Urban gardening maximizes limited outdoor spaces like balconies and rooftops to grow fresh herbs, vegetables, and flowers, enhancing city living with sustainable practices. Indoor gardening offers year-round plant care with controlled environments, perfect for homes lacking outdoor areas and improving air quality and mental well-being. Choosing between them depends on space availability, climate, and personal lifestyle preferences.
Table of Comparison
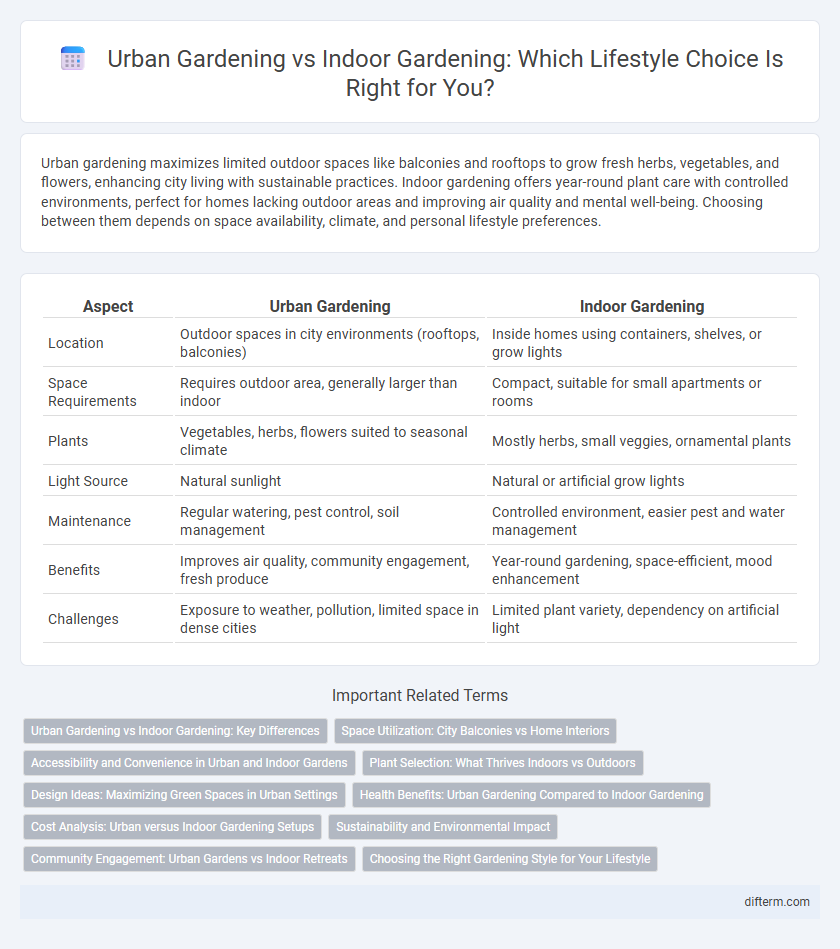
| Aspect | Urban Gardening | Indoor Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outdoor spaces in city environments (rooftops, balconies) | Inside homes using containers, shelves, or grow lights |
| Space Requirements | Requires outdoor area, generally larger than indoor | Compact, suitable for small apartments or rooms |
| Plants | Vegetables, herbs, flowers suited to seasonal climate | Mostly herbs, small veggies, ornamental plants |
| Light Source | Natural sunlight | Natural or artificial grow lights |
| Maintenance | Regular watering, pest control, soil management | Controlled environment, easier pest and water management |
| Benefits | Improves air quality, community engagement, fresh produce | Year-round gardening, space-efficient, mood enhancement |
| Challenges | Exposure to weather, pollution, limited space in dense cities | Limited plant variety, dependency on artificial light |
Urban Gardening vs Indoor Gardening: Key Differences
Urban gardening typically involves cultivating plants in outdoor city spaces such as balconies, rooftops, and community gardens, leveraging natural sunlight and fresh air. Indoor gardening, on the other hand, relies on controlled environments like grow lights and hydroponic systems to nurture plants inside homes or apartments. Both methods offer unique benefits for urban dwellers, with urban gardening promoting environmental sustainability and indoor gardening enabling year-round cultivation regardless of outdoor conditions.
