Raw veganism emphasizes consuming uncooked plant-based foods, including vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains, to maximize nutrient intake and enzymatic activity. Fruitarianism, a subset of raw veganism, restricts the diet primarily to fruits, nuts, and seeds, highlighting a natural, effortless approach to eating. Both lifestyles promote plant-centered nutrition but differ in food variety and philosophical focus on natural consumption.
Table of Comparison
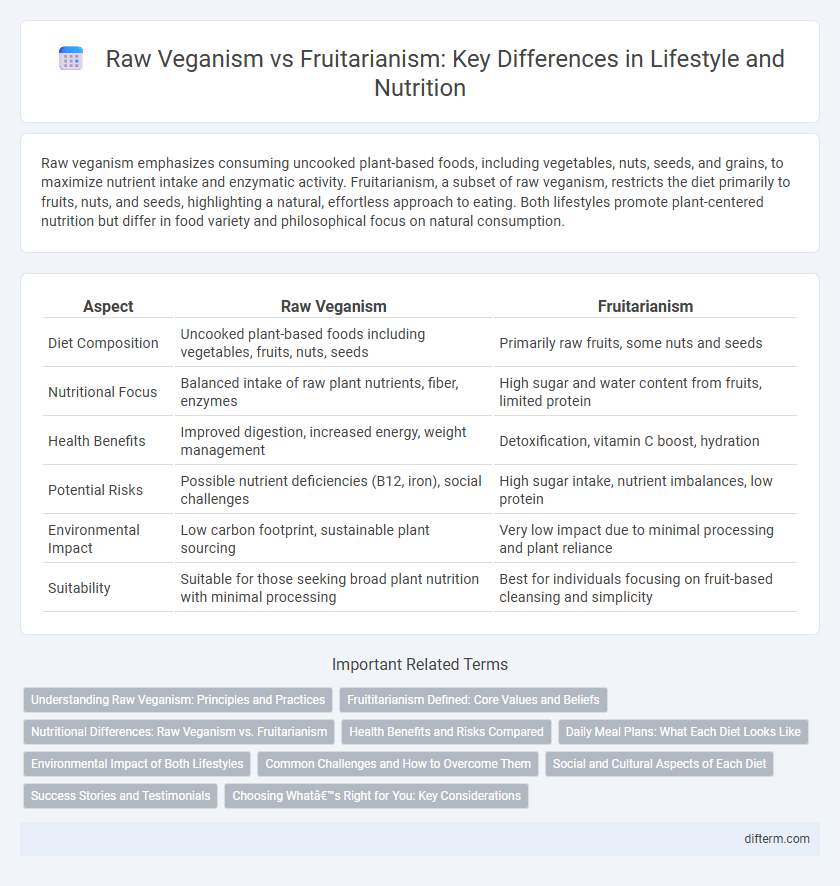
| Aspect | Raw Veganism | Fruitarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Diet Composition | Uncooked plant-based foods including vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds | Primarily raw fruits, some nuts and seeds |
| Nutritional Focus | Balanced intake of raw plant nutrients, fiber, enzymes | High sugar and water content from fruits, limited protein |
| Health Benefits | Improved digestion, increased energy, weight management | Detoxification, vitamin C boost, hydration |
| Potential Risks | Possible nutrient deficiencies (B12, iron), social challenges | High sugar intake, nutrient imbalances, low protein |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable plant sourcing | Very low impact due to minimal processing and plant reliance |
| Suitability | Suitable for those seeking broad plant nutrition with minimal processing | Best for individuals focusing on fruit-based cleansing and simplicity |
Understanding Raw Veganism: Principles and Practices
Raw veganism emphasizes consuming uncooked, plant-based foods to preserve natural enzymes and nutrients, promoting optimal health and digestion. This lifestyle excludes all animal products and processed foods, highlighting fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and sprouted grains. Followers adopt techniques such as dehydration and blending to maintain food integrity and maximize nutrient absorption.
