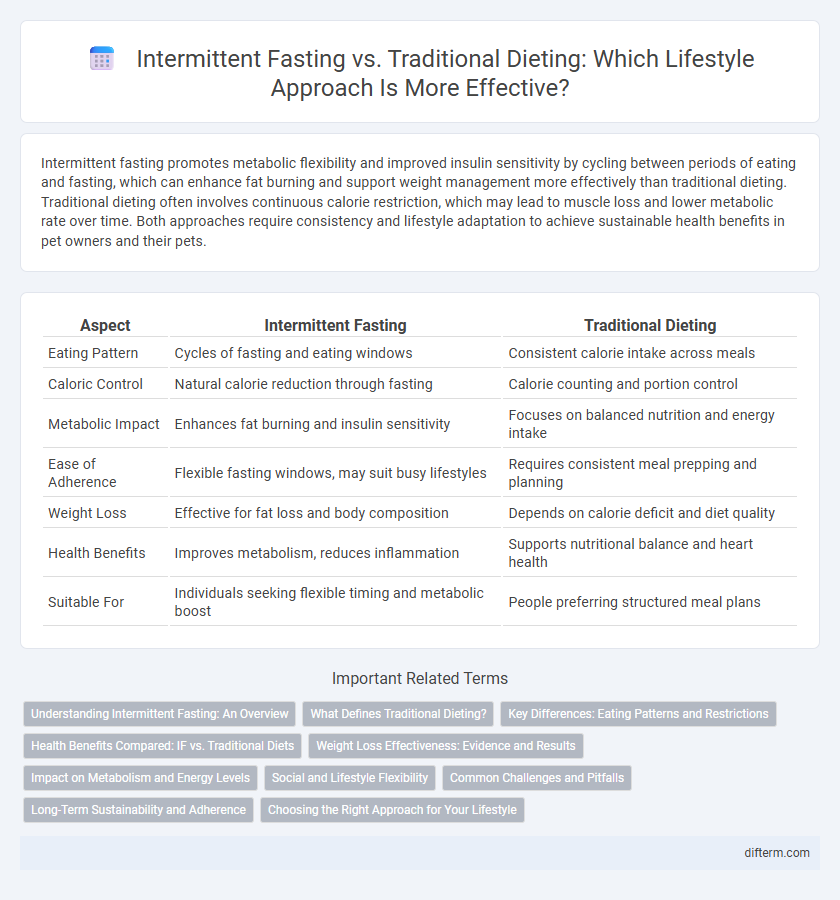
Intermittent fasting promotes metabolic flexibility and improved insulin sensitivity by cycling between periods of eating and fasting, which can enhance fat burning and support weight management more effectively than traditional dieting. Traditional dieting often involves continuous calorie restriction, which may lead to muscle loss and lower metabolic rate over time. Both approaches require consistency and lifestyle adaptation to achieve sustainable health benefits in pet owners and their pets.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Intermittent Fasting | Traditional Dieting |
|---|---|---|
| Eating Pattern | Cycles of fasting and eating windows | Consistent calorie intake across meals |
| Caloric Control | Natural calorie reduction through fasting | Calorie counting and portion control |
| Metabolic Impact | Enhances fat burning and insulin sensitivity | Focuses on balanced nutrition and energy intake |
| Ease of Adherence | Flexible fasting windows, may suit busy lifestyles | Requires consistent meal prepping and planning |
| Weight Loss | Effective for fat loss and body composition | Depends on calorie deficit and diet quality |
| Health Benefits | Improves metabolism, reduces inflammation | Supports nutritional balance and heart health |
| Suitable For | Individuals seeking flexible timing and metabolic boost | People preferring structured meal plans |
Understanding Intermittent Fasting: An Overview
Intermittent fasting involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting, which can promote fat loss and improve metabolic health by reducing insulin levels and increasing human growth hormone production. Unlike traditional dieting, which often restricts calorie intake daily, intermittent fasting emphasizes when to eat rather than what to eat, making it flexible and sustainable for many individuals. Research indicates that this pattern can enhance weight management, support cellular repair processes, and improve markers of longevity and overall well-being.
