The flexitarian diet emphasizes a primarily plant-based approach while allowing occasional meat consumption, promoting flexibility and sustainability. In contrast, the reducetarian diet focuses on consciously reducing overall meat intake without eliminating it entirely, aiming to improve health and decrease environmental impact. Both diets offer practical alternatives for pet owners seeking to balance nutrition, ethics, and ecological responsibility in their pets' lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
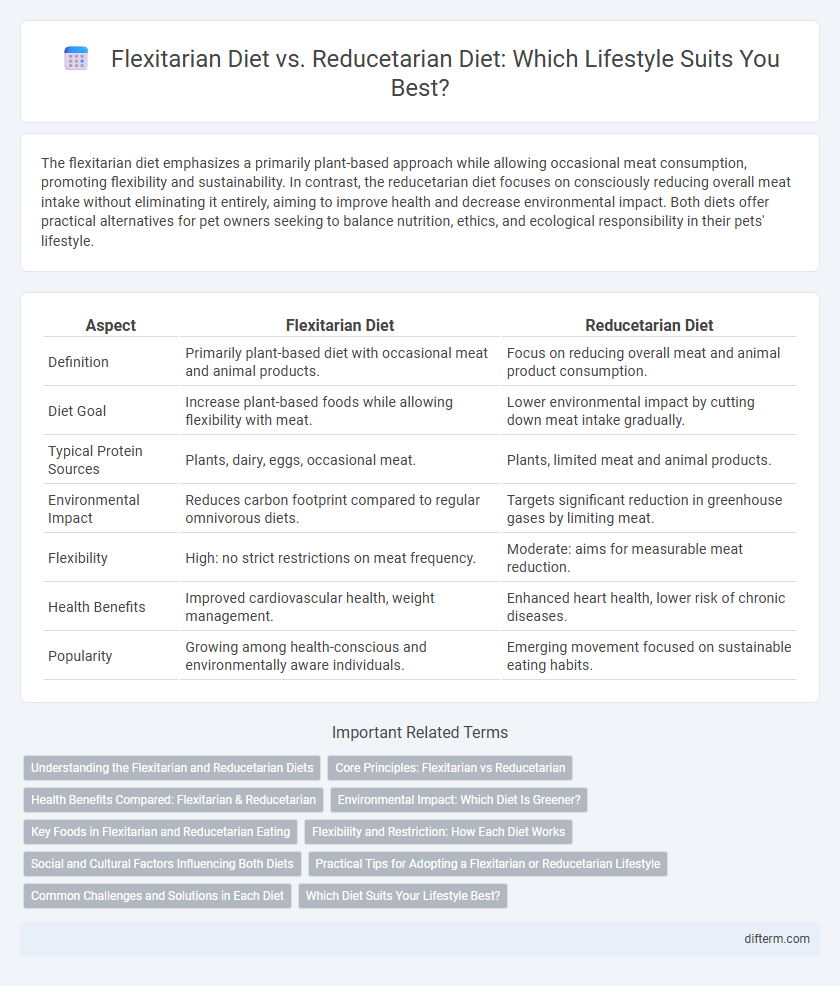
| Aspect | Flexitarian Diet | Reducetarian Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Primarily plant-based diet with occasional meat and animal products. | Focus on reducing overall meat and animal product consumption. |
| Diet Goal | Increase plant-based foods while allowing flexibility with meat. | Lower environmental impact by cutting down meat intake gradually. |
| Typical Protein Sources | Plants, dairy, eggs, occasional meat. | Plants, limited meat and animal products. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint compared to regular omnivorous diets. | Targets significant reduction in greenhouse gases by limiting meat. |
| Flexibility | High: no strict restrictions on meat frequency. | Moderate: aims for measurable meat reduction. |
| Health Benefits | Improved cardiovascular health, weight management. | Enhanced heart health, lower risk of chronic diseases. |
| Popularity | Growing among health-conscious and environmentally aware individuals. | Emerging movement focused on sustainable eating habits. |
Understanding the Flexitarian and Reducetarian Diets
The Flexitarian Diet emphasizes primarily plant-based meals while allowing occasional meat consumption, promoting a balanced approach to reducing animal product intake. The Reducetarian Diet encourages a gradual reduction in meat consumption without strict rules, focusing on sustainability and health benefits. Both diets support environmental conservation and improved well-being by minimizing excessive reliance on animal products.