Fruititarianism Defined: Core Values and Beliefs
Fruitarianism centers on a diet exclusively composed of raw fruits, emphasizing purity, naturalness, and minimal environmental impact. Core beliefs include aligning with a lifestyle that respects animal life and promotes optimal health through nutrient-dense, unprocessed fruits. This philosophy often merges ethical considerations with a spiritual connection to nature, advocating for harmony between humans and the earth.
Nutritional Differences: Raw Veganism vs. Fruitarianism
Raw veganism emphasizes a diet of uncooked plant-based foods including vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains, providing a broad spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Fruitarianism centers on consuming primarily raw fruits, leading to higher sugar intake but potential deficiencies in protein, fats, vitamin B12, and iron. The nutritional gap between raw veganism and fruitarianism necessitates careful planning to ensure adequate macronutrient and micronutrient intake for optimal health.
Health Benefits and Risks Compared
Raw veganism emphasizes consuming uncooked plant-based foods, providing high levels of vitamins, enzymes, and fiber that support digestion and immune function. Fruitarianism, primarily centered on raw fruits, offers abundant antioxidants and hydration but risks nutrient deficiencies like protein, vitamin B12, and essential fats. Both diets require careful planning to avoid malnutrition and sustain overall health, balancing benefits such as weight management and reduced chronic disease risk against potential drawbacks like decreased bone density and energy levels.
Daily Meal Plans: What Each Diet Looks Like
Raw veganism daily meal plans emphasize fresh vegetables, nuts, seeds, and sprouted grains consumed uncooked to preserve nutrients. Fruitarianism meal plans center predominantly around raw fruits such as apples, bananas, berries, and tropical fruits, often consumed throughout the day with minimal nuts or seeds. Both diets avoid cooked foods, but raw vegans incorporate a wider variety of plant-based foods compared to the fruit-focused selection in fruitarianism.
Environmental Impact of Both Lifestyles
Raw veganism emphasizes consuming uncooked plant-based foods, significantly reducing carbon footprint by eliminating animal agriculture emissions and reducing water usage compared to omnivorous diets. Fruitarianism, which restricts intake to primarily fruits, often relies on higher consumption of seasonal and local produce, potentially lowering transportation emissions, but can increase land use and water resources due to the demand for intensive fruit cultivation. Both lifestyles promote sustainability, yet raw veganism generally offers a broader environmental benefit through diverse plant sourcing and lower resource demands.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Raw veganism and fruitarianism both present challenges such as nutrient deficiencies, social dining difficulties, and limited food variety. Ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids can be achieved through fortified foods or supplements. Building a supportive community and meal planning with diverse raw fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds helps overcome social and dietary limitations.
Social and Cultural Aspects of Each Diet
Raw veganism emphasizes a diverse intake of uncooked plant foods, fostering community events like potlucks and workshops that promote ethical living and environmental awareness. Fruitarianism, centered around fruit consumption, often aligns with minimalist and spiritual lifestyles, cultivating niche social groups that prioritize natural harmony and personal purity. Both diets influence social identity and cultural practices by encouraging conscious food choices and unique communal experiences.
Success Stories and Testimonials
Raw veganism has empowered individuals to achieve remarkable health transformations, including significant weight loss and enhanced energy levels, as documented in numerous testimonials. Fruitarianism success stories highlight improved digestion and clearer skin, with practitioners often praising the diet's simplicity and alignment with natural eating habits. Both lifestyles garner praise for fostering mental clarity and emotional well-being, reinforcing their potential benefits in holistic health journeys.
Choosing What’s Right for You: Key Considerations
Raw veganism emphasizes consuming uncooked plant foods to preserve nutrients and enzymes, while fruitarianism primarily limits intake to fruits, occasionally including nuts and seeds. When choosing between these lifestyles, consider factors such as nutritional balance, potential nutrient deficiencies like vitamin B12 or protein, and personal health goals. Understanding your body's response and consulting with a healthcare professional can help ensure a sustainable and healthful dietary choice.
Raw Veganism vs Fruitarianism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com