Space Utilization: City Balconies vs Home Interiors
Urban gardening on city balconies maximizes limited outdoor space by utilizing vertical planters and compact containers to grow vegetables, herbs, and flowers in a small footprint. Indoor gardening leverages home interiors by incorporating smart lighting systems and hydroponic setups that optimize plant growth without natural sunlight. Both methods prioritize efficient space utilization to enhance greenery and fresh produce access in urban living environments.
Accessibility and Convenience in Urban and Indoor Gardens
Urban gardening offers accessible green spaces by utilizing rooftops, balconies, and community plots, making it convenient for city dwellers with limited outdoor areas. Indoor gardening provides year-round growing opportunities regardless of weather or season, using compact setups like vertical gardens and hydroponic systems. Both approaches enhance convenience by reducing travel time to outdoor areas and enabling easy care routines within urban living environments.
Plant Selection: What Thrives Indoors vs Outdoors
Urban gardening typically favors hardy, sun-loving plants such as tomatoes, peppers, and herbs that thrive in outdoor environments with ample sunlight and airflow. Indoor gardening excels with shade-tolerant and low-maintenance plants like snake plants, pothos, and succulents that adapt well to limited natural light and controlled temperatures. Choosing the right plants based on their light, space, and climate requirements is essential for successful growth in either urban or indoor gardening setups.
Design Ideas: Maximizing Green Spaces in Urban Settings
Urban gardening maximizes green spaces through rooftop gardens, vertical planters, and balcony beds that integrate nature into cityscapes while optimizing limited outdoor areas. Indoor gardening leverages smart containers, hydroponic systems, and grow lights to cultivate plants in compact living spaces, enhancing air quality and aesthetic appeal. Combining both methods creates a cohesive green environment that supports sustainability and urban biodiversity.
Health Benefits: Urban Gardening Compared to Indoor Gardening
Urban gardening offers greater exposure to natural sunlight and fresh air, which enhances vitamin D synthesis and boosts mental well-being more effectively than indoor gardening. The physical activity involved in tending outdoor gardens improves cardiovascular health and reduces stress through increased endorphin production. Urban gardening also promotes biodiversity and environmental engagement, contributing to a healthier lifestyle beyond the confines of indoor spaces.
Cost Analysis: Urban versus Indoor Gardening Setups
Urban gardening typically requires a higher initial investment due to the need for soil preparation, raised beds, and outdoor infrastructure, whereas indoor gardening often demands expenses for grow lights, hydroponic systems, and climate control equipment. Ongoing costs for urban gardens may include water usage and pest management, while indoor setups incur electricity costs for lighting and ventilation. Overall, indoor gardening can have higher energy expenses, but urban gardening demands more frequent material replenishment and outdoor maintenance.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Urban gardening maximizes sustainable land use by transforming rooftops and vacant lots into green spaces, reducing urban heat islands and enhancing biodiversity. Indoor gardening minimizes water consumption through controlled environments and recycles organic waste, contributing to lower carbon footprints. Both practices promote local food production, cutting transportation emissions and supporting eco-friendly lifestyle choices.
Community Engagement: Urban Gardens vs Indoor Retreats
Urban gardening fosters strong community engagement by transforming shared public spaces into vibrant hubs of social interaction and collective sustainability efforts. In contrast, indoor gardening offers a personal retreat that enhances individual well-being but limits opportunities for neighborhood collaboration and communal learning. Community-driven urban green spaces contribute to local food systems and environmental awareness, reinforcing social bonds and collective responsibility.
Choosing the Right Gardening Style for Your Lifestyle
Urban gardening maximizes outdoor spaces like balconies and rooftops, offering direct sunlight and natural airflow essential for growing vegetables and herbs. Indoor gardening suits limited spaces and climate control, using containers, grow lights, and hydroponics to cultivate plants year-round. Selecting the ideal style depends on available space, time commitment, and desired plant types to ensure a sustainable and enjoyable gardening experience.
urban gardening vs indoor gardening Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com