance and reducing ad fatigue. This format drives higher click-through rates and fosters trust by matching the style and tone of the surrounding editorial content. Brands utilizing native advertising benefit from improved customer interaction, deeper emotional connections, and longer attention spans compared to traditional display ads.
Programmatic Advertising: Advantages for Campaign Efficiency
Programmatic advertising leverages automated technology and real-time bidding to optimize media buying, significantly enhancing campaign efficiency by targeting precise audience segments with minimal manual intervention. This approach reduces costs and maximizes return on ad spend through data-driven decisions and dynamic ad placements across multiple channels. Enhanced scalability and fast campaign adjustments allow marketers to respond swiftly to market trends, boosting overall performance and engagement.
Targeting Capabilities: Native vs Programmatic Advertising
Native advertising enables precise targeting by seamlessly integrating ads within relevant content, enhancing user engagement through contextually aligned messaging. Programmatic advertising leverages advanced algorithms and real-time bidding to optimize ad placement across diverse platforms, allowing granular audience segmentation based on demographics, behavior, and interests. Both approaches maximize relevance, but programmatic offers superior scalability and dynamic targeting capabilities for efficient budget allocation.
Creative Strategies in Native and Programmatic Campaigns
Native advertising leverages seamless content integration and storytelling to create engaging, non-disruptive user experiences that drive higher brand affinity and consumer trust. Programmatic advertising uses data-driven, automated buying to optimize ad placement and audience targeting, enabling personalized creative variations at scale for better conversion rates. Combining native's creative authenticity with programmatic's precision targeting enhances campaign effectiveness through tailored, contextually relevant messaging.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Native and Programmatic Ads
Measuring success in native advertising centers on engagement-based KPIs such as click-through rates (CTR), time spent on content, and social shares, reflecting the ad's integration with editorial content. Programmatic advertising success is often tracked through real-time metrics like impressions, conversion rates, cost per acquisition (CPA), and return on ad spend (ROAS), leveraging automated data for performance optimization. Both strategies rely on precise analytics platforms to assess audience targeting effectiveness and campaign ROI, enabling marketers to fine-tune their advertising investments.
Challenges and Limitations of Native and Programmatic Advertising
Native advertising faces challenges such as maintaining authentic user engagement while avoiding ad fatigue, complicated content integration, and difficulties in measuring return on investment due to its seamless format. Programmatic advertising struggles with issues like ad fraud, inventory quality concerns, and privacy regulations limiting data availability for precise targeting. Both approaches require constant optimization to balance effectiveness with brand safety and user experience.
Choosing the Right Approach: Native or Programmatic for Your Brand
Selecting the right advertising strategy depends on your brand's goals and audience engagement preferences, with native advertising offering seamless, content-integrated experiences that enhance user trust and increase click-through rates. Programmatic advertising leverages automated, data-driven targeting to optimize ad placements in real time, improving efficiency and scale across multiple digital channels. Brands aiming for authentic storytelling and consumer connection should prioritize native ads, while those seeking precision targeting and rapid campaign adjustments benefit more from programmatic methods.
Native advertising vs programmatic advertising Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com