Urban gardening transforms small city spaces into green havens, promoting self-sufficiency and fresh produce for pet owners who prioritize natural food sources. Vertical farming maximizes limited urban areas with stacked layers, optimizing crop yield and reducing environmental impact, making it ideal for sustainable pet lifestyle practices. Both approaches enhance access to nutrient-rich plants that can improve pets' health and well-being through organic, homegrown ingredients.
Table of Comparison
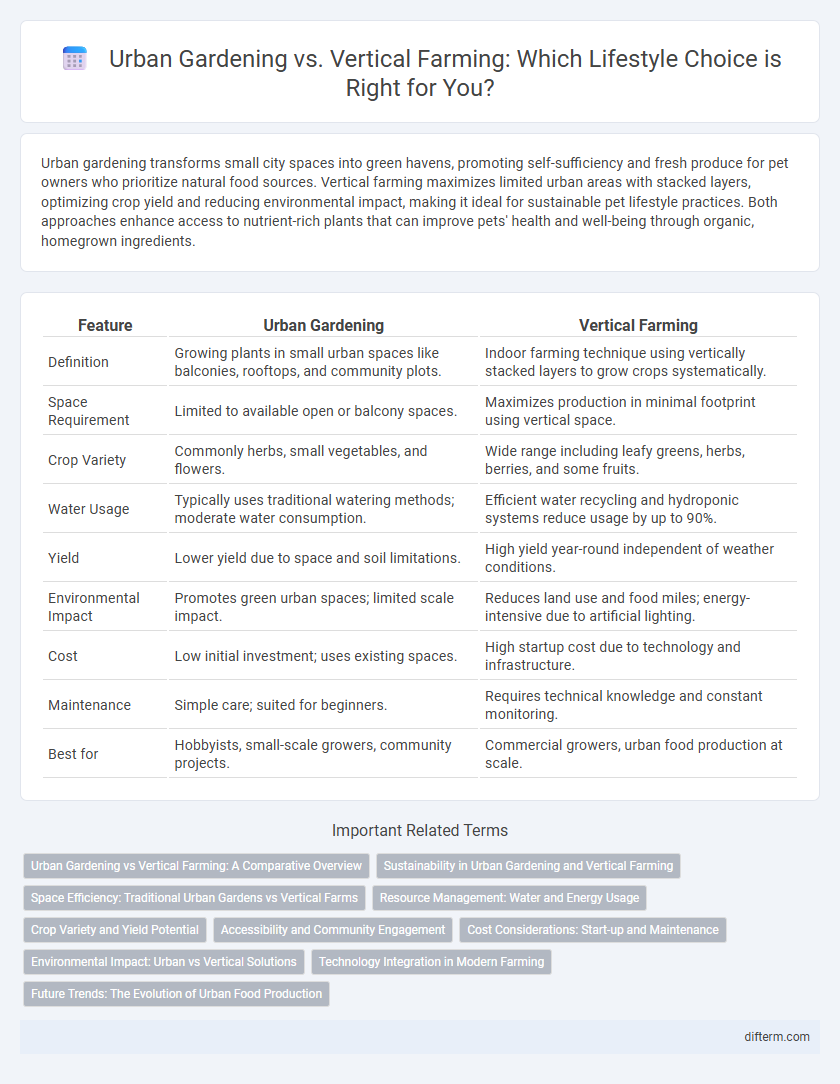
| Feature | Urban Gardening | Vertical Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing plants in small urban spaces like balconies, rooftops, and community plots. | Indoor farming technique using vertically stacked layers to grow crops systematically. |
| Space Requirement | Limited to available open or balcony spaces. | Maximizes production in minimal footprint using vertical space. |
| Crop Variety | Commonly herbs, small vegetables, and flowers. | Wide range including leafy greens, herbs, berries, and some fruits. |
| Water Usage | Typically uses traditional watering methods; moderate water consumption. | Efficient water recycling and hydroponic systems reduce usage by up to 90%. |
| Yield | Lower yield due to space and soil limitations. | High yield year-round independent of weather conditions. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes green urban spaces; limited scale impact. | Reduces land use and food miles; energy-intensive due to artificial lighting. |
| Cost | Low initial investment; uses existing spaces. | High startup cost due to technology and infrastructure. |
| Maintenance | Simple care; suited for beginners. | Requires technical knowledge and constant monitoring. |
| Best for | Hobbyists, small-scale growers, community projects. | Commercial growers, urban food production at scale. |
Urban Gardening vs Vertical Farming: A Comparative Overview
Urban gardening utilizes small-scale, home-based methods to grow plants in city environments, promoting local food production and sustainable living. Vertical farming involves multi-layered, controlled-environment agriculture using advanced technology to maximize crop yields in limited urban spaces. Both approaches enhance urban sustainability, but vertical farming offers greater efficiency and scalability for meeting growing food demands.