What Defines Traditional Dieting?
Traditional dieting is defined by consistent daily calorie restriction and structured meal plans aimed at gradual weight loss or maintenance. It often emphasizes balanced macronutrient intake, portion control, and frequent meals throughout the day to regulate metabolism. Unlike intermittent fasting, traditional dieting involves continuous energy intake without extended fasting periods, focusing on steady nutritional discipline.
Key Differences: Eating Patterns and Restrictions
Intermittent fasting emphasizes timed eating windows, such as 16:8 or 5:2 schedules, restricting caloric intake during fasting periods to promote fat loss and metabolic health. Traditional dieting focuses on consistent daily caloric reduction and nutrient balance without specific fasting intervals, allowing more frequent meals. The primary difference lies in the timing of food intake versus the quantity and quality of calories consumed.
Health Benefits Compared: IF vs. Traditional Diets
Intermittent fasting (IF) promotes improved insulin sensitivity and cellular repair processes through autophagy, which traditional dieting often lacks. IF has shown more consistent reductions in inflammation and oxidative stress markers compared to caloric restriction alone. Studies indicate that IF can lead to better metabolic health, fat loss preservation, and improved cardiovascular markers than conventional diet plans.
Weight Loss Effectiveness: Evidence and Results
Intermittent fasting has demonstrated significant weight loss effectiveness by promoting fat burning and metabolic health through timed eating windows, often leading to reductions in body fat percentage and improved insulin sensitivity. Traditional dieting, which typically involves continuous calorie restriction, achieves weight loss by creating a sustained caloric deficit but may result in muscle loss and metabolic slowdown over time. Clinical studies reveal intermittent fasting can yield comparable or superior results in weight loss and metabolic markers compared to traditional calorie-restricted diets, making it a viable option for long-term fat reduction.
Impact on Metabolism and Energy Levels
Intermittent fasting enhances metabolism by promoting fat oxidation and improving insulin sensitivity, leading to more stable energy levels throughout the day. Traditional dieting often reduces calorie intake continuously, which can slow metabolic rate and cause energy fluctuations or fatigue. Studies show intermittent fasting supports sustained energy and metabolic flexibility better than conventional calorie-restrictive diets.
Social and Lifestyle Flexibility
Intermittent fasting offers greater social and lifestyle flexibility compared to traditional dieting by allowing individuals to eat without strict calorie restrictions during specific time windows, making it easier to adapt to social gatherings and varying schedules. Traditional dieting often requires continuous calorie monitoring and food restrictions, which can limit spontaneity and complicate social interactions. This flexibility of intermittent fasting supports a balanced lifestyle without compromising social engagements or personal routines.
Common Challenges and Pitfalls
Intermittent fasting often presents challenges like managing hunger during fasting windows and potential nutrient deficiencies if meal timing limits food variety. Traditional dieting may struggle with maintaining calorie restrictions long-term and coping with psychological effects such as food cravings or deprivation. Both approaches require mindful planning and consistency to avoid pitfalls like metabolic slowdown or binge eating.
Long-Term Sustainability and Adherence
Intermittent fasting enhances long-term sustainability by simplifying eating patterns and reducing calorie tracking, which often leads to better adherence compared to traditional dieting methods. Studies show intermittent fasting can improve metabolic health markers while maintaining muscle mass, supporting prolonged commitment. Traditional diets frequently involve complex meal planning and restrictions that contribute to higher dropout rates and weight regain over time.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Lifestyle
Intermittent fasting offers flexible eating windows that can enhance metabolic health and simplify meal planning, making it ideal for those with busy schedules. Traditional dieting, with its focus on calorie counting and balanced nutrition, suits individuals who prefer structured eating and steady weight management. Evaluating personal energy levels, social commitments, and long-term sustainability helps determine which approach best aligns with your lifestyle goals.
Intermittent Fasting vs Traditional Dieting Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com