Core Principles: Flexitarian vs Reducetarian
The Flexitarian diet emphasizes primarily plant-based foods while allowing occasional meat or animal products, focusing on flexibility and gradual reduction in meat consumption. The Reducetarian diet advocates for consciously reducing overall meat intake without strict elimination, encouraging mindful eating and environmental impact awareness. Both diets promote health benefits and sustainability by decreasing reliance on animal-based foods but differ in their approach to dietary restrictions and flexibility.
Health Benefits Compared: Flexitarian & Reducetarian
The flexitarian diet, emphasizing mostly plant-based foods with occasional meat, supports improved heart health, weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases through increased fiber and nutrient intake. The reducetarian diet focuses on consciously reducing meat consumption rather than eliminating it, which can lower inflammation, improve gut health, and contribute to better metabolic outcomes. Both diets offer significant health benefits by promoting higher consumption of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and plant proteins while decreasing red and processed meat intake.
Environmental Impact: Which Diet Is Greener?
The flexitarian diet, emphasizing occasional meat consumption alongside mostly plant-based foods, reduces greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 30-40% compared to a typical omnivorous diet. The reducetarian diet, encouraging a significant but less strict reduction in animal products, can lower environmental impact by about 20-30%. Overall, flexitarianism tends to be greener due to its stronger emphasis on plant-based eating, contributing to reduced land use, water consumption, and carbon footprint.
Key Foods in Flexitarian and Reducetarian Eating
Flexitarian diets emphasize plant-based foods like vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds while allowing occasional meat or fish. Reducetarian eating focuses on significantly reducing animal products, prioritizing plant proteins such as beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh alongside seasonal vegetables and whole grains. Both approaches promote flexibility and balance, encouraging nutrient-rich, minimally processed foods to improve health and sustainability.
Flexibility and Restriction: How Each Diet Works
The Flexitarian diet emphasizes flexibility by encouraging mostly plant-based foods while allowing occasional meat or animal products, making it adaptable to various preferences and lifestyles. In contrast, the Reducetarian diet focuses on consciously reducing overall meat consumption without strict exclusion, promoting incremental changes to decrease environmental impact and improve health. Both diets balance dietary choices by moderating restriction levels, with Flexitarian offering more variety and Reducetarian advocating gradual reduction.
Social and Cultural Factors Influencing Both Diets
Flexitarian and reducetarian diets are shaped by social acceptance and cultural norms surrounding meat consumption and environmental consciousness. Flexitarianism often reflects a balance between traditional eating habits and modern health trends, influenced by social media and community support for sustainable food choices. Reducetarianism gains traction in cultural contexts where gradual dietary shifts are encouraged as practical responses to climate change and animal welfare concerns.
Practical Tips for Adopting a Flexitarian or Reducetarian Lifestyle
Incorporate more plant-based meals gradually by replacing meat with legumes, grains, and vegetables at least three times a week to ease into a flexitarian or reducetarian lifestyle. Prioritize meal planning and preparation to ensure balanced nutrition with sufficient protein sources such as beans, tofu, and nuts. Utilize online resources and community support groups for recipes and motivation to sustain long-term dietary changes.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Each Diet
Flexitarian and reducetarian diets both face challenges such as maintaining nutritional balance while reducing meat intake and managing social or cultural food preferences. Flexitarians often struggle with inconsistent meat consumption patterns, solved by planning versatile plant-based meals that ensure adequate protein and micronutrients. Reducetarians address gradual reduction difficulty through goal-setting and community support, fostering sustainable dietary shifts without feeling restricted.
Which Diet Suits Your Lifestyle Best?
The Flexitarian Diet emphasizes mostly plant-based foods while allowing occasional meat, ideal for those seeking balance without strict restrictions. The Reducetarian Diet focuses on reducing overall meat consumption without eliminating it entirely, perfect for individuals aiming for gradual lifestyle changes and environmental impact reduction. Choosing between these diets depends on your commitment level to dietary flexibility and personal health or sustainability goals.
Flexitarian Diet vs Reducetarian Diet Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com