Conscious consumerism emphasizes awareness of the impact products have on health and the environment, encouraging sustainable choices in lifestyle pet care such as eco-friendly toys and organic pet food. Ethical consumerism goes further by prioritizing animal welfare and fair trade practices, ensuring that pet products are cruelty-free and sourced responsibly. Both approaches promote a mindful lifestyle that supports the well-being of pets, people, and the planet.
Table of Comparison
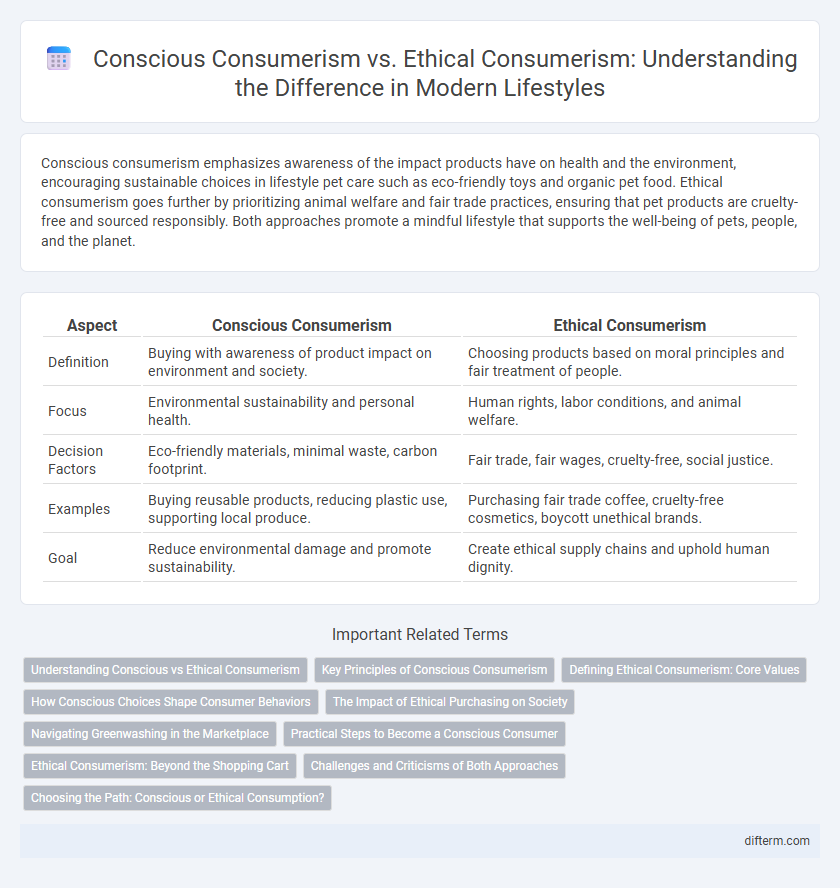
| Aspect | Conscious Consumerism | Ethical Consumerism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying with awareness of product impact on environment and society. | Choosing products based on moral principles and fair treatment of people. |
| Focus | Environmental sustainability and personal health. | Human rights, labor conditions, and animal welfare. |
| Decision Factors | Eco-friendly materials, minimal waste, carbon footprint. | Fair trade, fair wages, cruelty-free, social justice. |
| Examples | Buying reusable products, reducing plastic use, supporting local produce. | Purchasing fair trade coffee, cruelty-free cosmetics, boycott unethical brands. |
| Goal | Reduce environmental damage and promote sustainability. | Create ethical supply chains and uphold human dignity. |
Understanding Conscious vs Ethical Consumerism
Conscious consumerism emphasizes informed purchasing decisions based on personal values and awareness of product impact, prioritizing sustainability and social responsibility. Ethical consumerism extends this by actively seeking products that do no harm to society or the environment, often involving boycott or support of specific brands based on moral criteria. Both approaches promote mindful consumption, but ethical consumerism demands a stronger commitment to justice and accountability in the supply chain.
Key Principles of Conscious Consumerism
Conscious consumerism emphasizes mindfulness in purchasing decisions, focusing on sustainability, fair labor practices, and reducing environmental impact. Key principles include prioritizing products made from eco-friendly materials, supporting brands with transparent supply chains, and minimizing waste through reusable or recyclable packaging. This approach fosters responsible consumption that benefits both society and the planet.
Defining Ethical Consumerism: Core Values
Ethical consumerism centers on buying products that align with values such as fairness, sustainability, animal welfare, and human rights, ensuring that purchasing decisions support social and environmental justice. It emphasizes transparency in supply chains, responsible sourcing, and the reduction of harm to communities and the planet. This approach contrasts with conscious consumerism by prioritizing moral principles and systemic change over individual awareness and minimal impact.
How Conscious Choices Shape Consumer Behaviors
Conscious choices in consumer behavior prioritize awareness of the environmental and social impact of purchases, leading to increased demand for sustainable and cruelty-free products. Ethical consumerism emphasizes fairness and responsibility, driving support for brands with transparent supply chains and labor practices. Together, these approaches foster market shifts towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns.
The Impact of Ethical Purchasing on Society
Ethical purchasing drives positive social change by supporting fair labor practices and promoting environmental sustainability. Consumers who prioritize ethical products help reduce exploitation and encourage companies to adopt responsible manufacturing processes. This shift creates a market that values human rights and ecological preservation, fostering long-term improvements in community well-being.
Navigating Greenwashing in the Marketplace
Conscious consumerism emphasizes awareness of environmental impacts when making purchases, while ethical consumerism prioritizes social justice and fair labor practices alongside sustainability. Navigating greenwashing requires critical evaluation of product claims, certifications, and corporate transparency to distinguish genuine eco-friendly brands from misleading marketing. Consumers equipped with knowledge about common greenwashing tactics can make informed decisions that truly support sustainable and ethical business practices.
Practical Steps to Become a Conscious Consumer
To become a conscious consumer, prioritize purchasing products with transparent supply chains and verified certifications such as Fair Trade or Organic. Support brands committed to reducing environmental impact by using sustainable materials and minimizing waste through eco-friendly packaging. Evaluate the lifecycle of products by choosing durable, repairable items that promote a circular economy and reduce overall consumption.
Ethical Consumerism: Beyond the Shopping Cart
Ethical consumerism extends beyond purchasing decisions to encompass lifestyle choices that prioritize environmental sustainability, social justice, and fair trade practices. Consumers practicing ethical consumerism actively support businesses with transparent supply chains, cruelty-free products, and labor rights compliance. This commitment transforms everyday habits into powerful statements advocating for systemic change in global production and consumption patterns.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Approaches
Conscious consumerism and ethical consumerism face challenges such as greenwashing, where companies exaggerate their environmental or social efforts, misleading consumers. Both approaches struggle with accessibility and affordability, limiting their adoption to higher-income groups and creating inequalities. Critics argue that these consumption-based solutions may shift responsibility away from systemic changes needed in corporate regulation and environmental policy.
Choosing the Path: Conscious or Ethical Consumption?
Conscious consumerism emphasizes awareness of the environmental and social impacts of purchasing decisions, encouraging mindful consumption to reduce waste and support sustainability. Ethical consumerism goes further by actively seeking out products and brands committed to fair labor practices, animal welfare, and human rights. Choosing between conscious and ethical consumption involves balancing personal values with the availability of transparent, responsibly produced goods that align with one's commitment to global social and environmental justice.
conscious consumerism vs ethical consumerism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com