Zero Waste Home emphasizes eliminating all disposable waste by adopting reusable, compostable, and sustainable alternatives, creating a strict goal of producing no landfill trash. Low Waste Living encourages significant waste reduction through mindful consumption and recycling habits, allowing some flexibility without demanding absolute zero waste. Both approaches aim to minimize environmental impact, with Zero Waste Home offering a more stringent lifestyle commitment and Low Waste Living presenting a practical, gradual path.
Table of Comparison
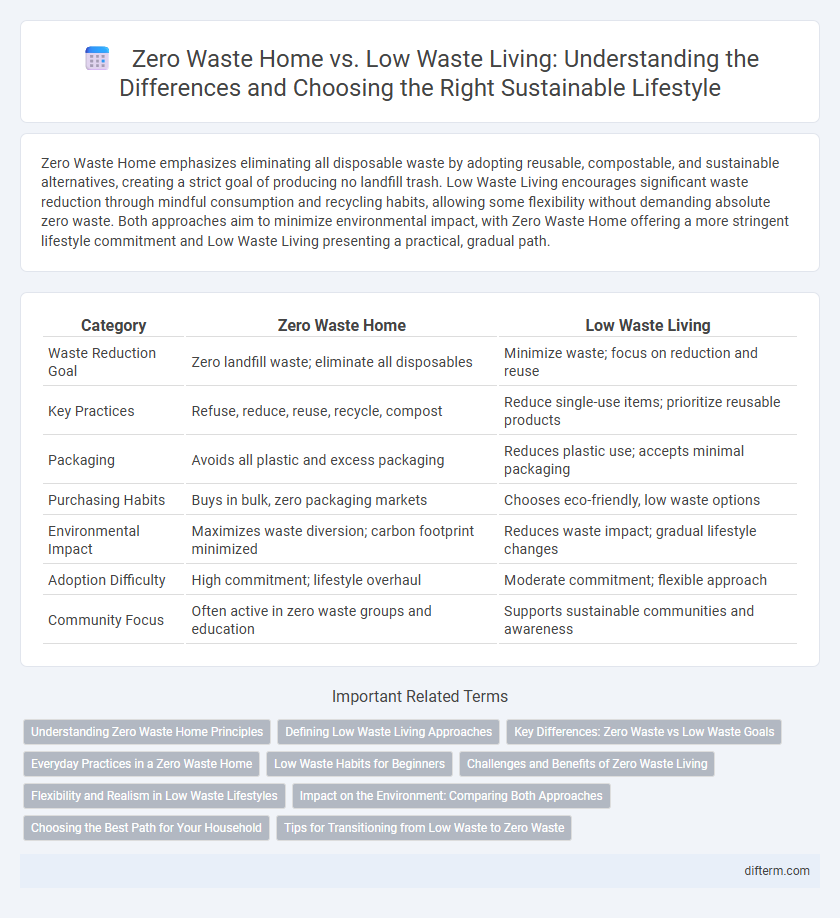
| Category | Zero Waste Home | Low Waste Living |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Reduction Goal | Zero landfill waste; eliminate all disposables | Minimize waste; focus on reduction and reuse |
| Key Practices | Refuse, reduce, reuse, recycle, compost | Reduce single-use items; prioritize reusable products |
| Packaging | Avoids all plastic and excess packaging | Reduces plastic use; accepts minimal packaging |
| Purchasing Habits | Buys in bulk, zero packaging markets | Chooses eco-friendly, low waste options |
| Environmental Impact | Maximizes waste diversion; carbon footprint minimized | Reduces waste impact; gradual lifestyle changes |
| Adoption Difficulty | High commitment; lifestyle overhaul | Moderate commitment; flexible approach |
| Community Focus | Often active in zero waste groups and education | Supports sustainable communities and awareness |
Understanding Zero Waste Home Principles
Zero Waste Home principles emphasize eliminating waste through strategies like refusing, reducing, reusing, and recycling to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainable living. Unlike low waste living, which accepts some minimal waste generation, zero waste aims for complete waste diversion from landfills and incineration, stressing conscious consumption and long-term lifestyle changes. Key practices include using reusable products, composting organic materials, and advocating for systemic change in packaging and product design.