Sustainability in Urban Gardening and Vertical Farming
Urban gardening promotes sustainability by utilizing available city spaces to grow food locally, reducing transportation emissions and minimizing carbon footprints. Vertical farming enhances resource efficiency with controlled environments that optimize water usage and nutrient delivery, significantly cutting waste and energy consumption. Both methods contribute to urban sustainability by supporting biodiversity, decreasing reliance on industrial agriculture, and fostering community engagement in eco-friendly practices.
Space Efficiency: Traditional Urban Gardens vs Vertical Farms
Vertical farms maximize space efficiency by utilizing stacked layers of crops in controlled environments, enabling high-density plant growth within limited urban areas. Traditional urban gardens typically occupy horizontal ground spaces, which restricts the volume of produce per square foot. The innovative design of vertical farming allows for year-round cultivation and significantly higher yields compared to conventional urban gardening methods.
Resource Management: Water and Energy Usage
Urban gardening utilizes rainwater harvesting and manual irrigation techniques to minimize water consumption, making it ideal for small-scale, localized food production. Vertical farming employs advanced technologies such as hydroponics and LED grow lights, significantly reducing water use by up to 90% compared to traditional agriculture while optimizing energy efficiency through controlled environments. Both methods contribute to sustainable resource management, but vertical farming offers greater scalability and precision in water and energy conservation.
Crop Variety and Yield Potential
Urban gardening allows for a diverse range of crops grown in small, personalized spaces, enhancing biodiversity and local food security. Vertical farming maximizes yield potential through controlled environments and stacked layers, enabling year-round production with higher efficiency. Combining both methods can optimize crop variety and boost overall productivity in urban settings.
Accessibility and Community Engagement
Urban gardening offers widespread accessibility by utilizing small-scale spaces like balconies and rooftops, promoting personal involvement and local community bonding. Vertical farming, often requiring significant initial investment and technology, tends to be less accessible to individual urban dwellers but fosters community engagement through organized cooperative projects and educational programs. Both methods enhance urban green spaces, supporting sustainable living and strengthening neighborhood connections.
Cost Considerations: Start-up and Maintenance
Urban gardening typically requires lower start-up costs, involving basic tools, soil, and seeds, making it accessible for most households. Vertical farming demands significant initial investment in infrastructure, technology, and climate control systems, raising both capital and maintenance expenses. Over time, urban gardens have minimal upkeep costs, while vertical farms incur ongoing energy and equipment maintenance costs, impacting long-term budget planning.
Environmental Impact: Urban vs Vertical Solutions
Urban gardening reduces carbon footprints by utilizing existing green spaces and promoting local food production, which minimizes transportation emissions and soil degradation. Vertical farming optimizes space with controlled environments, drastically reducing water usage and pesticide reliance while enabling year-round crop production. Both solutions contribute to urban sustainability, but vertical farming offers higher energy efficiency and waste reduction through advanced technology integration.
Technology Integration in Modern Farming
Urban gardening leverages smart sensors and IoT devices to optimize water usage and monitor plant health, enhancing sustainability in limited spaces. Vertical farming employs advanced LED lighting, climate control systems, and hydroponics to maximize yield and reduce resource consumption. Both methods exemplify the integration of cutting-edge technology in modern farming to address urban food security challenges.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Urban Food Production
Urban gardening and vertical farming represent pivotal advancements in the future of urban food production, with urban gardening emphasizing community-driven, small-scale cultivation, while vertical farming leverages technology for high-density, year-round crop yields. Innovations such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and AI-controlled environments are accelerating vertical farming's scalability in metropolitan areas. These trends indicate a shift towards sustainable, space-efficient agriculture that meets rising global food demands while reducing carbon footprints.
urban gardening vs vertical farming Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com