Defining Low Waste Living Approaches
Low waste living emphasizes reducing waste through mindful consumption, reusable products, and minimal packaging, often tailored to individual lifestyles and community resources. Unlike the zero waste home, which aims for near-complete waste elimination, low waste living adopts flexible, practical strategies such as composting, bulk buying, and upcycling. This approach balances environmental impact with everyday convenience, making sustainable habits more accessible and manageable.
Key Differences: Zero Waste vs Low Waste Goals
Zero Waste Home aims for complete waste elimination by redesigning consumption and lifestyle to produce zero landfill output, focusing on long-term sustainability and systemic change. Low Waste Living prioritizes significant waste reduction through practical, flexible habits that minimize environmental impact while recognizing occasional waste generation. The key difference lies in Zero Waste Home's strict no-waste principle versus Low Waste Living's realistic, incremental waste reduction goals.
Everyday Practices in a Zero Waste Home
Everyday practices in a zero waste home emphasize eliminating single-use items by adopting reusable alternatives such as cloth bags, stainless steel containers, and glass jars for storage and shopping. Meal planning, composting organic waste, and choosing products with minimal or no packaging significantly reduce landfill contributions while promoting sustainable consumption patterns. These habits foster a circular lifestyle that minimizes environmental impact and supports resource conservation.
Low Waste Habits for Beginners
Low waste living emphasizes simple, practical habits such as reusable shopping bags, bulk purchasing, and mindful consumption, making it more accessible for beginners than the comprehensive strategies of a zero waste home. Adopting low waste habits gradually reduces environmental impact without the pressure of eliminating all waste. Focusing on reducing single-use plastics and composting food scraps helps build a sustainable lifestyle foundation that can evolve into more advanced zero waste practices.
Challenges and Benefits of Zero Waste Living
Zero Waste Living involves a strict commitment to eliminating all waste by reusing, recycling, and composting, which can be challenging due to the need for significant lifestyle changes and limited product availability. Benefits of Zero Waste Living include a substantial reduction in environmental impact, lower household costs over time, and fostering a strong sense of environmental responsibility. Compared to Low Waste Living, Zero Waste demands more rigorous routines but results in a deeper contribution to waste reduction and sustainability goals.
Flexibility and Realism in Low Waste Lifestyles
Low waste living emphasizes flexibility and realism by encouraging gradual reduction of waste tailored to individual lifestyles, unlike zero waste home approaches that often demand strict adherence to eliminating all waste. This pragmatic mindset accommodates busy schedules and limited resources, making sustainable habits more accessible and sustainable long-term. Prioritizing incremental changes, such as using reusable items and mindful consumption, promotes consistent progress without overwhelming lifestyle adjustments.
Impact on the Environment: Comparing Both Approaches
Zero Waste Home emphasizes eliminating all waste by redesigning lifestyles to avoid disposables, significantly reducing landfill contributions and resource consumption. Low Waste Living focuses on minimizing waste generation through conscious purchasing and reuse, leading to decreased environmental pollution and lower carbon footprints. Both approaches reduce environmental impact, but Zero Waste Home typically achieves greater waste diversion, promoting a more transformative effect on sustainability.
Choosing the Best Path for Your Household
Zero Waste Home aims for eliminating all single-use waste by adopting reusable, compostable, or recyclable alternatives, creating a comprehensive system for waste reduction. Low Waste Living emphasizes gradual changes and practical solutions, focusing on reducing waste incrementally while maintaining convenience for everyday routines. Selecting the best path depends on your household's commitment level, lifestyle needs, and willingness to implement sustainable habits consistently.
Tips for Transitioning from Low Waste to Zero Waste
Transitioning from low waste living to a zero waste home requires adopting more comprehensive habits such as eliminating all single-use plastics, investing in durable, reusable products, and composting organic waste to minimize landfill contributions. Prioritize bulk shopping, DIY household cleaners, and mindful consumption to further reduce your environmental footprint. Gradually implement these changes while tracking waste reduction progress to maintain sustainable long-term habits.
Zero Waste Home vs Low Waste Living Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com